Understanding the complexities of the global conflict that reshaped the 20th century requires a deep dive into its major events, figures, and consequences. By exploring the causes and effects of this tumultuous period, we can gain a clearer picture of how it impacted the world we live in today. This section is designed to provide students with essential information to navigate through various topics related to this historical era.
From military strategies to the personal stories of individuals caught in the struggle, each aspect offers valuable lessons. Exploring the decisions that led to the outbreak of hostilities and the alliances formed throughout the conflict will help grasp its profound influence on international relations.
By analyzing key moments and understanding the motivations behind crucial actions, students can better appreciate the enduring legacies of this era. This approach will foster a more comprehensive knowledge of the events that defined the 20th century.
WW2 Exam Answers for History Students
This section provides crucial insights into the key topics that students need to understand when preparing for their history assessments on the major global conflict of the 20th century. With a focus on pivotal events, influential figures, and lasting outcomes, it equips learners with the knowledge to approach related questions with confidence and clarity.
Important Events and Turning Points
Key battles, political decisions, and strategic movements played critical roles in shaping the course of the conflict. Understanding the significance of moments like the Battle of Stalingrad or the Normandy Invasion offers a deeper appreciation of military tactics and the high stakes involved in this widespread struggle.
Impact on Global Relations
Long-term consequences of the conflict extend beyond the battlefield. The post-war era witnessed major shifts in power dynamics, with the rise of new superpowers and the establishment of global organizations like the United Nations. A solid grasp of these changes will help students better comprehend the transformation of world politics following the conclusion of hostilities.
Key Events in World War II
This section highlights the defining moments that altered the trajectory of the global conflict. These critical episodes not only changed the course of military actions but also reshaped international relations and social dynamics. Understanding these events is essential for recognizing the broader implications of the war.
From the early days of aggression to the eventual conclusion of hostilities, key battles, strategic decisions, and diplomatic shifts played pivotal roles in determining the outcome. Events such as the invasion of Poland, the attack on Pearl Harbor, and the D-Day landings stand out as milestones that influenced the strategies and alliances throughout the struggle.
Important Leaders of WW2
This section explores the key individuals whose leadership shaped the course of the global conflict. Their decisions, strategies, and political influence were instrumental in the successes and failures of various factions during the struggle. A deep understanding of these figures is essential for comprehending the dynamics of the war.
Allied Leaders
The leaders of the Allied nations played crucial roles in organizing resistance and ultimately achieving victory. Figures like Franklin D. Roosevelt, Winston Churchill, and Joseph Stalin were central to the formation of strategies and alliances that led to the defeat of the Axis powers. Their collaboration and differing ideologies shaped the post-conflict world order.
Axis Powers Leadership
On the other side, the Axis powers were led by influential figures such as Adolf Hitler, Benito Mussolini, and Emperor Hirohito. Their ambitions for territorial expansion and authoritarian rule fueled much of the conflict. Understanding their leadership and decisions offers insights into the motivations behind the war’s aggression.
Impact of the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles, signed at the conclusion of the First World War, had far-reaching consequences that shaped the political landscape of the 20th century. Its terms were intended to restore peace and prevent further conflict, but in many ways, it laid the groundwork for future tensions and instability. The treaty’s provisions deeply affected both the defeated powers and the global balance of power.
Economic and Political Consequences
One of the most significant outcomes was the harsh economic reparations imposed on the defeated nations, particularly Germany. These financial penalties weakened economies and led to widespread resentment, contributing to political instability and the rise of extremist movements. The treaty’s restrictive terms also led to territorial losses, leaving lasting scars on national pride and sovereignty.
Long-term Effects on International Relations
The Treaty of Versailles also had a lasting effect on international relations. The creation of the League of Nations aimed to prevent future conflicts, but the absence of key powers, including the United States, undermined its effectiveness. The treaty’s failure to address underlying issues contributed to the rise of new conflicts, eventually leading to another global war.
Role of Women During WW2
During the global conflict, women played a crucial role in supporting their countries’ war efforts, both on the home front and in various military capacities. As men went off to fight, women stepped into jobs and responsibilities that were traditionally held by men, showcasing their resilience and determination in challenging times.
Women in the Workforce
With large numbers of men enlisted in the military, women became an essential part of the industrial workforce. They worked in factories, shipyards, and offices, producing weapons, vehicles, and other vital supplies for the military. This shift marked a significant change in gender roles, as women were seen as vital contributors to the national effort.
Women in the Armed Forces
In addition to their roles in civilian industries, many women also served in auxiliary military units. They took on positions as nurses, clerks, and communication officers, supporting the armed forces directly. Their involvement in these roles was instrumental in maintaining military efficiency and offering vital support to soldiers in the field.
Technological Advances in WW2
The global conflict spurred rapid advancements in technology, which had a profound impact on warfare strategies and the outcome of the struggle. Innovations in weaponry, communication, and transportation not only changed the nature of military engagements but also laid the foundation for post-war technological developments.
Advancements in Weaponry
New weapons such as advanced aircraft, tanks, and automatic firearms revolutionized battlefield tactics. The development of more powerful bombs, including the atomic bomb, altered the strategic landscape, leading to new methods of combat and deterrence. These innovations pushed the boundaries of what was possible in terms of destruction and defense.
Improved Communication and Intelligence
Technological progress in communication systems, such as radar and encryption methods, played a critical role in the success of military operations. These breakthroughs enhanced the ability to gather intelligence, coordinate attacks, and ensure the security of strategic information, all of which were crucial to achieving military objectives.
Major Battles and Campaigns
The conflict saw numerous decisive battles and military campaigns that played a significant role in shaping the overall outcome. These operations were not only pivotal in terms of military tactics but also in their impact on the morale and strategic direction of both sides. Understanding these key confrontations helps reveal the complexities of warfare and the shifting momentum throughout the period.
Turning Points in Europe
Major engagements on the European front, such as the Battle of Stalingrad and the Normandy landings, marked critical turning points. These battles shifted the balance of power, leading to the eventual downfall of the Axis forces in Europe. The courage and resilience displayed by the soldiers during these operations were essential in changing the course of the war.
Pacific Theater Operations
In the Pacific, battles like Midway and Iwo Jima were key in weakening the Axis powers’ control and shifting the momentum in favor of the Allied forces. Naval confrontations and island-hopping campaigns were crucial in gaining strategic footholds, leading to the eventual defeat of Japan and the end of the conflict in the Pacific.
Causes Behind the WW2 Conflict

The origins of the global conflict can be traced back to several interconnected factors that created an environment ripe for large-scale warfare. These causes were not just the result of isolated events, but rather a culmination of political, economic, and social tensions that escalated over time.
Political Instability and Aggression
- Treaty of Versailles: The harsh terms imposed on defeated nations, particularly Germany, fueled resentment and nationalistic fervor, setting the stage for future aggression.
- Rise of Totalitarian Regimes: The emergence of dictatorships in countries like Germany, Italy, and Japan led to expansionist policies and territorial ambitions.
- Failure of Diplomacy: The inability of international institutions, such as the League of Nations, to prevent aggression and resolve conflicts contributed to the escalation of tensions.
Economic and Social Factors
- Great Depression: The global economic downturn created instability and desperation, making populations more susceptible to extremist ideologies promising recovery.
- Resource Scarcity: Competition for valuable resources, particularly in Asia and Europe, heightened tensions between emerging powers and established nations.
These factors, combined with a lack of effective conflict resolution and growing militarization, ultimately led to the outbreak of the global struggle that shaped the 20th century.
Effect of Global Conflict on Politics
The global struggle had a profound impact on political landscapes across the world, reshaping alliances, power structures, and ideologies. The aftermath of the conflict saw a new world order emerge, with major shifts in influence and the creation of international organizations aimed at maintaining peace and stability.
Shift in Global Power
- Rise of Superpowers: The United States and the Soviet Union emerged as the dominant global powers, marking the beginning of the Cold War and a new era of geopolitical competition.
- Decline of European Dominance: European empires, weakened by the war, began to retreat from colonies, leading to the rise of newly independent nations and the end of colonialism.
- Emergence of New Alliances: The formation of military and political alliances, such as NATO and the Warsaw Pact, solidified the division of the world into two opposing blocs.
Creation of International Institutions
- United Nations: Established to prevent future global conflicts and promote cooperation, the United Nations became a central platform for diplomacy and conflict resolution.
- International Economic Institutions: Organizations like the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank were created to stabilize global economies and prevent another depression.
The consequences of this period were felt not just in the political arenas of the victors and losers, but throughout the entire international system, shaping the policies and relationships that continue to influence global affairs today.
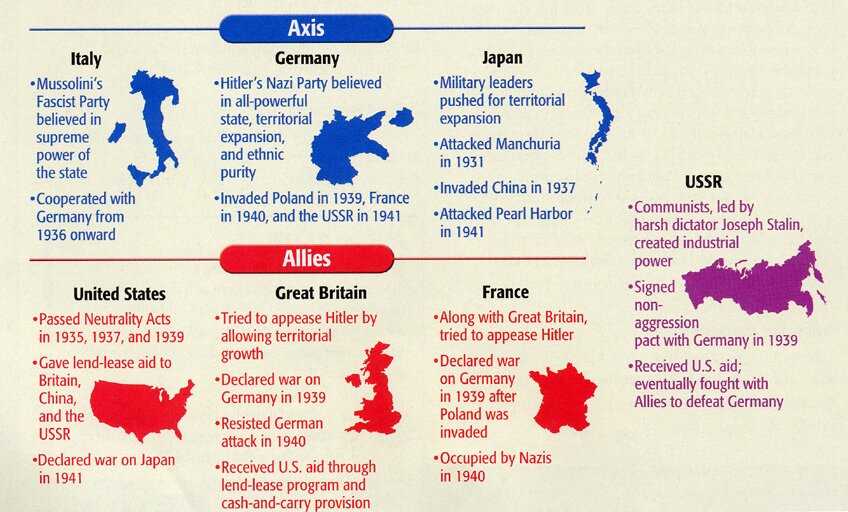
Military Alliances Explained
During the global conflict, various nations formed strategic coalitions to enhance their military strength, share resources, and achieve common objectives. These alliances played a crucial role in shaping the outcome of the war, with both sides benefiting from their respective partnerships. Understanding these alliances is key to comprehending the complex geopolitical dynamics that influenced the course of the conflict.
Major Alliances
| Alliance Name | Key Members | Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Allied Powers | United States, United Kingdom, Soviet Union, France, China | Defeat the Axis powers, restore peace, and prevent future conflicts. |
| Axis Powers | Germany, Italy, Japan | Expand territorial control, establish dominance, and disrupt existing power structures. |
| Commonwealth Nations | Canada, Australia, New Zealand, India | Support the United Kingdom and maintain global peace. |
These alliances were not only military but also political, with each coalition striving to secure its dominance in the global arena. The cooperation among countries in these alliances often determined the strategic decisions and eventual success or failure on the battlefield.
Resistance Movements in WW2
Throughout the global conflict, numerous underground groups emerged in occupied territories, committed to fighting oppression and resisting enemy forces. These movements, fueled by the desire for freedom, played a pivotal role in undermining the strength of occupying powers. From sabotage operations to intelligence gathering, their contributions were crucial in altering the course of the war.
Notable Resistance Groups
- French Resistance: Operating in German-occupied France, this movement coordinated acts of sabotage, gathered vital intelligence, and assisted Allied forces.
- Polish Home Army: In Poland, this group fought both Nazi and Soviet forces, focusing on guerrilla warfare and intelligence operations.
- Yugoslav Partisans: Led by Josip Broz Tito, this group engaged in armed resistance against Axis forces in the Balkans.
- Norwegian Resistance: Engaged in sabotage and assisted in the safe transport of refugees, mainly targeting Nazi installations and supply lines.
- Italian Partisans: After Italy’s surrender, partisan groups fought against German forces occupying their country, playing a key role in the liberation of Italy.
These resistance movements often operated under difficult conditions, facing immense challenges from their occupiers. Despite the risks, their actions had a significant impact on the overall strategy of the conflict, weakening enemy forces and providing critical support to the Allied campaigns.
Significance of the D-Day Landing
The large-scale invasion on the beaches of Normandy marked a turning point in the conflict, as it set the stage for the liberation of Western Europe from oppressive forces. This decisive military operation demonstrated the unity of Allied nations and their determination to reclaim occupied territories. The success of this maneuver not only weakened the enemy’s grip but also boosted morale, offering hope for the end of the prolonged struggle.
Strategic Importance
The landings in Normandy were a pivotal moment in the overall military strategy of the Allied forces. By establishing a foothold in Western Europe, they were able to launch further offensives, drawing Axis attention away from other fronts. This invasion disrupted the enemy’s control over vital resources, providing the Allies with a much-needed advantage in both personnel and supplies.
Impact on the War’s Outcome
The successful landing was a critical step in the eventual downfall of the Axis powers. It forced the enemy to fight on multiple fronts, weakening their ability to defend effectively. It also expedited the liberation of several countries, signaling the beginning of the end for the occupying forces in Europe.
WW2 and the Holocaust
The dark chapter of systematic genocide during the conflict stands as one of the most horrific events in human history. Targeting specific groups, millions of innocent people were subjected to unimaginable brutality under the guise of racial and ideological superiority. The scale and severity of the atrocities committed during this period left an indelible scar on the collective conscience of humanity.
Key Figures and the Execution of the Plan
The orchestration of this mass extermination was led by the ruling regime, with many influential figures involved in the planning and execution. Concentration camps, ghettos, and death squads were the instruments used to carry out the systematic destruction of entire communities. The ideology behind these actions was rooted in a deeply flawed and hateful worldview that dehumanized millions.
Impact and Consequences
The effects of this genocidal campaign are still felt today. The aftermath led to international efforts to prevent such horrors from ever occurring again. This tragic period has also sparked continued conversations about human rights, justice, and the importance of remembering the atrocities to ensure they are never repeated.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Victims | Jews, Roma, disabled individuals, political dissidents, and other minority groups were targeted. |
| Methods | Concentration camps, mass shootings, starvation, forced labor, and gas chambers were employed to carry out the atrocities. |
| Global Impact | The aftermath led to the formation of international laws and the creation of organizations like the United Nations, focused on preventing future genocides. |
Post-WW2 Economic Rebuilding
After the end of global hostilities, nations faced the enormous task of revitalizing their economies, recovering from widespread devastation, and addressing the needs of a war-torn population. Reconstruction efforts were essential not only to restore physical infrastructure but also to create sustainable economic systems that could support long-term growth and stability. The period that followed the cessation of the conflict witnessed significant efforts to rebuild industries, reintegrate workers into the economy, and stimulate international cooperation for recovery.
Key Strategies in Economic Recovery
The approach to rebuilding varied between regions but generally included efforts to stabilize currencies, encourage trade, and provide financial aid to devastated economies. Government policies, both domestic and international, played a crucial role in reshaping economic landscapes and fostering development. Large-scale programs, such as the Marshall Plan, helped countries rebuild essential industries, while reforms at the national level sought to address issues such as inflation, unemployment, and food shortages.
International Cooperation and Aid
In addition to national efforts, international organizations and agreements facilitated collaboration between nations to ensure the global economy could recover. These initiatives provided financial aid, technical expertise, and market access, contributing to the rebuilding of economies in both Europe and Asia. The aim was to create a more integrated global economy and prevent future conflicts through mutual economic support and cooperation.
| Economic Strategy | Details |
|---|---|
| Marshall Plan | U.S. initiative to provide aid to Western European countries for reconstruction, aiming to revive industries and curb the spread of communism. |
| Currency Stabilization | Efforts to control inflation and stabilize national currencies to promote economic confidence and investment. |
| International Aid Programs | Collaboration between nations, including the United Nations and the World Bank, to provide financial assistance and technical support to war-affected countries. |
WW2’s Influence on Modern Warfare
The major conflict of the 20th century had a profound effect on how wars are fought today. The technological, strategic, and tactical innovations developed during this time laid the foundation for modern military practices. Many concepts and tools that are essential to contemporary combat were first introduced or perfected during this era, influencing the design of weapons, the structure of military organizations, and the way conflicts are approached globally.
Technological Advancements in Combat
Several technological breakthroughs during the era have had lasting effects on warfare tactics. These advancements have shaped both conventional and unconventional military operations, allowing for more precise and efficient methods of engagement. The following innovations were pivotal:
- Radar Technology: Allowed for long-range detection of enemy aircraft and ships, significantly changing defensive and offensive strategies.
- Jet Aircraft: The development of faster, more agile aircraft revolutionized air combat, influencing air forces today.
- Modern Tanks: The introduction of more powerful and versatile armored vehicles shaped ground combat strategies that are still in use.
- Missile Systems: Early ballistic and guided missiles set the stage for modern missile defense and offense capabilities.
Strategic Evolution in Warfare

The approach to warfare saw substantial changes during this period, which continue to influence military strategy and tactics. Key developments included:
- Joint Operations: Coordination between air, sea, and ground forces became crucial for success, a practice still central to modern military strategies.
- Strategic Bombing: The use of airpower to destroy enemy infrastructure and morale reshaped the concept of total warfare.
- Intelligence Gathering: The importance of reconnaissance, espionage, and codebreaking emerged as critical components of operational success.
Modern military forces continue to refine these strategies and technologies, drawing on lessons learned during this pivotal period in history. The legacy of these advancements is evident in today’s sophisticated defense systems, multinational cooperation, and the ongoing evolution of military tactics and equipment.
Lessons Learned from WW2
The global conflict of the 20th century left an indelible mark on the world, offering critical insights that continue to shape international relations, military strategies, and governance. The aftermath revealed both the dangers of unchecked power and the resilience of nations in the face of adversity. From the profound human cost to the strategic mistakes made, these experiences have guided modern policy and conflict resolution practices.
Key Strategic and Tactical Lessons
Several military and political lessons were learned during this time, which have influenced both future conflicts and peacekeeping efforts:
- The Importance of Early Diplomacy: Failing to address tensions early on led to widespread destruction. Diplomacy and negotiation play crucial roles in preventing large-scale conflicts.
- The Value of Intelligence: Effective intelligence gathering can decisively change the course of a conflict, as demonstrated by breakthroughs in espionage and codebreaking.
- Cooperation Over Isolation: The success of international alliances showed that collective security and cooperation among nations is more effective than isolationist policies.
- The Impact of Technology: Advances in weaponry, communication, and transportation revolutionized warfare, highlighting the need for continuous innovation and adaptation.
Humanitarian and Ethical Reflections

The immense suffering experienced during this time led to profound changes in international law and human rights protection:
- The Need for Human Rights Protections: The atrocities committed during this period underscored the necessity for a global commitment to protecting civilians and preventing genocide.
- The Importance of Post-Conflict Recovery: Rebuilding after devastation is vital for long-term peace, as seen in the reconstruction of Europe and Japan, which helped to stabilize the world economy.
- Prevention of Totalitarianism: The rise of oppressive regimes served as a reminder of the dangers of authoritarianism, leading to global efforts to promote democratic governance.
These lessons have profoundly influenced modern governance, conflict resolution, and the approach to international cooperation, making the world more vigilant against repeating the mistakes of the past.