When preparing for a high-stakes certification in critical care, it’s crucial to understand both the subject matter and the best strategies for tackling difficult questions. Mastering the essential skills in the intensive care environment requires more than just memorization–it demands practical knowledge, quick decision-making, and a deep understanding of patient care procedures.
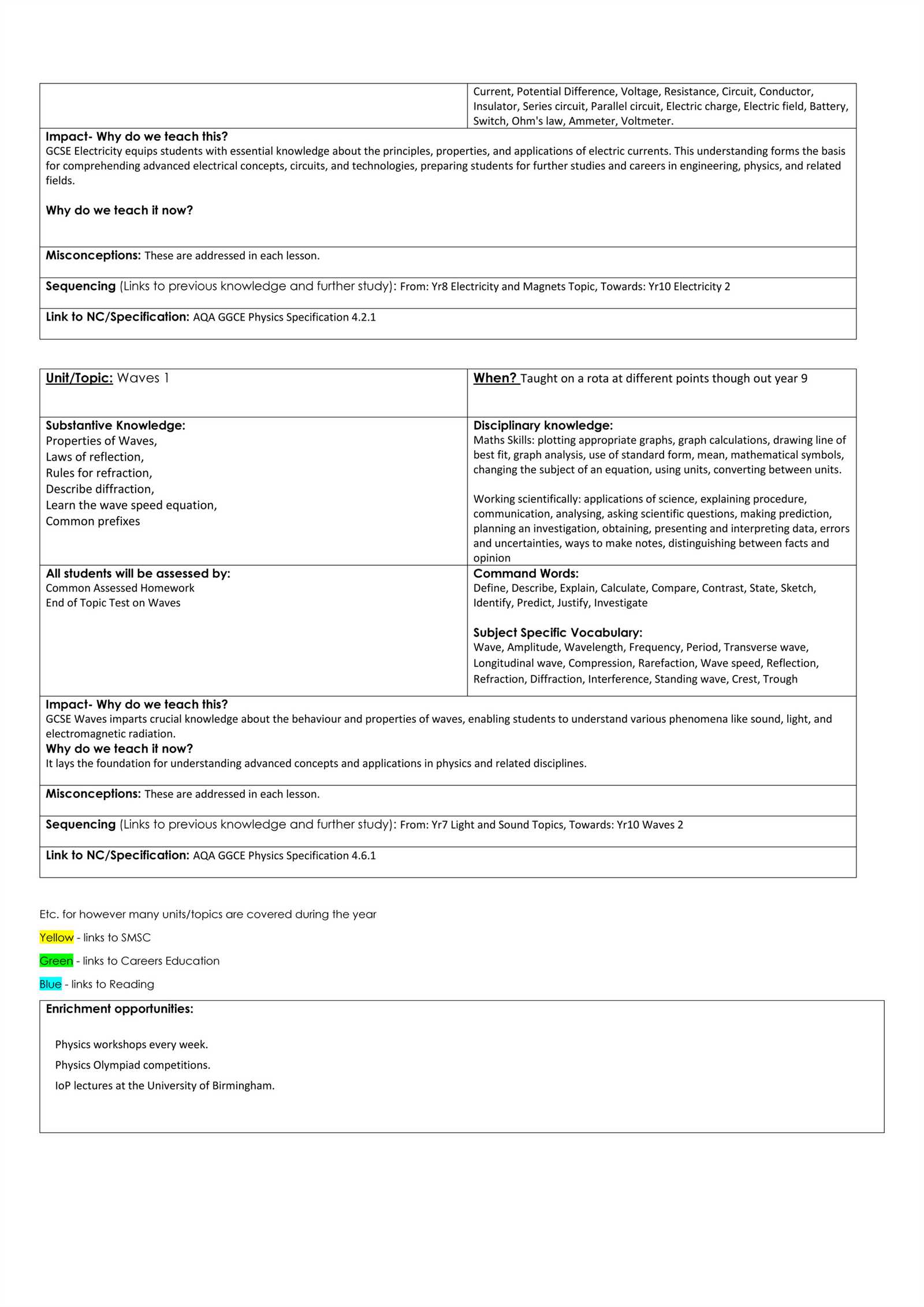
Effective preparation hinges on focusing not only on theoretical knowledge but also on the application of that knowledge in real-world situations. This guide aims to provide you with the tools to navigate complex tests and enhance your clinical judgment through a structured approach. From time management techniques to key areas of focus, we’ll cover the strategies that can help you succeed.
Whether you’re tackling intricate pharmacological scenarios or interpreting vital signs under pressure, being well-prepared will boost your confidence. Stay organized and prioritize learning materials that will address the most critical aspects of your upcoming assessments. The path to certification can be challenging, but with the right resources and mindset, you can excel in this demanding field.
Critical Care Certification Overview
Achieving certification in critical care requires more than just theoretical knowledge. It involves understanding how to apply critical thinking and clinical expertise in high-pressure situations. This section explores the key components of a structured evaluation process for healthcare professionals in this field, focusing on the essential topics and skills that are evaluated during assessments.
Key Topics Covered in the Evaluation
Healthcare providers are tested on a wide range of topics, including patient monitoring, drug administration, and emergency response protocols. The focus is on the ability to make quick, informed decisions while ensuring the highest standard of care. Each area of the test is designed to assess the depth of knowledge and the ability to apply it in real-life scenarios. Key topics often include respiratory management, cardiovascular stability, and fluid therapy.
Approach to Study and Preparation
Effective preparation involves a combination of study techniques and practical application. Familiarizing yourself with the test format and practicing under time constraints can significantly improve performance. Focusing on understanding rather than rote memorization will ensure that you are equipped to handle the complex scenarios that may arise during the evaluation. Regular self-assessment and review of clinical guidelines are crucial for success.
Understanding Critical Care Assessment Structure
Preparing for a certification in critical care requires an understanding of how the evaluation process is organized. These assessments are carefully structured to measure both theoretical knowledge and practical skills required for high-level patient care in intense environments. The format is designed to challenge candidates in various critical areas of healthcare, testing their ability to respond effectively in emergencies and manage complex clinical situations.
Components of the Assessment
The structure of the test typically includes multiple components that assess a broad range of knowledge and practical expertise. These sections are designed to evaluate candidates’ skills in real-world scenarios, focusing on both technical knowledge and the ability to apply that knowledge under pressure. Key areas of evaluation include:
- Cardiovascular monitoring and intervention
- Respiratory management and ventilation techniques
- Pharmacology and medication administration
- Fluid and electrolyte balance
- Advanced life support protocols
- Patient assessment and clinical judgment
Test Format and Delivery
The structure of the test is often divided into written sections and practical simulations. Written portions focus on theoretical understanding, while practical scenarios require candidates to demonstrate decision-making and problem-solving skills in a controlled environment. The format may include:
- Multiple-choice questions (MCQs) that test factual knowledge
- Case studies that challenge critical thinking and application of knowledge
- Simulation-based assessments that mimic real-world clinical situations
- Practical skills testing, where candidates perform key procedures under observation
Understanding the structure of this assessment will help candidates approach their preparation with confidence, ensuring they focus on the most critical areas for success.
Key Concepts to Focus On
In order to excel in critical care assessments, it is essential to focus on the fundamental concepts that are evaluated in various healthcare situations. These key topics not only form the basis of the test but also reflect the critical areas of knowledge required for providing optimal patient care in high-pressure environments. Mastery of these concepts will enhance clinical decision-making and ensure preparedness for challenging clinical scenarios.
Essential Clinical Areas
There are several core areas that candidates should prioritize in their preparation. These areas cover both theoretical knowledge and practical application, and they are crucial for making informed decisions during emergency situations. Below is an overview of the most important concepts to focus on:
| Concept | Details |
|---|---|
| Cardiac Monitoring | Understanding heart rhythms, interpreting ECG results, and managing cardiac emergencies |
| Respiratory Management | Ventilation techniques, oxygen therapy, and airway management in critical conditions |
| Pharmacology | Knowledge of medications used in intensive care, their effects, dosages, and interactions |
| Fluid and Electrolyte Balance | Monitoring and adjusting fluid levels and electrolytes to maintain homeostasis |
| Advanced Life Support | Protocols for resuscitation and life-saving interventions in critical care settings |
Clinical Skills and Decision-Making
While knowledge is crucial, clinical skills and the ability to make swift, accurate decisions are equally important. Focusing on practical skills, such as emergency response procedures and patient assessment techniques, is vital for success. Understanding the various tools and technologies used in critical care settings, along with the ability to adapt to rapidly changing conditions, will prepare candidates for the challenges they will face in real-life situations.
Top Resources for Certification Preparation
To succeed in a critical care certification, having access to high-quality study materials and resources is essential. These resources provide comprehensive coverage of key concepts, clinical skills, and testing strategies, ensuring that you are well-prepared for the assessment. In this section, we highlight the most effective study tools and materials that will aid in your preparation process.
Recommended Study Materials
When preparing for a critical care certification, it’s important to use a variety of materials to cover all aspects of the test. Here are some top resources to guide your studies:
- Textbooks and Clinical Guidelines: These offer in-depth explanations and foundational knowledge on critical care practices.
- Online Courses: Interactive online learning platforms provide structured lessons on key topics with quizzes and practice tests.
- Study Guides: Compact, focused study guides summarize essential concepts, perfect for quick reviews.
- Practice Tests: Practice tests help familiarize you with the test format and identify areas where further review is needed.
- Flashcards: These are helpful for memorizing important facts, drug names, and protocols.
Practical Tools and Simulations
In addition to theoretical materials, practical tools and simulations can help you apply your knowledge in a clinical setting. These resources allow you to practice real-life scenarios and develop your critical decision-making skills:
- Simulation Software: Virtual simulations recreate high-stress clinical situations to help you practice decision-making and emergency interventions.
- Clinical Workshops: Hands-on workshops offer practical experience with equipment, tools, and real-life procedures.
- Peer Study Groups: Collaborating with fellow candidates in study groups can enhance learning through discussion and shared resources.
Utilizing these top resources will ensure that you have a well-rounded approach to your preparation, increasing your chances of success in the certification process.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When preparing for a critical care certification, avoiding common pitfalls can significantly improve your chances of success. Many candidates make mistakes that can hinder their performance, whether it’s through ineffective study strategies or misunderstanding key concepts. In this section, we highlight the most frequent errors made during preparation and offer tips on how to prevent them.
One of the biggest mistakes is relying too heavily on memorization rather than understanding the underlying principles. Simply memorizing facts without grasping how to apply them in real-world scenarios can lead to confusion during the assessment. It’s important to focus on comprehension and practice using the information in clinical contexts.
Another mistake is neglecting to practice time management. During high-stakes tests, time is limited, and failing to pace yourself can result in incomplete answers or unnecessary stress. Regularly timing your practice sessions will help you build the skill of answering questions efficiently within the allotted time frame.
Additionally, skipping review of weak areas is a common misstep. Focusing only on the topics you are comfortable with can lead to gaps in your knowledge. Be sure to allocate time for reviewing all areas, especially those that you find more challenging.
Lastly, underestimating the importance of practical skills and simulations can also be detrimental. While theoretical knowledge is crucial, real-life decision-making and technical proficiency are equally important. Hands-on practice and exposure to clinical simulations will help you better prepare for the practical demands of critical care environments.
How to Approach Critical Care Questions
Successfully answering questions in critical care assessments requires a strategic approach. These questions often test not only your knowledge but also your ability to think critically and make decisions under pressure. To perform well, it’s important to adopt effective strategies that help you analyze, prioritize, and apply your understanding of clinical practices. This section will guide you through techniques that can enhance your problem-solving skills and improve your performance on assessment day.
Breaking Down the Question
The first step when encountering a critical care question is to carefully read and analyze it. Look for key details such as patient symptoms, medical history, and specific scenarios. Pay attention to the phrasing of the question, as it often gives clues about the expected answer. Breaking the question into smaller parts can help you identify the most relevant information and avoid getting overwhelmed by unnecessary details.
Applying Clinical Knowledge
Once you have identified the critical components, apply your clinical knowledge to the situation. Recall the principles, guidelines, and protocols you’ve studied, and think about how they relate to the scenario presented. Prioritize your response based on what would be most appropriate for the patient’s condition. Consider possible complications or risks, and make decisions that reflect safe and effective care practices.
By focusing on the core details and applying your understanding of critical care, you can approach each question with confidence and precision. With consistent practice, this method will help you develop the decision-making skills required in real-world clinical settings.
Effective Time Management Tips
Time management is a crucial skill when preparing for high-stakes healthcare certifications. The ability to organize study sessions efficiently and allocate time wisely can make a significant difference in your performance. With the volume of information to review and the need to stay focused, mastering time management techniques will help you balance thorough study with effective practice.
To enhance your time management during preparation, consider implementing structured strategies that prioritize your study areas, maximize productivity, and reduce stress. These tips will help you stay organized and ensure that you cover all necessary material in a timely manner.
| Tip | Details |
|---|---|
| Prioritize Key Topics | Focus on the areas most likely to appear on the test. Identify your weak spots and allocate more time for review in those areas. |
| Create a Study Schedule | Set specific study goals each day, breaking large tasks into smaller, manageable chunks. This prevents procrastination and ensures steady progress. |
| Use Time Blocks | Work in short, focused bursts (e.g., 25-30 minutes) followed by brief breaks. This method, known as the Pomodoro technique, helps maintain focus and energy. |
| Practice Under Time Constraints | Regularly take timed practice tests or quizzes to simulate the test environment. This helps improve speed and decision-making under pressure. |
| Minimize Distractions | Set a quiet, organized study space free from distractions. Turn off notifications and avoid multitasking to maintain focus on the material. |
By applying these time management strategies, you will improve both your study efficiency and your ability to handle the pressure of a timed assessment. Consistent planning and practice will prepare you for success when the time comes to take the certification test.
Strategies for Answering Complex Questions
Handling complex questions requires a structured approach that allows you to break down intricate scenarios into manageable parts. These questions often involve multiple concepts or scenarios that require careful consideration and application of knowledge. By using effective strategies, you can navigate these challenging questions with confidence and ensure that your responses are clear and accurate.
Breaking Down the Question
The first step in answering complex questions is to break them down into smaller, more digestible components. Read the question thoroughly and identify the key details, such as the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and specific instructions. Look for any keywords or phrases that hint at the primary focus of the question. This will help you avoid getting overwhelmed by unnecessary information and will guide you toward the most relevant concepts.
Applying Logical Reasoning
Once you’ve identified the key elements, use logical reasoning to apply your knowledge. Consider the most likely outcomes based on the clinical information presented. Think through the possible choices, evaluating them based on their clinical relevance and alignment with established guidelines. By systematically narrowing down your options, you can eliminate irrelevant or incorrect answers and focus on the most appropriate solution.
By approaching complex questions with a methodical strategy, you will be able to reduce uncertainty and improve your ability to make informed decisions under pressure. This approach not only helps with exams but also prepares you for real-world clinical decision-making in high-stress environments.
Study Plan for Success
Creating a structured study plan is essential for achieving success in high-stakes certifications. A well-organized approach allows you to manage your time effectively, prioritize important topics, and track your progress. By breaking down the preparation into manageable tasks, you can reduce stress and ensure comprehensive coverage of all necessary material.
Setting Realistic Goals
The first step in crafting a successful study plan is setting clear, realistic goals. Start by identifying the key areas you need to focus on, then break these into smaller objectives. Set daily or weekly targets to keep yourself on track. Make sure your goals are specific, measurable, and achievable, such as mastering a particular topic by the end of the week or completing a practice test every few days. This method will help you build momentum and keep your motivation high.
Balanced Study Sessions
A balanced study schedule is crucial for maintaining productivity without burnout. Alternate between different types of content to keep things engaging. For example, spend one session reviewing theoretical concepts, followed by another where you focus on practical applications or simulations. Incorporating variety into your study routine will help reinforce learning and improve retention.
In addition, be sure to allocate time for regular reviews of previously studied material. This will help reinforce your knowledge and ensure you retain information long-term. Scheduling frequent breaks will also help maintain focus and prevent fatigue during study sessions.
By adhering to a structured study plan, you’ll be able to efficiently cover all necessary topics, boost your confidence, and significantly improve your chances of success. Remember, consistency and careful planning are key to a well-rounded preparation strategy.
Importance of Practice Tests
Practice tests are an invaluable tool in preparing for certification assessments, offering a way to simulate the real testing experience. These assessments not only help reinforce the material you’ve studied but also allow you to familiarize yourself with the test format and timing constraints. By regularly testing your knowledge, you can identify areas of strength and areas that need further review, ultimately improving your performance on the actual exam.
In addition to reinforcing your knowledge, practice tests help build confidence. When you know you’ve successfully answered practice questions, you feel more assured in your ability to handle the real test. They also teach time management skills, as you learn to pace yourself and allocate the right amount of time to each section. This preparation reduces anxiety and increases your efficiency on exam day.
Furthermore, taking practice tests helps you become more adept at interpreting complex questions. These tests often contain scenarios similar to those you will encounter in the real assessment, allowing you to hone your decision-making skills under pressure. Regular practice ensures that you’re not only recalling information but applying it correctly in a variety of contexts.
Reviewing Key Cardiovascular Topics
When preparing for healthcare assessments, it is essential to focus on fundamental cardiovascular concepts that form the foundation for many clinical scenarios. A solid understanding of these topics will help you not only in answering questions but also in applying critical thinking in real-world situations. This section covers the most important areas to review and provides guidance on how to approach complex cardiovascular-related questions.
Core Cardiovascular Diseases
Begin by reviewing the core cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure, myocardial infarction, arrhythmias, and hypertension. Understanding the pathophysiology, treatment options, and clinical presentations of these conditions is crucial. Pay particular attention to the management protocols and the signs that differentiate one disease from another. Knowing when to use specific medications, as well as recognizing red flags, can significantly improve your diagnostic accuracy.
Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures
Another key area to focus on is the diagnostic tools used to assess cardiovascular health. These include ECG interpretation, echocardiography, and stress testing. Familiarize yourself with the various types of diagnostic imaging and their specific indications. Understanding how to interpret these tests is essential in making timely and accurate clinical decisions. Additionally, know the common complications and contraindications associated with each diagnostic procedure.
By thoroughly reviewing these key cardiovascular topics, you will ensure that you are well-prepared to address clinical questions with confidence and precision. Mastery of these areas will help you not only in assessments but also in delivering high-quality patient care.
Understanding Drug Dosages in Critical Care
Accurate drug dosing is critical in intensive care settings, where patients often require specialized treatment protocols. A clear understanding of drug dosages ensures that patients receive the proper medications in the right amounts, minimizing the risk of adverse effects and improving outcomes. In this section, we will explore the key factors that influence drug dosages in critical care and provide an overview of essential medications commonly used in such settings.
Key Factors Affecting Dosage Decisions

Drug dosages are determined by several factors, including the patient’s age, weight, renal function, and underlying medical conditions. Healthcare providers must also consider the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of each drug. Pharmacokinetics refers to how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and excretes a drug, while pharmacodynamics focuses on how the drug interacts with the body to produce its therapeutic effects.
For example, a patient with impaired kidney function may require reduced dosages of renally cleared drugs to avoid toxicity. Similarly, drugs used in emergency situations may need to be adjusted based on real-time assessments of a patient’s response. Continuous monitoring and adjustments are often necessary to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Commonly Used Medications in Critical Care

| Medication | Indication | Typical Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Furosemide | Edema, heart failure | 20-40 mg IV bolus |
| Dobutamine | Cardiogenic shock, heart failure | 2-20 mcg/kg/min IV infusion |
| Heparin | Anticoagulation | Loading dose: 60-70 units/kg IV |
| Noradrenaline | Hypotension, shock | 0.01-3 mcg/kg/min IV infusion |
Each medication requires careful consideration of dosing intervals, monitoring parameters, and potential drug interactions. Accurate calculations and consistent tracking of patients’ responses are key to ensuring that treatments remain effective and safe throughout the care process. Understanding these principles is essential for any healthcare provider working in critical care environments.
Monitoring Vital Signs in ICU Settings
In intensive care units (ICU), continuous monitoring of vital signs is essential for detecting early signs of deterioration, guiding treatment decisions, and ensuring patient safety. Vital signs provide real-time data that healthcare providers use to assess the physiological status of critically ill patients. Regular assessment of these signs allows clinicians to make informed decisions regarding interventions and adjustments to care plans.
Key Vital Signs to Monitor
The core vital signs that need to be continuously monitored in ICU settings include:
- Heart Rate: Indicates cardiac function and can reveal arrhythmias or hemodynamic instability.
- Blood Pressure: Assesses perfusion and organ function; abnormal readings may signal sepsis, shock, or bleeding.
- Respiratory Rate: Reflects respiratory function and oxygenation status. It can indicate respiratory distress, failure, or the need for ventilation support.
- Oxygen Saturation (SpO2): Measures the level of oxygen in the blood, crucial for detecting hypoxemia and guiding oxygen therapy.
- Temperature: Helps in identifying infections, inflammation, or hypothermic states.
Technological Tools for Monitoring
Modern ICU settings rely heavily on advanced equipment to monitor these vital signs. Some of the commonly used tools include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Provides continuous heart rate and rhythm monitoring, essential for detecting arrhythmias.
- Pulse Oximeter: Non-invasive tool used to measure oxygen saturation levels in the blood.
- Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring: Used to track blood pressure and cardiac output through catheters, especially in critically ill patients.
- Capnography: Measures carbon dioxide levels in exhaled air, aiding in the assessment of respiratory function.
By continuously monitoring these parameters, healthcare providers can quickly identify any significant changes in a patient’s condition, allowing for timely interventions and the adjustment of treatment strategies. Understanding the importance of accurate and consistent monitoring is crucial for managing critically ill patients in the ICU environment.
How to Interpret Lab Results
Interpreting laboratory results is a critical skill for healthcare professionals, as these results provide essential insights into a patient’s health condition. Lab tests help identify diseases, monitor ongoing treatment effectiveness, and track recovery progress. Proper understanding of lab values is key to making informed clinical decisions and ensuring patient safety.
Key Factors to Consider
When interpreting lab results, several factors should be taken into account to ensure accuracy and relevance:
- Reference Ranges: Compare the patient’s results with the standard reference ranges, but always consider age, gender, and individual health conditions, as these can influence normal values.
- Clinical Context: Always interpret lab results within the broader context of the patient’s clinical presentation. Laboratory results should never be analyzed in isolation.
- Trends Over Time: A single lab result may not tell the whole story. Observing trends in lab values over time can provide better insights into disease progression or treatment effectiveness.
- Pre-Analytical Variables: Ensure that samples are collected, stored, and transported correctly to avoid inaccurate results due to improper handling.
Common Lab Results and Their Significance
Some of the most frequently tested lab parameters and what they indicate are:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Evaluates the overall health of the patient by measuring different components of the blood, such as red and white blood cells, hemoglobin, and platelets. Abnormalities can point to infections, anemia, or blood disorders.
- Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP): Measures electrolyte levels, kidney function, and blood sugar. Imbalances can indicate dehydration, kidney dysfunction, or metabolic disturbances.
- Liver Function Tests (LFTs): Assess liver health by measuring enzymes like ALT, AST, and bilirubin. Elevated levels often suggest liver damage or disease.
- Coagulation Profile: Includes tests like PT, aPTT, and INR, which evaluate blood clotting. Abnormal results can indicate bleeding disorders or excessive clotting risks.
Interpreting lab results requires careful attention to detail and an understanding of their limitations. Always correlate lab findings with the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and other diagnostic information to arrive at an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Dealing with High-Stress Scenarios
In healthcare settings, particularly in critical care environments, high-pressure situations are common. The ability to remain calm and make quick, effective decisions is crucial for patient safety and successful outcomes. These high-stress scenarios demand a combination of mental clarity, practical skills, and emotional resilience to manage effectively.
Strategies for Staying Calm
Maintaining composure under pressure is essential for making clear decisions. Here are some strategies that can help in high-stress situations:
- Controlled Breathing: Deep, slow breaths can help reduce immediate feelings of anxiety and promote focus.
- Prioritize Tasks: Quickly assess the situation and focus on the most urgent needs. Address life-threatening conditions first before moving on to less critical issues.
- Stay Present: Focus on the current task rather than worrying about potential outcomes. Staying in the moment can help reduce stress and improve efficiency.
- Use Checklists: In chaotic environments, following a pre-established checklist ensures that no critical steps are missed during an emergency.
Teamwork and Communication
Working effectively as a team is a key element in managing high-stress situations. Clear, concise communication can prevent misunderstandings and promote better collaboration. Consider these techniques:
- Clear Instructions: Use simple, direct language when giving or receiving orders. This minimizes confusion during critical moments.
- Delegate Tasks: Trust your team members with specific responsibilities. Sharing the workload helps manage stress and ensures all tasks are covered.
- Support Each Other: Acknowledge the emotional toll these situations take on everyone. Providing support and encouragement can help team members stay focused and motivated.
By developing strategies for remaining calm, prioritizing tasks, and fostering strong teamwork, healthcare professionals can better navigate high-stress scenarios and provide optimal care in critical moments.
Exam Day Preparation Checklist
Preparing for a high-stakes assessment requires organization and focus. On the day of the evaluation, it’s crucial to ensure that all logistics are handled, mental readiness is achieved, and resources are in place to succeed. A well-prepared approach can help reduce stress and boost confidence, leading to better performance.
Key Steps for the Morning of the Assessment
- Get Plenty of Rest: Ensure you have a good night’s sleep the night before. Rest is essential for cognitive function and focus.
- Eat a Nutritious Breakfast: Fuel your body and mind with a balanced meal, including protein, whole grains, and healthy fats. Avoid heavy or sugary foods that may cause energy crashes.
- Review Your Materials: Briefly go over your study materials to reinforce your understanding. Avoid cramming but focus on key concepts.
- Gather Required Documents: Ensure that all necessary identification, registration information, and any other required materials are packed and ready.
Practical Steps for During the Evaluation
- Arrive Early: Arriving ahead of time gives you a chance to settle in, organize your space, and calm any nerves.
- Manage Your Time: Be mindful of time during the assessment. Use any allotted breaks to refresh, but avoid wasting too much time on any single question.
- Stay Calm and Focused: If you feel anxious, practice deep breathing techniques to stay composed. Focus on each question without rushing.
- Read Each Question Carefully: Ensure you understand what is being asked before answering. Don’t rush through the questions, as accuracy is key.
By following these preparation steps, you can enter the evaluation with confidence and readiness. Being organized and calm will allow you to focus on demonstrating your skills effectively.
After the Exam: Next Steps
Once the assessment is complete, the process is far from over. There are several crucial steps to take to ensure a smooth transition to the next phase, whether you’re awaiting results, planning further studies, or preparing for future challenges. These actions can help you maintain focus, stay organized, and be ready for whatever comes next.
Immediate Actions Post-Assessment
- Take a Moment to Relax: After completing the test, it’s important to take a break. Clear your mind by engaging in a relaxing activity, whether it’s going for a walk or practicing deep breathing.
- Review Your Performance: While it’s not always possible to get instant feedback, reflect on the areas where you felt confident and areas that might need more attention. This self-assessment will guide your future efforts.
- Avoid Obsessing Over Details: It’s easy to second-guess yourself after completing an assessment. Resist the temptation to dwell on individual questions or answers. Instead, focus on moving forward.
Post-Evaluation Preparation
- Monitor for Results: Stay updated on when and how results will be released. Make sure you’re prepared to receive them and understand how to interpret the feedback.
- Plan for Further Study: If areas of improvement were identified during the assessment, develop a study plan to address these gaps. Use the assessment as a learning tool to enhance your knowledge for future opportunities.
- Stay Engaged with Your Network: Continue connecting with peers or mentors who can offer guidance or support as you move through the next steps. Sharing experiences can provide valuable insights.
By following these post-assessment steps, you can effectively manage the outcome and set yourself up for success in future endeavors. Whether it’s waiting for results, analyzing your performance, or planning further learning, staying proactive will help you move forward with confidence.
Maintaining Skills After Passing the Exam
Achieving success in a professional assessment is a significant milestone, but the journey doesn’t end there. To remain proficient and ensure that the knowledge gained stays relevant, it’s essential to continue practicing and updating your skills. Maintaining expertise over time requires ongoing effort, continuous learning, and exposure to real-world applications.
Strategies for Skill Retention
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated on the latest developments in your field by reading relevant journals, attending workshops, or taking advanced courses.
- Practical Application: Actively apply the knowledge in daily tasks or simulations. The more you engage in hands-on practice, the stronger your retention.
- Peer Interaction: Regularly collaborate with colleagues or join professional networks. This interaction provides valuable insights and helps reinforce what you’ve learned.
- Set Regular Goals: Create short-term and long-term goals to challenge yourself. These goals should focus on areas where you want to improve or refine your skills.
Tracking Your Progress
Tracking progress is a crucial part of maintaining your skill set. By reviewing your achievements and identifying areas of improvement, you ensure that you stay on track. Here’s a table with suggestions for monitoring ongoing development:
| Method | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Self-assessment | Monthly | Evaluate areas of improvement |
| Peer reviews | Quarterly | Gain feedback from colleagues |
| Advanced Training | Annually | Enhance and update knowledge |
| Case Studies | Ongoing | Apply knowledge to real-world scenarios |
By following these strategies and regularly evaluating your progress, you can ensure that your skills remain sharp and continue to grow even after you have successfully passed the initial assessment.