In academic and professional settings, ensuring the originality of your work is essential for maintaining credibility and integrity. Whether you’re crafting a research paper or completing an assignment, it’s important to express your ideas clearly while respecting the work of others. Understanding the various ways to avoid duplicating existing content will strengthen your academic journey and enhance the quality of your submissions.
Originality in writing goes beyond simply avoiding direct copying. It involves developing your thoughts, properly incorporating external sources, and showcasing your understanding through meaningful paraphrasing and citation. Developing these skills will not only help you follow ethical guidelines but also foster your growth as a thinker and writer.
By learning how to effectively handle external content, you’ll be able to confidently present your work with the necessary respect for intellectual property. This practice will allow you to avoid common pitfalls and confidently present ideas that are both your own and properly attributed to their original sources.
Understanding the Concept of Plagiarism

In academic and professional writing, integrity is crucial. One key aspect of maintaining this integrity is ensuring that all sources of information are properly acknowledged. Failure to do so, whether intentionally or unintentionally, can lead to serious ethical violations. This section explores how to navigate the fine line between using external sources and maintaining your own voice in writing.
The Importance of Acknowledging Sources
When you incorporate someone else’s ideas, research, or findings into your work, it is essential to clearly indicate where that information comes from. Properly attributing ideas not only gives credit to the original author but also strengthens your own credibility. Failing to do this may result in accusations of misrepresentation or intellectual theft.
Recognizing Unintentional Missteps
Many individuals unknowingly cross ethical boundaries by neglecting to cite sources or by paraphrasing too closely. Understanding the boundaries of what constitutes common knowledge and what requires citation can help prevent these errors. Being mindful of these distinctions ensures that you respect the intellectual property of others while maintaining the authenticity of your own work.
Why Academic Honesty Matters
Maintaining integrity in academic work is essential for both personal development and the credibility of the educational system. When students and professionals adhere to ethical standards, it fosters an environment of trust and respect. Upholding these principles ensures that the knowledge shared is accurate, reliable, and genuinely earned, which is crucial for the progression of education and research.
Academic honesty also plays a key role in shaping the character of individuals. It encourages critical thinking, creativity, and a deep understanding of the subject matter. By producing original work and properly attributing ideas, individuals build a reputation based on hard work and intellectual honesty, which is vital for their future academic and professional endeavors.
Common Missteps Leading to Plagiarism
Even the most well-intentioned individuals can make mistakes that compromise the originality of their work. A lack of awareness, poor research habits, or rushing to meet deadlines can result in unintentional violations of academic integrity. It is important to recognize these common errors and learn how to avoid them to ensure the credibility of your work.
Failure to Properly Cite Sources
One of the most frequent mistakes is not giving appropriate credit to the original authors or researchers. Whether it’s direct quotes or paraphrased ideas, failing to include proper references can lead to misunderstandings about the origin of the content. This includes:
- Not using quotation marks for direct quotes.
- Neglecting to cite sources after paraphrasing.
- Using someone else’s ideas without acknowledgment.
Confusion About Common Knowledge
Another common error is misjudging what qualifies as common knowledge and what doesn’t. Information that is widely known or universally accepted may not need citation, but the boundaries can sometimes be unclear. Some examples include:
- Stating widely recognized facts without citation.
- Assuming that any information gathered from the internet is common knowledge.
- Using statistics or data from an unknown source without verifying it.
Being aware of these missteps and taking the necessary precautions can help avoid unintended breaches of academic integrity. Developing good research habits and always double-checking your sources is essential for maintaining the trust and respect of both your peers and instructors.
Effective Methods to Identify Plagiarism
Identifying copied or unoriginal content is crucial to maintaining academic integrity. Various tools and techniques can help determine whether a piece of work contains material that has been improperly reused from other sources. Being familiar with these methods enables both educators and students to ensure that all ideas are properly attributed and no intellectual property is misused.
Using Digital Detection Tools
One of the most effective ways to uncover copied content is by using online detection services. These platforms compare submitted text against a large database of publications, academic papers, and online content to flag similarities. Some of the most commonly used tools include:
- Turnitin
- Copyscape
- Grammarly’s plagiarism checker
These tools provide detailed reports that highlight exact matches and provide links to the original sources, making it easier to verify the authenticity of the work.
Manual Techniques for Spotting Reused Content
While digital tools are useful, manual techniques can also help identify issues. Common methods include:
- Searching for unusual changes in writing style or vocabulary.
- Checking for inconsistencies in citation formatting.
- Using search engines to look for specific phrases or sentences.
These approaches can help identify sections of text that may have been copied from other sources, even if the student or writer has attempted to disguise it.
Tools for Checking Originality
Ensuring the originality of written content is crucial in both academic and professional settings. Various tools have been developed to help assess whether a piece of work has been copied or overly influenced by other sources. These tools compare submitted text with a vast array of online content, academic papers, and publications to provide a detailed analysis of its uniqueness.
Using advanced software and online platforms can help detect any similarities between the submitted work and existing materials. Some of the best tools for this purpose include:
- Turnitin: A widely used platform that compares student submissions against a vast database of academic journals, websites, and other student papers.
- Copyscape: A tool that checks for duplicate content across the web, often used by content creators and website owners.
- Quetext: Offers both free and paid versions that analyze text for similarities and provide detailed reports on any matches.
- Grammarly’s Plagiarism Checker: A versatile tool that not only checks grammar but also scans documents for originality against a broad range of sources.
These tools provide valuable insights into the authenticity of a document, allowing users to ensure that their work maintains the highest level of integrity and originality.
Steps to Properly Cite Sources
Correctly acknowledging the work of others is a vital part of maintaining academic and professional integrity. Proper citation not only ensures that original authors receive credit for their ideas, but it also strengthens the credibility of your own work by demonstrating that your research is grounded in reliable sources. Below are the essential steps to follow when citing any external material in your work.
1. Choose the Right Citation Style
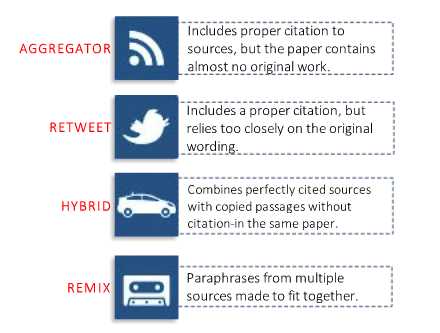
There are several citation styles used across different fields of study. The choice of style often depends on the academic discipline or the guidelines provided by your instructor or publisher. Some of the most common styles include:
- APA (American Psychological Association) – often used in social sciences.
- MLA (Modern Language Association) – common in humanities and literature.
- Chicago – used in history and some social sciences.
- Harvard – frequently used in business and economics.
2. Include All Necessary Information
Each citation style requires specific information to be included in the reference. However, most require the following basic details:
- Author(s) or editor(s) names
- Title of the work (book, article, website, etc.)
- Publisher or journal name
- Date of publication
- Page numbers (if applicable)
- URL or DOI (for online sources)
3. Properly Format Your Citations
Ensure that your citations are formatted correctly according to the chosen style guide. This includes paying attention to punctuation, capitalization, and the order of information. Incorrect formatting can lead to confusion and may even be considered a mistake by reviewers or educators.
4. Provide In-Text Citations
In addition to the full reference list at the end of your document, it is essential to include in-text citations whenever you reference someone else’s work. These citations direct the reader to the full citation in your bibliography or reference list. Depending on the citation style, in-text citations may look like:
- (Author, Year) – APA
- (Author Page Number) – MLA
- Footnotes or Endnotes – Chicago style
5. Review and Double-Check Your Citations
Before submitting your work, carefully review your citations to ensure all information is accurate and properly formatted. Using citation management tools like Zotero, EndNote, or Mendeley can help organize and check your references, saving you time and reducing the chance of errors.
How Paraphrasing Can Prevent Issues
Rephrasing someone else’s ideas in your own words is an essential skill that helps maintain the integrity of your work while demonstrating your understanding of the material. When done correctly, paraphrasing allows you to incorporate external sources without directly copying text, thus reducing the risk of ethical violations. This technique is a key element in producing original content while still drawing on the knowledge of others.
Paraphrasing helps in several ways:
- It shows comprehension: Rewriting ideas in your own style indicates that you understand the material, not just that you can repeat someone else’s words.
- It maintains originality: By transforming the original text, you avoid using someone else’s phrasing verbatim, which keeps your work fresh and unique.
- It strengthens your argument: Paraphrasing allows you to integrate supporting points more seamlessly, presenting them in a way that aligns with your own analysis and flow of thought.
However, it is important to remember that even when paraphrased, the source of the idea must still be properly cited. Simply rewording an idea without attribution can still lead to ethical concerns. Paraphrasing correctly involves not only changing the structure and wording but also ensuring that credit is given where it’s due.
Recognizing Unintentional Plagiarism Risks
Even with the best of intentions, it is easy to make mistakes that can lead to the improper use of others’ work. Unintentional errors can occur when you fail to recognize the need for proper attribution or when you misunderstand what qualifies as original content. Understanding and recognizing these risks can help you avoid serious issues and ensure the authenticity of your work.
Common Causes of Unintentional Misuse
There are several situations in which you may unknowingly use someone else’s ideas or text without proper credit. Some of the most common causes include:
- Misunderstanding Fair Use: Many individuals mistakenly believe that small excerpts of text or common knowledge do not need citation.
- Overreliance on Online Sources: Copying and pasting text from websites without proper citation can easily lead to unintentional misrepresentation of original ideas.
- Unclear Paraphrasing: When paraphrasing, failing to sufficiently change the wording or structure of the original content can lead to similarity with the source material.
Recognizing Potential Risks Early
To minimize the chances of these mistakes, it is important to stay aware of when you might be at risk of misusing someone else’s work. Some proactive strategies include:
- Double-checking citations: Always ensure that every external source is properly referenced.
- Using plagiarism detection tools: Running your work through a tool can help identify any potential matches with existing content.
- Being cautious with paraphrasing: Make sure you truly understand and reframe the original ideas, not just tweak a few words.
By being vigilant and mindful of these potential pitfalls, you can avoid unintentionally compromising the integrity of your work.
The Role of References in Research
In any research work, referencing plays a pivotal role in grounding your ideas within the existing body of knowledge. By acknowledging the work of others, references serve as a framework that supports your arguments and strengthens the credibility of your own conclusions. Properly citing sources not only demonstrates the depth of your research but also allows readers to trace the origins of your information and evaluate its reliability.
Why References Matter
References are not just about giving credit; they also serve several critical functions in research. Here are a few key reasons why they are essential:
- Validation: Citing authoritative sources backs up your claims, showing that your work is based on credible information.
- Engagement with Existing Knowledge: References demonstrate that you are part of an ongoing academic conversation and aware of relevant studies and theories.
- Transparency: Providing full details about your sources allows readers to check the original materials and verify your findings.
Common Types of References
The following table outlines the common types of references you may encounter in academic research:
| Type of Source | Example |
|---|---|
| Books | Author(s), Book Title, Publisher, Year |
| Journal Articles | Author(s), Article Title, Journal Name, Volume, Issue, Year |
| Websites | Author(s), Title of Webpage, Website Name, URL, Date Accessed |
| Conference Papers | Author(s), Paper Title, Conference Name, Location, Year |
Each reference type has its own format, depending on the citation style being used, but they all share the same purpose: to allow others to track down the source material and verify the information provided.
How to Use Plagiarism Detectors
Using automated tools to check for the originality of your work has become an essential part of the research and writing process. These tools compare your content against a vast database of published works to identify any similarities or matches. By running your content through these systems, you can ensure that all the ideas are properly attributed and that your work remains fully authentic.
Steps to Effectively Use Detection Tools
Here’s a basic guide on how to use these tools effectively:
- Select a Reliable Tool: Choose a reputable detector that has access to a wide range of sources, including academic journals, articles, and websites.
- Upload Your Content: Copy and paste your text into the tool or upload your document directly to the system. Many tools support various file types, such as Word and PDF.
- Review the Results: After the analysis is complete, carefully examine the report. It will highlight any areas that resemble other published work, showing where citations or rephrasing may be necessary.
- Take Corrective Actions: If the tool identifies unintentional matches, you can either paraphrase the content or add the necessary references to ensure proper attribution.
Limitations of Detection Tools
While plagiarism detection systems are incredibly useful, they are not flawless. Some limitations include:
- False Positives: The tool might flag common phrases or properly cited references as similar, leading to unnecessary revisions.
- Limited Access: Not all tools scan the same databases, so some may miss potential matches from niche sources or unpublished works.
- Accuracy Variations: The reliability of results can vary depending on the tool used, so it’s important to cross-check findings with other methods when possible.
Despite these limitations, plagiarism detectors remain a valuable resource in maintaining the integrity of your work and ensuring proper originality before submission.
Crafting Authentic Content for Assignments
Creating original work for academic assignments requires a thoughtful approach that showcases your understanding and critical thinking. When you develop content from your own perspective, it not only reflects your individual voice but also demonstrates a deep engagement with the subject. By focusing on producing fresh, well-researched ideas, you can maintain integrity while meeting the expectations of your assignments.
Steps to Ensure Your Content is Unique
To produce content that is both original and of high quality, follow these steps:
- Start with Research: Begin by gathering information from multiple credible sources to get a broad understanding of the topic.
- Organize Your Thoughts: Create an outline that organizes your ideas logically and supports the main argument you intend to make.
- Use Your Own Voice: While research is essential, make sure to express ideas and concepts in your own words. Avoid simply rephrasing what others have said.
- Provide Evidence: Use examples, data, or quotes to support your claims. Always cite the sources where you gathered this information.
Why Paraphrasing and Summarizing Matter
To avoid the temptation of copying ideas directly, it’s essential to master the art of paraphrasing and summarizing. Instead of repeating the original text verbatim, try to restate the concepts in your own terms, while still preserving the core meaning. This not only strengthens your understanding but also demonstrates your ability to synthesize information from various sources.
By following these guidelines, you will be able to create authentic and well-crafted content that not only adheres to academic standards but also showcases your individual thought process and creativity.
Improving Research Skills for Accuracy
Effective research is crucial to ensuring that your work is credible and well-supported by reliable data. By enhancing your research skills, you can ensure that your findings are accurate, relevant, and up-to-date. Strong research techniques also help avoid the risk of relying on incorrect or misleading information, which can undermine the quality of your work.
To improve your research abilities, consider the following strategies:
| Research Technique | Benefits | How to Implement |
|---|---|---|
| Use Multiple Sources | Ensures diverse perspectives and comprehensive understanding of the topic. | Consult academic journals, books, reputable websites, and primary sources. |
| Evaluate Source Credibility | Helps ensure the reliability and authority of the information used. | Check the author’s qualifications, publication history, and the source’s reputation. |
| Organize Information Effectively | Improves clarity and focus in presenting findings. | Use tools like mind maps, outlines, or digital note-taking apps to categorize information. |
| Stay Updated | Ensures that your research reflects the most current developments. | Regularly check academic databases and subscribe to relevant journals or newsletters. |
By refining these research strategies, you can enhance the accuracy and integrity of your work, which is essential for producing high-quality assignments or projects. Strong research skills lead to more reliable and credible results, reflecting the depth of your understanding and the value of your contributions.
Consequences of Violating Plagiarism Rules
Failing to adhere to academic integrity standards can lead to serious repercussions, both in educational and professional contexts. When individuals fail to properly credit their sources or attempt to pass off others’ work as their own, they risk facing penalties that can significantly affect their academic or career path. Understanding the potential consequences is essential for maintaining a responsible and ethical approach to research and writing.
The repercussions of not following proper citation and originality guidelines can range from academic penalties to long-term damage to one’s reputation. Institutions and employers typically have strict policies in place to address violations, and these consequences can be severe.
- Academic Consequences: Students may face failing grades, suspension, or even expulsion for not following proper citation practices or for submitting unoriginal work.
- Loss of Credibility: A violation can result in a damaged reputation, which may affect future opportunities in both education and the workforce.
- Legal Penalties: In some cases, individuals could face legal actions if intellectual property rights are violated through unauthorized use of copyrighted materials.
- Long-Term Career Impacts: Once an integrity violation is recorded, it can impact professional relationships, academic references, and the potential for career advancement.
By understanding these risks, it becomes clear that maintaining honesty and integrity in all aspects of academic and professional work is crucial. These principles not only safeguard personal reputation but also contribute to the credibility of the academic and professional communities at large.
Educational Strategies to Avoid Copying
Developing strategies to ensure original work is essential for both students and professionals. By embracing key educational practices, individuals can foster a deeper understanding of subjects and produce authentic contributions. These methods focus on enhancing skills in research, critical thinking, and proper source attribution, which are all integral to preventing the temptation of copying others’ ideas or content.
Adopting the following strategies can greatly reduce the likelihood of unoriginal work, while promoting academic integrity:
Effective Learning Techniques
- Active Note-Taking: Instead of directly copying content, take notes in your own words to ensure better understanding and retention of material.
- Summarizing Key Points: Practice summarizing sections of text in your own style, helping to internalize concepts and avoid reliance on external sources.
- Research Beyond Surface-Level: Engage with primary sources, explore multiple viewpoints, and critically analyze information to deepen your understanding and reduce the temptation to copy.
Proper Citation and Source Management
- Learn Citation Styles: Familiarize yourself with various citation formats (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) and apply them consistently to properly attribute the work of others.
- Utilize Plagiarism Checkers: Make use of tools to double-check your work for proper referencing and ensure that no unintentional copying has occurred.
- Keep Detailed Notes on Sources: Maintain a thorough record of where your information comes from so you can cite it accurately and avoid unintentional omissions.
By incorporating these techniques, individuals can cultivate skills that lead to producing authentic and well-supported work. Developing good habits early on not only prevents issues related to copying but also contributes to personal growth and academic success.
Building Confidence in Original Writing
Developing confidence in creating original work is essential for anyone looking to express their thoughts clearly and authentically. This confidence doesn’t come overnight, but through consistent practice, understanding the value of independent thought, and embracing one’s unique voice. By focusing on the process of research, analysis, and synthesis, writers can build the self-assurance necessary to produce work that is both creative and academically sound.
The following strategies can help individuals strengthen their belief in their own writing abilities:
- Practice Regular Writing: The more frequently you write, the more comfortable and confident you become in producing original content. Make writing a part of your daily routine.
- Understand Your Voice: Trust in your personal writing style and perspective. Don’t feel pressured to mimic others–your voice is valuable and worth sharing.
- Break Down Complex Ideas: Start with simple ideas and build up to more complex arguments. This helps you manage the process of creating unique work while ensuring clarity.
By focusing on these methods, writers can grow more comfortable with their own voice and avoid the temptation to lean on external sources. Confidence in writing stems from knowing that your ideas and analysis are valuable and that your work represents your true academic or creative potential.
Mastering Proper Quotation Techniques
Using quotations correctly is an essential skill for presenting others’ ideas while maintaining the integrity of your own work. Properly incorporating someone else’s words into your writing not only gives credit to the original author but also strengthens your argument or analysis. Mastering the art of quoting allows you to support your claims effectively without misrepresenting the original source.
To ensure quotations are used correctly, it’s important to understand the guidelines and techniques involved. Here are a few key principles to follow:
Understanding When to Quote
Quotes should be used sparingly and only when the exact wording is crucial to your point. Use quotes for:
- Direct statements that support your argument or analysis.
- Historical or literary sources where wording is significant.
- Expert opinions that lend authority to your work.
Proper Formatting of Quotes
Follow these formatting rules to ensure accuracy and clarity:
- Short quotes: For quotes that are fewer than 40 words, include them within your text, enclosed in quotation marks.
- Long quotes: If the quote exceeds 40 words, set it off from the rest of the text by indenting it and omitting quotation marks.
By applying these techniques, you can properly incorporate external sources into your work, making your writing more credible and well-supported while respecting the intellectual property of others.