
Becoming a licensed healthcare professional requires passing a series of rigorous assessments that evaluate your knowledge, skills, and readiness to practice. These evaluations are designed to ensure that only qualified individuals are allowed to provide medical care, safeguarding patient health and safety. The process varies by country and region, but it generally includes several key steps.
Successful completion of these assessments marks a significant milestone in a medical career, allowing candidates to pursue their professional goals. Preparation is crucial, as the tests cover a wide range of topics that reflect the responsibilities and challenges of practicing medicine. Understanding the structure and requirements of these evaluations can help streamline the preparation process and reduce stress.
In this guide, we will explore the essential components of medical licensing exams, from eligibility to preparation strategies, helping you navigate this critical phase of your healthcare journey with confidence.
Medical Licensing Process Overview
Becoming a certified healthcare professional requires meeting several standards set by regulatory bodies. These requirements ensure that individuals are adequately prepared to provide quality care. The process typically involves a series of assessments that test knowledge, clinical skills, and decision-making abilities necessary for medical practice. It serves as a vital step in verifying the competence of future practitioners, ensuring they meet the expected level of expertise and responsibility.
Steps in the Licensing Journey
The journey toward professional certification often starts with completing formal education and training in a recognized medical field. Afterward, candidates must pass various evaluations to demonstrate their understanding and proficiency. These assessments may include written tests, practical evaluations, and oral exams, depending on the jurisdiction. Successfully completing these stages paves the way for becoming a fully licensed healthcare provider, ready to serve the community.
Role of Regulatory Bodies
Each country or region typically has a governing organization responsible for overseeing the licensing process. These bodies establish the criteria and ensure that all candidates meet the required qualifications before granting certification. They also set regulations that help maintain high standards of care within the medical profession. The requirements may vary slightly depending on local laws, but they all aim to uphold the integrity of healthcare delivery.
Understanding the Licensing Process
The path to becoming a recognized healthcare professional involves a structured process designed to evaluate an individual’s qualifications. This process ensures that only those who have the required knowledge and skills are authorized to practice in the medical field. While specific steps may vary depending on the region or country, the core principles remain consistent: demonstrating expertise, completing required training, and meeting the standards set by governing bodies.
Initial Steps for Certification
Before being eligible for the final assessments, candidates must first complete an accredited education program in their chosen medical field. This typically includes several years of intensive study and hands-on training. After completing the educational requirements, candidates must then fulfill other prerequisites, such as accumulating supervised clinical hours or completing certain types of internships, depending on the regulations of the country or state.
Final Evaluation and Certification
Once the educational and practical training requirements are fulfilled, candidates must undergo a final evaluation. This assessment tests their understanding and clinical capabilities, ensuring they are ready to handle real-world medical challenges. Upon successful completion, individuals are granted the certification necessary to practice independently, providing them with the authority to serve patients in their specialty.
Eligibility Criteria for Medical Exams
To participate in the certification process, candidates must meet specific eligibility requirements set by regulatory bodies. These criteria are designed to ensure that individuals are sufficiently prepared and qualified to pursue a career in healthcare. The requirements vary depending on the region, but they generally focus on education, training, and professional experience.
The most common prerequisites include completing an accredited medical program, which provides the necessary academic foundation and practical experience. In addition to educational qualifications, candidates may be required to demonstrate a certain level of hands-on clinical training or internship experience. Some regions may also have age or citizenship requirements, as well as a clean criminal record, to ensure that candidates meet ethical standards.
In some cases, candidates must also provide proof of proficiency in specific medical subjects, such as anatomy, physiology, or pharmacology. These requirements are in place to ensure that all applicants are well-versed in the core principles needed for effective practice. Meeting these eligibility conditions is a critical step in the journey toward becoming a licensed healthcare provider.
How to Prepare for the Exam
Preparation is key to succeeding in the certification process. Candidates must focus on developing a deep understanding of medical concepts, clinical skills, and problem-solving abilities. Effective study strategies and planning are essential to ensure readiness for the assessment. This involves not only reviewing academic material but also honing practical skills that reflect real-world medical scenarios.
Study Strategies for Success
A well-organized study plan is crucial to manage the vast amount of material that needs to be covered. Breaking down the content into manageable sections and setting specific goals for each study session can help keep the process on track. In addition to traditional study methods, such as reading textbooks and attending review courses, using practice questions and mock tests can be valuable for reinforcing knowledge and gaining experience with the format of the assessment.
Practical Training and Clinical Experience
Hands-on training is just as important as theoretical knowledge. Candidates should take every opportunity to gain clinical experience in real-world settings. Working under supervision during internships or residencies helps build the practical skills needed to excel in the test. This experience provides invaluable exposure to patient care, medical procedures, and decision-making processes that will be tested during the certification process.
| Preparation Step | Action | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Study Plan | Organize topics into manageable sections | Improved retention and focus |
| Practice Questions | Complete mock tests and review answers | Familiarity with question formats |
| Clinical Training | Gain experience in medical settings | Build real-world skills and confidence |
What to Expect During the Test

When the time comes for the certification process, candidates will face a structured assessment designed to evaluate their knowledge and clinical competence. This phase is crucial for determining whether the individual is prepared to practice independently. Understanding what to expect during the evaluation helps reduce anxiety and ensures better performance. The assessment typically involves multiple components that test both theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
Types of Questions and Assessments

The evaluation consists of various types of questions, each targeting different aspects of medical knowledge. Written components often include multiple-choice, short-answer, or essay-style questions that assess the candidate’s understanding of medical principles, procedures, and ethical considerations. In addition to written tests, some regions may require practical demonstrations or oral interviews to assess clinical abilities and decision-making skills.
Test Environment and Guidelines
On the day of the assessment, candidates will be required to follow specific guidelines and adhere to a set of rules to ensure fairness. The test environment is designed to minimize distractions and allow individuals to focus fully on the task at hand. Personal items may be restricted, and security measures, such as ID verification, may be in place to maintain integrity during the process.
| Assessment Type | Purpose | Format |
|---|---|---|
| Written Test | Evaluate theoretical knowledge | Multiple choice, short-answer, essays |
| Practical Test | Assess clinical skills and decision-making | Hands-on scenarios, simulations |
| Oral Interview | Gauge communication and diagnostic abilities | Interactive discussions with assessors |
Key Exam Components and Subjects
The certification assessment is designed to evaluate a wide range of knowledge and skills necessary for healthcare practice. It is divided into several key components that test both theoretical understanding and practical application. The subjects covered are fundamental to ensuring that candidates can provide safe and effective care to patients in various clinical settings.
Core Knowledge Areas

The following subjects are typically assessed during the certification process. These topics are essential for ensuring that candidates are well-prepared to address the diverse challenges they will face in their practice.
- Medical Knowledge: Covers anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, pathology, and medical terminology.
- Clinical Decision Making: Assesses the ability to diagnose, treat, and manage patient conditions based on clinical data.
- Ethics and Professionalism: Evaluates the understanding of ethical principles and professional conduct in medical practice.
- Patient Care: Tests the ability to perform physical exams, manage patient health, and provide therapeutic interventions.
- Medical Procedures: Involves knowledge of common medical procedures, techniques, and technologies used in healthcare settings.
Practical Assessment and Skills

In addition to theoretical subjects, candidates must demonstrate proficiency in various practical areas. These components help assess hands-on skills that are critical for effective patient care.
- Clinical Skills: Testing real-world abilities in diagnosing and treating patients in simulated environments.
- Communication: Evaluating interpersonal skills, including patient interaction and collaboration with medical teams.
- Critical Thinking: Assessing the ability to make informed, timely decisions in high-pressure situations.
Common Challenges in the Certification Process
The path to becoming a licensed healthcare professional is rigorous and often presents a number of challenges. These obstacles can range from managing the sheer volume of information to coping with the pressure of the assessment. Understanding the common difficulties candidates face can help in preparing for and overcoming these hurdles. By being aware of potential challenges, candidates can adopt strategies to mitigate stress and perform at their best.
One of the primary challenges is the vast scope of material covered. Candidates are required to have an in-depth understanding of multiple medical disciplines, each with its own set of complex concepts and terminology. This extensive knowledge base can feel overwhelming, especially when it comes to balancing study with clinical experience.
Another common challenge is the format of the assessment itself. Many candidates find it difficult to adjust to the high-pressure environment, particularly during practical or oral assessments. The ability to think critically and respond effectively under time constraints can be a significant stressor. Additionally, the emotional toll of self-doubt and fear of failure can affect performance during the process.
Finally, the diverse nature of the assessment – which may include multiple-choice questions, simulations, and interviews – requires candidates to be versatile. The ability to adapt quickly to different testing formats and expectations is key to success, but it can be a challenging transition for those who have primarily prepared for written tests.
Tips for Effective Exam Studying
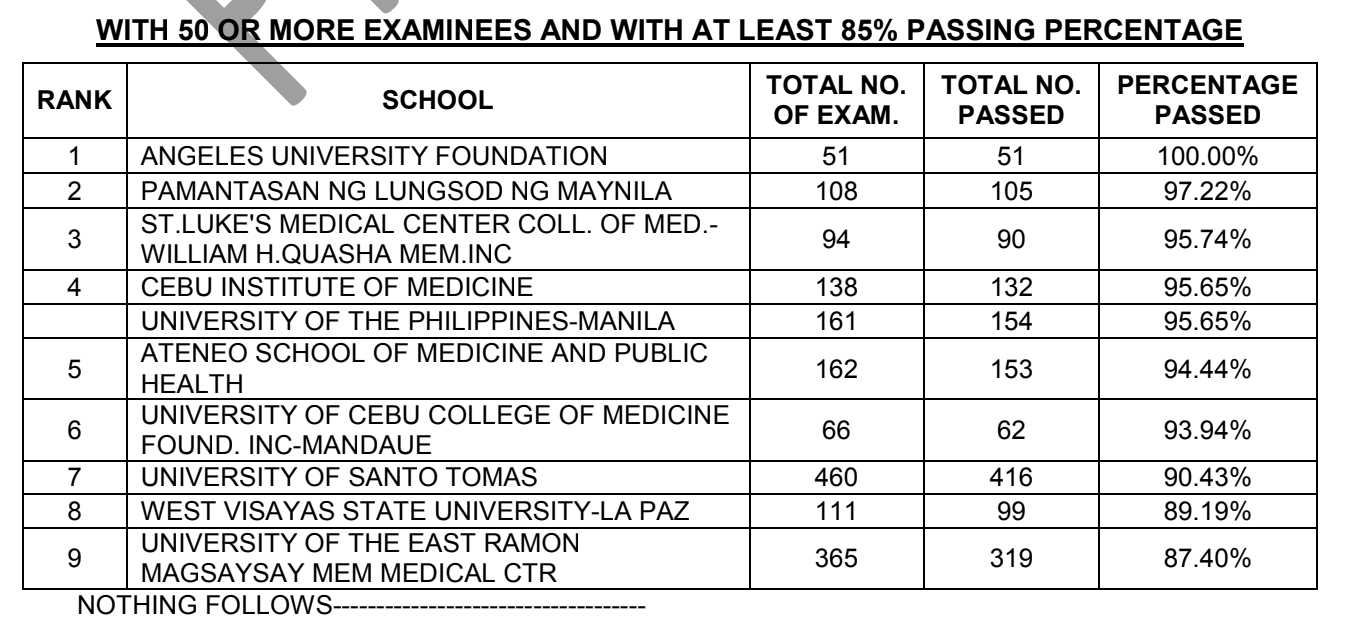
Successful preparation for the certification process requires a strategic approach to studying. It is not just about putting in the hours but making sure that time is used effectively to absorb and retain key concepts. Whether you’re a first-time candidate or retaking the assessment, implementing the right study techniques can greatly enhance your chances of success.
Study Strategies to Maximize Retention

To improve retention and understanding, it’s important to adopt focused study techniques. The following tips can help optimize your study sessions:
- Organize Your Study Schedule: Break down the material into manageable sections and allocate enough time to each topic based on its complexity.
- Active Recall: Instead of simply reading, actively quiz yourself on the material to reinforce memory.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards for key concepts, definitions, and medical terms to quickly review and test your knowledge.
- Group Study: Studying with others can help you understand different perspectives and clarify difficult topics through discussion.
Additional Tips for Effective Practice

In addition to theoretical learning, applying your knowledge through practice is equally important. The following methods can help you prepare for the real-world assessment:
- Simulate Test Conditions: Take timed practice tests to get used to the pressure and improve time management.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Identify your weaknesses and dedicate more time to improving those areas.
- Review Past Questions: Familiarize yourself with the types of questions that commonly appear in the assessment.
- Stay Consistent: Regular, consistent studying is more effective than cramming at the last minute.
Exam Dates and Scheduling Information
Understanding the timeline and scheduling process is essential for candidates preparing for the certification process. The dates for assessments are typically set in advance and may vary depending on the region or specific testing agency. Proper planning and early registration are key to securing your spot and ensuring you have enough time for preparation.
It is important to keep track of registration deadlines and the available testing windows. Some areas offer multiple opportunities throughout the year, while others may have a fixed schedule. Candidates should also be aware of any prerequisites or documentation needed before scheduling their assessment.
Key Dates to Remember
Here are some important dates and timeframes candidates should keep in mind when planning for the certification:
- Registration Period: Most testing centers open registration several months before the assessment. Be sure to register early to avoid last-minute complications.
- Testing Windows: Assessments are usually offered during specific timeframes. Ensure you are aware of these to plan your study schedule accordingly.
- Late Registration: If you miss the regular registration deadline, you may still be able to register late, but be prepared for higher fees and limited testing availability.
- Results Release: After the assessment, candidates will receive their results within a specific timeframe. Know when to expect your results to plan next steps.
Scheduling Your Assessment
Once you are aware of the available dates, you will need to schedule your assessment. Below are some steps to guide you through the process:
- Choose a Testing Location: Select a convenient and accessible testing center. Some regions offer both in-person and online options.
- Confirm Requirements: Make sure you meet all eligibility criteria and have any necessary documents ready before booking.
- Book Early: Testing slots can fill up quickly, so it is advisable to book your spot as soon as possible.
- Check for Special Accommodations: If you require any special accommodations, such as extra time or specific facilities, ensure that these are requested during the scheduling process.
Costs and Fees Associated with Certification

Becoming a certified healthcare professional involves various costs, which can vary depending on the region, testing agency, and specific requirements. It’s important to be aware of all associated fees and to plan your finances accordingly. These costs can include registration fees, study materials, and potential retake fees if necessary. Understanding the full financial scope will help you avoid surprises and manage your expenses effectively.
Common Costs to Consider

The following are some of the most common fees candidates may encounter during the certification process:
- Registration Fees: These are the fees required to sign up for the assessment. The amount can vary depending on the testing organization and location.
- Study Materials: Preparing for the certification may require purchasing textbooks, online courses, or practice tests. These materials are essential to ensure thorough preparation.
- Application Fees: Some regions or agencies may charge additional application processing fees, especially for first-time candidates or those applying for multiple certifications.
- Late Fees: If you miss the standard registration deadline, you may have to pay higher fees for late registration.
Additional Fees and Costs
Aside from direct assessment-related fees, there are other potential costs to keep in mind:
- Retake Fees: In case of a failed attempt, retaking the assessment often involves additional fees. These can sometimes be higher than the original registration fee.
- Accommodation Costs: If special accommodations are required, such as extra time or specific facilities, there may be additional charges for these services.
- Travel and Lodging: If the testing center is located far from your home, you may need to account for travel expenses, including transportation and accommodation costs.
Costs and Fees Associated with Certification
Becoming a certified healthcare professional involves various costs, which can vary depending on the region, testing agency, and specific requirements. It’s important to be aware of all associated fees and to plan your finances accordingly. These costs can include registration fees, study materials, and potential retake fees if necessary. Understanding the full financial scope will help you avoid surprises and manage your expenses effectively.
Common Costs to Consider
The following are some of the most common fees candidates may encounter during the certification process:
- Registration Fees: These are the fees required to sign up for the assessment. The amount can vary depending on the testing organization and location.
- Study Materials: Preparing for the certification may require purchasing textbooks, online courses, or practice tests. These materials are essential to ensure thorough preparation.
- Application Fees: Some regions or agencies may charge additional application processing fees, especially for first-time candidates or those applying for multiple certifications.
- Late Fees: If you miss the standard registration deadline, you may have to pay higher fees for late registration.
Additional Fees and Costs
Aside from direct assessment-related fees, there are other potential costs to keep in mind:
- Retake Fees: In case of a failed attempt, retaking the assessment often involves additional fees. These can sometimes be higher than the original registration fee.
- Accommodation Costs: If special accommodations are required, such as extra time or specific facilities, there may be additional charges for these services.
- Travel and Lodging: If the testing center is located far from your home, you may need to account for travel expenses, including transportation and accommodation costs.
Important Documentation You Need
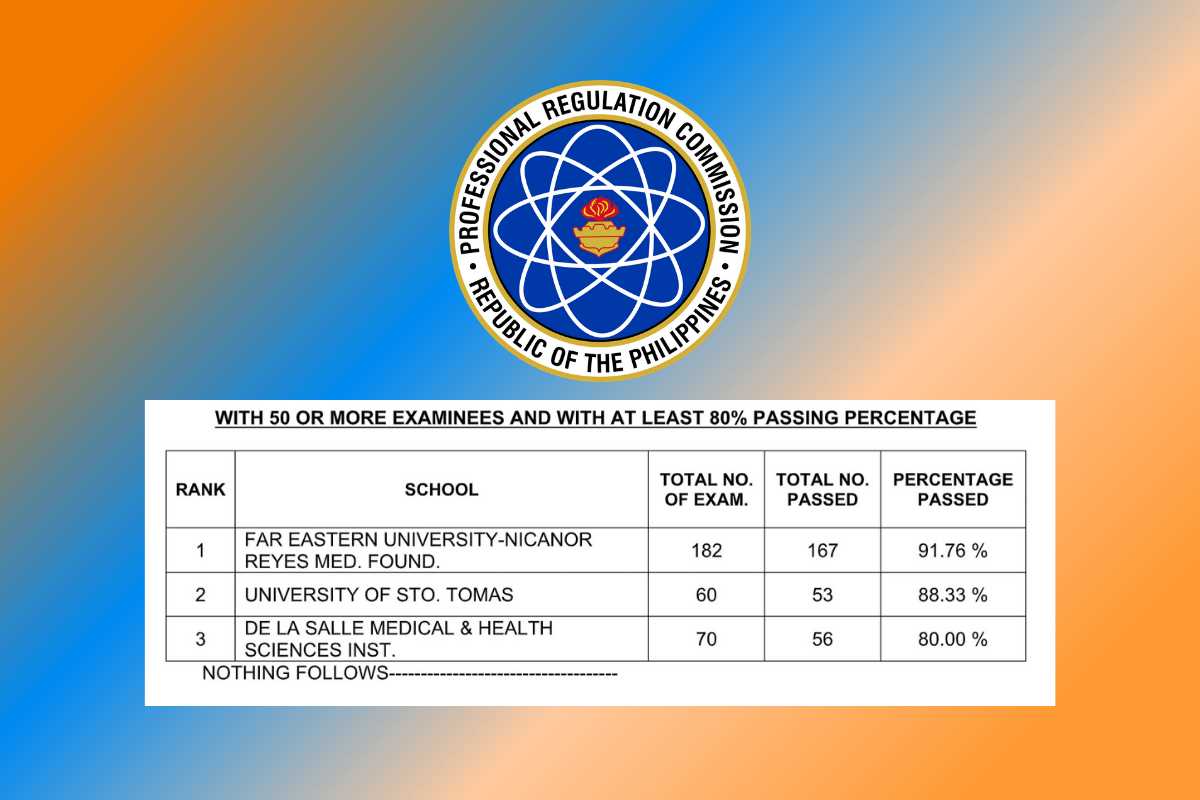
When preparing for the certification process, it is crucial to ensure that you have all the necessary documentation in place. Proper paperwork is required to verify your qualifications, educational background, and eligibility for the assessment. Missing or incomplete documents can lead to delays or complications in the registration process, so being well-prepared is essential.
Essential Documents for Registration

The following documents are typically required when applying for the certification process:
- Identification Proof: A government-issued ID, such as a passport or driver’s license, is necessary to verify your identity during the registration and assessment process.
- Educational Credentials: Official transcripts from accredited institutions or proof of your academic qualifications are essential to demonstrate that you meet the required educational standards.
- Application Form: A completed application form, which may be submitted online or in paper format, is required to initiate the registration process.
- Proof of Experience: Some certifications may require proof of practical experience or training in the field, such as clinical hours or internships.
Additional Documentation for Special Circumstances

If you have special circumstances, such as requesting accommodations or applying from a foreign country, additional documents may be necessary:
- Medical Accommodations: If you require extra time or other accommodations during the assessment, documentation from a healthcare provider may be required to support your request.
- Foreign Credential Verification: For candidates who obtained their qualifications outside of the country, a verification process for foreign credentials may be needed to ensure that they meet local standards.
- Payment Confirmation: Proof of payment for the registration or application fees may be required as part of the submission process.
Understanding Test Scoring and Results
When undergoing a professional certification process, understanding how your performance is evaluated and how the results are communicated is crucial. The scoring system varies depending on the organization administering the assessment, but knowing how the points are allocated and the requirements for passing is essential for proper preparation. Familiarity with the process can help manage expectations and reduce anxiety.
How Scoring Works
The scoring method for most professional assessments typically includes a combination of multiple-choice questions, practical assessments, or written evaluations. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
- Point Allocation: Each question or task is assigned a certain number of points, with more complex or difficult questions often carrying higher value.
- Passing Threshold: The minimum passing score is usually set based on the overall performance of the candidates, and can differ depending on the region or organization.
- Grading Scale: Some organizations use a numerical scale, while others may provide a pass/fail outcome or even letter grades depending on the test type.
Receiving Your Results

Once the assessment has been completed, results are typically shared through one of the following methods:
- Online Portal: Many testing organizations provide access to results through an online portal, where candidates can view detailed feedback and scores.
- Email Notification: Some candidates may receive a formal email with their results, including any next steps in the certification process.
- Physical Mail: In certain cases, particularly for more formal processes, results may be sent via postal mail for added security or privacy.
What Happens After Passing the Exam
After successfully completing a professional assessment, candidates may wonder what the next steps are in the certification journey. Passing the assessment is a significant milestone, but it is only one part of the process. There are various administrative and procedural actions that follow to finalize your certification and grant you full authorization to practice in your chosen field.
Receiving Official Certification

Once you have successfully passed the assessment, the next step is often receiving official documentation that confirms your qualification. This certification is a formal recognition of your competence and may be issued in the following ways:
- Certificate or License: A formal certificate or license is issued, allowing you to legally practice in your profession. This document may include a unique registration number or other identifying information.
- Online Verification: Many certification bodies offer an online verification tool where employers or third parties can confirm your credential status.
Next Steps in Career Development
After passing the assessment and receiving your certification, there are still additional steps to take in your professional journey:
- Continuing Education: Many fields require ongoing education to ensure that professionals stay up-to-date with the latest practices and standards. This may involve periodic courses, workshops, or conferences.
- Career Opportunities: With certification in hand, you are eligible to pursue various career opportunities within your field. This could involve seeking employment, opening your own practice, or specializing further in a specific area.
- Renewal or Requalification: Depending on the profession, some certifications require renewal after a certain period. This may involve retaking assessments or fulfilling specific continuing education requirements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Exam
While undergoing a professional assessment, it is easy to make mistakes that could impact your performance. These errors can range from minor oversights to more significant missteps that may affect your score. Being aware of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them can help you approach the test with greater confidence and improve your chances of success.
Preparation and Time Management Errors
Many candidates make mistakes during the preparation phase that can influence their performance on the day of the test. It is essential to approach the assessment with a clear strategy:
- Procrastinating: Waiting until the last minute to study can lead to unnecessary stress and insufficient preparation. Ensure you have a study schedule that allows enough time to cover all topics.
- Ignoring Practice Questions: Skipping practice tests or sample questions can result in unpreparedness for the types of questions you may encounter. Take time to familiarize yourself with the format and content of the assessment.
- Overloading on Information: Trying to memorize too much material at once can lead to confusion. Focus on understanding key concepts rather than memorizing details.
During the Test: Avoid These Pitfalls
On the day of the test, it’s easy to fall into certain traps that can affect your results. Consider the following:
- Not Reading Instructions Carefully: Failing to read the instructions properly can lead to misunderstandings about the test format or requirements. Always take the time to review the guidelines before starting.
- Spending Too Much Time on One Question: If you get stuck on a difficult question, don’t waste valuable time. Move on and return to it later if you have time remaining.
- Rushing Through the Test: Conversely, rushing to finish the test can lead to careless mistakes. Take your time, and ensure that you are confident in your answers before submitting.
- Overthinking Questions: Sometimes the simplest answer is the correct one. Trust your instincts and avoid overanalyzing questions.
Licensing Requirements by State
Different regions have unique regulations and processes for granting professional credentials, making it essential for candidates to understand the specific requirements of the state in which they plan to practice. These regulations may vary in terms of educational prerequisites, application processes, required examinations, and additional certification. It is crucial to be familiar with the state-specific guidelines to avoid delays or complications in obtaining the necessary qualifications.
Some states may have stricter requirements, while others offer more flexibility. Additionally, certain regions might require additional assessments or residency programs before allowing individuals to practice. Understanding these differences is vital for anyone looking to embark on a career in healthcare and ensuring full compliance with local standards.
It is always recommended to consult the state medical board or the appropriate regulatory agency to stay up-to-date on any changes to the licensing procedures and to ensure all criteria are met in a timely manner.