
Understanding the laws and ethical guidelines surrounding healthcare practices is crucial for those working in the field. This knowledge ensures that professionals provide safe, effective care while adhering to legal requirements and protecting patient rights.
In this guide, we delve into the essential topics you need to grasp, including regulatory frameworks, professional responsibilities, and ethical considerations. By exploring these areas, you can build confidence in your ability to handle complex situations while maintaining compliance with industry standards.
Whether you are preparing for a certification test or seeking to enhance your understanding of legal principles, this resource offers valuable insights. It focuses on practical applications and key concepts to help you succeed in your professional journey.
Understanding Legal Principles in Healthcare
Grasping the foundational principles of law as they apply to the healthcare profession is a vital step for individuals in this field. These principles guide professionals in adhering to regulations, ensuring ethical behavior, and upholding the rights of those in their care.
Core Elements of Legal Guidelines
- Regulatory frameworks: Understanding the rules set by governing bodies ensures compliance and consistency in practice.
- Ethical standards: Balancing moral duties with professional obligations helps maintain trust and integrity in care delivery.
- Professional accountability: Recognizing the importance of personal responsibility fosters a culture of safety and excellence.
Practical Applications of Legal Knowledge
- Interpreting local laws: Familiarity with region-specific regulations ensures appropriate actions in varied situations.
- Conflict resolution: Applying legal concepts aids in navigating disputes effectively while preserving professional relationships.
- Risk management: Proactively addressing potential legal concerns mini
Legal Responsibilities in Healthcare Practice
Understanding and adhering to legal obligations is a critical aspect of healthcare practice. These responsibilities ensure that actions taken by professionals align with ethical standards and protect the rights and safety of all individuals involved.
Primary Areas of Accountability
- Informed decision-making: Providing individuals with comprehensive information to help them make educated choices about their care.
- Privacy protection: Safeguarding confidential information in accordance with legal and ethical guidelines.
- Adherence to regulations: Following established laws and policies to ensure compliance and prevent violations.
Approaches to Fulfilling Obligations

- Detailed record-keeping: Documenting all interactions and procedures accurately to maintain transparency and accountability.
- Continuous education: Keeping up-to-date with changes in legal frameworks and industry standards to remain compliant.
- Ethical conflict resolution: Addressing challenges professionally while respecting both legal mandates and moral considerations.
Ethical Principles in Healthcare Decision-Making
Healthcare professionals often face challenging situations where decisions must balance patient well-being, legal requirements, and ethical standards. Understanding the key ethical principles that guide these decisions is essential for providing compassionate and fair care.
Key Ethical Principles

- Autonomy: Respecting the individual’s right to make their own informed choices about their care.
- Beneficence: Acting in the best interest of the patient to promote well-being and positive outcomes.
- Non-maleficence: Avoiding actions that may harm the patient, ensuring safety and minimizing risks.
Applying Ethical Principles in Practice
- Open communication: Providing clear, honest information to patients and their families to support informed decision-making.
- Balancing competing needs: Navigating the complexity of patient needs while respecting personal beliefs and cultural values.
- Reflective practice: Continuously evaluating personal and professional decisions to ensure they align with ethical standards.
By embracing these ethical principles, healthcare professionals can foster trust, respect, and high-quality care, ensuring decisions are made with compassion and integrity in every aspect of practice.
Key Components of Professional Accountability
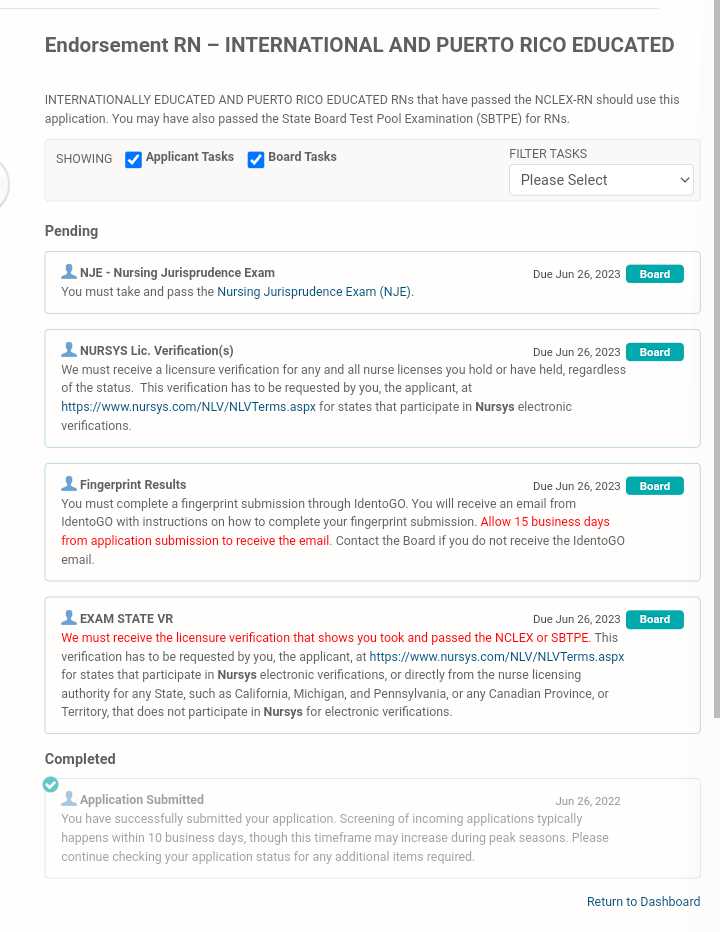
Accountability in healthcare practice is fundamental to ensuring that professionals act with integrity and uphold the highest standards. It involves taking responsibility for one’s actions, adhering to ethical guidelines, and being transparent in all aspects of patient care.
Essential Elements of Accountability
- Responsibility: Acknowledging the impact of decisions on patients and colleagues, and accepting the outcomes of those actions.
- Transparency: Openly sharing information with patients and other healthcare professionals to maintain trust and clarity.
- Continuous improvement: Committing to ongoing education and self-reflection to enhance skills and knowledge.
Accountability in Practice
Aspect Importance Application Decision-making Ensures ethical, patient-centered choices Weighing all factors before taking action Communication Fosters trust and collaboration Clear, honest dialogue with patients and colleagues Documentation Supports legal and professional accountability Accurate and detailed record-keeping By integrating these key components into daily practice, healthcare professionals uphold their commitment to ethical conduct, fostering a culture of trust and respect. Accountability ensures that all actions are taken with care, diligence, and a focus on patient well-being.
Common Legal Issues in Patient Care

In healthcare, various legal challenges can arise that affect both the providers and recipients of care. These issues often stem from misunderstandings, miscommunications, or failure to follow legal and ethical guidelines. Understanding common legal concerns helps professionals navigate their responsibilities while ensuring the protection of patient rights and safety.
Some of the most frequent legal concerns in patient care include:
- Informed consent: Ensuring that patients fully understand the risks, benefits, and alternatives before undergoing any medical procedures.
- Negligence: Failing to provide the standard level of care expected, which may lead to patient harm or injury.
- Confidentiality breaches: Improper disclosure of patient information without consent, violating privacy regulations.
- Abandonment: Discontinuing patient care without proper transition or notification, leading to potential harm.
- Wrongful death: Legal action taken when a patient’s death results from a healthcare provider’s actions or inaction.
By being aware of these potential legal issues, healthcare professionals can take proactive steps to prevent conflicts, ensure compliance, and ultimately provide high-quality care that respects the rights of the individuals they serve.
Preparing Effectively for Jurisprudence Exams
Successful preparation for any professional assessment requires understanding the subject matter, strategic study techniques, and proper time management. Whether you’re aiming to test your legal knowledge or validate your ability to apply rules within a healthcare setting, the right approach can significantly impact your results. This section focuses on methods that enhance learning and boost confidence in approaching these crucial evaluations.
Key Preparation Strategies
To prepare effectively, it’s essential to have a clear plan that incorporates various study tactics:
- Review the key concepts: Understand the core principles related to legal and ethical standards. Focus on guidelines that govern professional behavior and patient rights.
- Practice with sample questions: Use mock tests to familiarize yourself with the format and identify areas where more focus is needed.
- Understand the laws and regulations: Thoroughly study the applicable laws that healthcare professionals are required to follow in different scenarios.
Staying Organized and Focused
Consistency and organization play vital roles in successful exam preparation. Consider the following tips:
- Create a study schedule: Break down your study sessions into manageable time blocks, allocating enough time for each topic.
- Stay up to date: Regularly review materials and stay informed about any updates in the field of practice that may impact the exam content.
- Group study sessions: Collaborating with peers can help clarify concepts and provide different perspectives on challenging topics.
By following these strategies, you can approach the assessment confidently, knowing you are well-prepared to tackle any challenges it presents.
State Regulations Every Nurse Should Know
Healthcare professionals are required to follow a set of legal guidelines that ensure safe and effective patient care. These guidelines vary by state and cover essential aspects of practice, from licensure requirements to specific duties and restrictions in various healthcare settings. Understanding state-specific regulations is critical for compliance and protecting both the professional and the patient.
Key Areas of State Regulations
Here are some of the key regulatory areas every healthcare professional must be familiar with:
- Licensure Requirements: Each state has its own criteria for obtaining and renewing a professional license. Be sure to stay informed about renewal deadlines, continuing education requirements, and any necessary background checks.
- Scope of Practice: Regulations define the range of activities and responsibilities that professionals can perform based on their qualifications and licensure. It’s crucial to understand what tasks are within your scope and what requires additional training or supervision.
- Patient Rights: State laws also protect patients’ rights, such as confidentiality, informed consent, and the right to make decisions about their healthcare. Knowledge of these laws ensures that professionals can advocate for patients while maintaining ethical practice.
Additional Considerations
Other important areas to consider include:
- Disciplinary Actions: Understanding the types of behavior that could result in disciplinary measures, including the misuse of drugs, ethical violations, and unprofessional conduct.
- Reporting Requirements: Healthcare professionals must be aware of mandatory reporting laws, such as those related to suspected abuse or neglect, and ensure they comply with state reporting guidelines.
- Emergency Protocols: Familiarity with state-specific emergency care regulations is crucial, especially in high-pressure situations that demand quick and effective responses.
By being informed about these regulations, healthcare professionals can better navigate the complexities of their practice while ensuring compliance with both state laws and ethical standards.
Rights and Duties of Nursing Professionals
Healthcare practitioners have a unique set of responsibilities and entitlements that ensure their ability to deliver effective care while maintaining ethical standards. These rights and obligations not only protect the well-being of patients but also safeguard the professional integrity and legal standing of healthcare providers. Understanding the balance between these rights and duties is essential for every professional in the field.
The rights of healthcare practitioners often include the ability to make independent judgments within their scope of practice, participate in ongoing education, and work in a safe, respectful environment. Meanwhile, their duties involve providing competent care, maintaining patient confidentiality, and adhering to legal and ethical standards at all times.
Both rights and responsibilities are crucial for creating a trustworthy and effective healthcare system where practitioners can perform their roles with confidence, and patients can receive the highest standard of care.
Documentation Standards in Healthcare Settings
Accurate and consistent record-keeping is essential in any medical environment, ensuring that healthcare providers have the information they need to make informed decisions. These standards not only help in delivering optimal care but also ensure compliance with legal requirements and ethical guidelines. Proper documentation is vital for maintaining a clear, accessible history of a patient’s treatment, diagnosis, and overall progress.
Clear and precise documentation helps minimize errors, supports effective communication among healthcare teams, and ensures that a patient’s care is properly tracked. In addition, it serves as a legal record that can be referenced if disputes or questions arise regarding the care provided.
Standards for documentation typically include the use of accurate medical terminology, timely entries, legible handwriting (or digital equivalents), and an organized system for accessing records. These guidelines are set to ensure that documentation is both useful in clinical practice and compliant with regulatory and legal standards.
In healthcare settings, the importance of following established documentation standards cannot be overstated. It supports patient safety, improves the quality of care, and protects both healthcare providers and patients in the event of legal scrutiny or review.
Handling Confidentiality and Privacy Challenges
Protecting patient information is a cornerstone of healthcare practice. The responsibility to safeguard personal and medical data is not only a legal obligation but an ethical imperative that supports trust between patients and their healthcare providers. As technology and healthcare systems evolve, new challenges arise in maintaining confidentiality and ensuring privacy across various platforms.
Challenges in Protecting Confidentiality
As healthcare providers increasingly rely on digital systems for record-keeping and communication, the risk of breaches grows. Unauthorized access to personal information, whether intentional or accidental, can have serious consequences. Below are some of the key challenges faced by healthcare professionals:
- Data breaches: Increasing reliance on electronic health records (EHR) increases the risk of unauthorized access or hacking.
- Miscommunication: Sharing information in casual settings or through unsecured communication channels can inadvertently expose sensitive details.
- Third-party access: Contractors, vendors, or outside personnel who have access to healthcare systems may inadvertently expose confidential information.
Best Practices for Ensuring Privacy
To address these challenges, healthcare providers must implement best practices to protect patient information and uphold privacy standards. These include:
- Implementing robust cybersecurity measures: This includes using encryption, secure passwords, and regular audits to detect vulnerabilities.
- Training staff: Regular training sessions on confidentiality laws, ethical standards, and data protection methods are essential.
- Clear protocols for sharing information: Setting specific guidelines for how and when patient information can be shared, ensuring it is done securely and only with authorized individuals.
Data Protection and Legal Implications
Healthcare providers must stay informed about the evolving legal landscape surrounding privacy and data protection. Violating confidentiality can lead to severe consequences, including legal penalties, loss of professional licensure, and damage to the reputation of the healthcare institution.
Type of Breach Potential Consequences Unauthorized Access Legal action, fines, loss of trust Data Leaks Legal liabilities, damage to reputation Improper Information Sharing Penalties, professional sanctions Maintaining confidentiality and privacy in healthcare is essential not only to meet legal requirements but to foster a relationship of trust between patients and their providers. It is vital that healthcare professionals understand their role in protecting sensitive information and follow best practices to prevent breaches.
Steps to Address Medical Negligence Claims
Addressing claims of negligence in the healthcare sector requires a systematic approach to ensure that the rights of both patients and healthcare providers are protected. Medical negligence can lead to significant legal, financial, and reputational consequences for practitioners and institutions. Responding effectively to such claims involves a careful review of the situation, gathering of evidence, and adherence to legal and ethical standards.
The first step in dealing with a medical negligence claim is to understand the allegations and the circumstances surrounding the situation. Once a claim is made, it is crucial to conduct a thorough investigation to assess the validity of the complaint. Below are the essential steps that healthcare providers should follow when handling such claims.
Step Description 1. Initial Review Review the claim thoroughly to understand the nature of the allegation and the patient’s history. Assess whether the situation involves a breach of duty. 2. Collect Evidence Gather medical records, witness statements, and any relevant documents that can support the defense or clarify the circumstances of the case. 3. Consult with Legal Counsel Engage with legal professionals to evaluate the claim’s merit and determine the best course of action to mitigate risks. 4. Communication with the Patient If appropriate, communicate with the patient or their family to address concerns, clarify misunderstandings, or offer an apology if warranted. 5. Settle or Defend Based on the evidence and legal advice, decide whether to settle the claim or proceed to court for defense. 6. Document Everything Ensure all communications, actions, and decisions related to the claim are carefully documented to protect the institution and involved personnel. Throughout this process, it is essential for healthcare providers to remain transparent, cooperative, and professional. Medical negligence claims can be stressful, but handling them with diligence and care can help protect the integrity of the practice and prevent future issues. By following these steps, healthcare professionals can address claims effectively and ensure that they uphold their responsibilities to patients and the law.
Importance of Patient Advocacy in Law
In the healthcare setting, advocating for patients is not only an ethical responsibility but also a legal necessity. Patient advocacy ensures that individuals receive the highest standard of care while safeguarding their rights and interests. The role of advocacy is central to ensuring that patients are informed, their voices are heard, and their needs are met within the boundaries of the law. By promoting patient rights, healthcare professionals help create a transparent and fair environment, reducing the risk of legal disputes and ensuring proper treatment for all individuals.
Advocacy in healthcare goes beyond just emotional support; it involves a proactive approach to protect patients from negligence, discrimination, or any form of mistreatment. Legal professionals, as well as healthcare providers, must understand the significance of advocating for patients’ rights and be equipped to intervene when necessary. This proactive engagement often leads to more informed and empowered patients who are better able to make decisions about their own care, contributing to overall improved health outcomes.
Compliance with Workplace Policies and Procedures
Adhering to workplace guidelines and protocols is fundamental to maintaining a functional, safe, and legally sound environment. Whether it involves patient care, safety protocols, or the handling of confidential information, compliance ensures that employees fulfill their duties responsibly and ethically. It is essential for all professionals to understand the specific expectations and regulations set by their workplace and to apply them consistently in their daily tasks.
When employees align with established procedures, it minimizes the risk of errors, promotes a positive work culture, and ensures that the organization remains in legal compliance. Additionally, proper adherence to workplace policies helps in protecting both staff and patients, guaranteeing that all actions taken are in line with legal and ethical standards.
- Understand and familiarize yourself with all workplace policies.
- Ensure compliance with safety and security protocols to safeguard both staff and patients.
- Follow proper documentation and reporting procedures to maintain accurate records.
- Participate in training programs and refresh your knowledge of policies regularly.
- Stay informed about updates or changes to procedures to remain compliant.
Risk Management Strategies for Nurses
Effective risk management is crucial in healthcare settings to ensure the safety of both patients and professionals. Identifying potential risks and implementing strategies to mitigate them is an essential aspect of providing high-quality care. By addressing possible hazards in advance, professionals can prevent negative outcomes, minimize errors, and enhance the overall effectiveness of healthcare services. A proactive approach to risk management not only protects patients but also safeguards the reputation and legal standing of healthcare organizations.
Key Strategies for Risk Mitigation
- Regular Training and Education: Continuous education on best practices, safety protocols, and legal guidelines helps ensure that professionals are prepared for potential risks.
- Clear Communication: Open and transparent communication between team members, patients, and their families is essential to reduce misunderstandings and errors.
- Accurate Documentation: Maintaining precise and up-to-date records is critical in mitigating risks related to patient care and legal accountability.
- Adherence to Protocols: Following established procedures and guidelines for patient care reduces the chances of mistakes and adverse events.
Responding to Risk Scenarios
When faced with risk situations, it is essential to act swiftly and efficiently. The response should always be aligned with established guidelines and protocols. Early detection of problems, quick reporting, and transparent documentation are key to managing and reducing risks effectively. Additionally, reviewing incidents to learn from them and implementing changes to prevent recurrence is crucial for continuous improvement.
Role of Consent in Medical Practice

Consent is a fundamental aspect of healthcare practice, ensuring that patients are fully informed and voluntarily agree to medical interventions. It establishes a collaborative relationship between the healthcare provider and the patient, promoting respect for individual autonomy and rights. By obtaining consent, professionals protect both patients’ welfare and their own legal standing, fostering trust and transparency within the care process.
Informed consent goes beyond simple agreement. It involves providing the patient with comprehensive information about the procedure, including potential risks, benefits, and alternatives. This empowers patients to make decisions that align with their values and preferences. Consent must be obtained voluntarily, without any coercion or undue influence, and patients should have the capacity to understand the information provided.
Types of Consent:
- Expressed Consent: This occurs when the patient explicitly agrees to a procedure or treatment, either verbally or in writing.
- Implied Consent: In certain situations, consent is implied by the patient’s actions, such as when they present themselves for treatment in an emergency setting.
- Informed Consent: A more detailed form of consent, where the patient is made fully aware of the potential risks and benefits of a treatment before agreeing to it.
Medical professionals must always ensure that consent is given freely, with full understanding, and is appropriately documented. This not only protects the rights of patients but also minimizes legal risks for healthcare providers.
Interpreting Regulations Across Jurisdictions
Understanding and navigating the regulatory landscape is a critical component of professional practice, particularly when healthcare providers operate across various legal environments. Regulations governing practice can differ widely depending on the jurisdiction, making it essential for professionals to be aware of the local laws and guidelines that apply to their specific field of work. These rules are designed to ensure that care is provided in a safe and ethical manner, but interpreting them correctly is key to avoiding legal challenges and ensuring compliance.
Key Factors to Consider
When interpreting regulations across different jurisdictions, it is important to focus on several key factors:
- Scope of Practice: Understanding the limitations and permissions granted to healthcare professionals in each jurisdiction is essential for ensuring that services provided align with local laws.
- Licensing Requirements: Each jurisdiction may have distinct licensing and certification requirements, affecting the ability of professionals to practice in a given area.
- Patient Rights: Legal frameworks often include guidelines on patient consent, privacy, and informed decision-making, which can vary significantly across regions.
Challenges in Compliance
One of the most significant challenges when dealing with varying regulations is maintaining compliance across different jurisdictions. What may be legally acceptable in one region may not be in another. Professionals must stay updated on legal changes and ensure their practice complies with all applicable regulations, which might require legal consultation or continuing education on regional laws.
By remaining vigilant and informed, healthcare providers can better navigate the complexities of varying regulations, thereby ensuring they continue to offer ethical and legally compliant care to their patients.
Commonly Tested Topics in Professional Legal Assessments

Professional legal assessments often focus on areas crucial for ensuring ethical and compliant practice. These assessments aim to evaluate a practitioner’s understanding of the laws and regulations that govern their profession. The topics frequently covered are designed to test an individual’s knowledge of key legal concepts, rights, and responsibilities they must adhere to while practicing within their field. Being well-versed in these subjects is vital for ensuring not only legal compliance but also the protection of patients and the professional’s own career.
Core Areas of Legal Knowledge
The following are some of the primary topics often featured in legal assessments for healthcare professionals:
- Patient Rights: This includes understanding patient confidentiality, informed consent, and the ethical implications of patient care decisions.
- Professional Ethics and Standards: Legal assessments test knowledge of the ethical duties and professional conduct expected in the healthcare field, including the standards that guide interactions with patients and colleagues.
- Licensing and Certification Laws: An essential topic that ensures practitioners are aware of the legal requirements for maintaining active certification and licenses in their region.
- Liability and Risk Management: Questions about how legal liability affects healthcare providers and what steps can be taken to minimize risk in practice.
Legal Compliance and Documentation
In addition to understanding patient rights and ethical standards, professionals must also be familiar with proper documentation practices. This includes how to properly record patient information, the importance of maintaining accurate and confidential records, and the legal consequences of inadequate documentation.
Mastering these key areas ensures that healthcare professionals are equipped to navigate the complexities of legal requirements in their practice, allowing them to provide high-quality care while protecting their professional integrity and mitigating legal risks.