When preparing for important academic assessments, understanding how to tackle the various components effectively is essential. By focusing on key areas, such as sentence structure, grammar, and comprehension, students can enhance their performance and increase their chances of success. This section is designed to guide you through some of the most challenging aspects of the evaluation process, offering strategies that go beyond simple memorization.
Each section of the exam tests a different set of skills, from identifying errors in passages to determining the best way to express an idea clearly and concisely. Knowing how to approach these sections with the right techniques can make a significant difference in your results. In this guide, we will walk you through some of the most common challenges and provide insights on how to overcome them efficiently.
Through careful analysis and practice, you can identify patterns in the types of questions that tend to appear and learn how to spot potential pitfalls before they affect your performance. Understanding these nuances not only helps with the specific test at hand but also improves your overall critical thinking and writing abilities.
ACT English Test Overview
The assessment is designed to evaluate a student’s ability to apply language skills in a structured and logical way. It examines a variety of elements, from grammar and punctuation to sentence clarity and organization. Each section provides a unique challenge, testing the student’s understanding of language mechanics and their ability to express ideas effectively.
Key Areas of Evaluation
- Grammar and Usage: Identifying proper grammatical structures and correcting errors in sentence construction.
- Sentence Structure: Assessing how well sentences are organized and whether they convey clear meaning.
- Punctuation: Understanding the correct use of commas, semicolons, colons, and other punctuation marks.
- Style and Tone: Evaluating how language can be adapted to fit the context and audience effectively.
Format and Question Types
Questions are presented in the form of passages, with each passage containing multiple questions. The goal is to identify errors and make improvements based on specific guidelines. The section focuses on:
- Correcting mistakes in sentence structure and punctuation.
- Improving clarity and conciseness of sentences.
- Choosing the most appropriate words and phrases to complete sentences or passages.
By understanding the types of questions and areas evaluated, students can develop targeted strategies to improve their performance and approach the sections with confidence.
Understanding the Structure of the Test
The evaluation process is carefully structured to measure a variety of language skills, including grammar, punctuation, and sentence organization. The overall format is divided into multiple sections, each targeting different aspects of language usage. Understanding the organization of these sections is crucial for effectively approaching each task and maximizing your potential score.
Sections and Their Focus
The examination consists of several distinct sections, each designed to assess specific competencies:
- Grammar and Usage: Focuses on the identification and correction of grammatical errors within sentences.
- Sentence Structure: Evaluates how well sentences are constructed and whether they flow logically.
- Punctuation and Mechanics: Tests the correct use of punctuation, including commas, periods, and semicolons, to ensure clarity and readability.
- Rhetorical Skills: Involves choosing the best word or phrase to improve a passage’s tone, style, or clarity.
How Questions are Presented
Questions are typically presented within context, with passages followed by multiple-choice questions. Each question requires the test taker to select the best option for improving or correcting the passage. While the passages may appear similar, the questions vary in their focus, providing a comprehensive assessment of a candidate’s language proficiency.
Key Tips for Improving Scores
Improving performance on language assessments requires a combination of strategy, preparation, and focused practice. By honing specific skills and refining test-taking techniques, students can maximize their potential and achieve higher results. These tips will guide you through essential steps to boost your score, focusing on both general approaches and specific areas for improvement.
One of the most effective ways to improve is to familiarize yourself with the types of questions you will face. The more you practice with similar content, the easier it becomes to identify patterns and anticipate what is being asked. In addition, learning to manage time wisely ensures that you can approach each section without feeling rushed.
Additionally, focusing on core language skills–such as grammar, sentence clarity, and punctuation–will provide a strong foundation. Regular review of these fundamental concepts, along with targeted exercises, can enhance your accuracy and efficiency under exam conditions.
Common Mistakes in ACT English
Many students encounter specific challenges when completing language-based assessments, often making avoidable mistakes that can significantly impact their scores. Understanding these common errors and knowing how to avoid them can make a big difference in your performance. This section highlights frequent pitfalls and provides tips on how to navigate them effectively.
Overlooking Grammar Details

Grammatical errors are one of the most frequent mistakes. These may include subject-verb agreement issues, misplaced modifiers, or incorrect use of tense. While these may seem minor, they can negatively affect the clarity and correctness of your sentences. Regular practice with grammar exercises and reviewing basic rules can help prevent these errors.
Misinterpreting Sentence Structure
Many students struggle with sentence structure, confusing complex sentences or failing to spot awkward phrasing. For example, recognizing when a sentence is overly wordy or confusing can be challenging, but it’s crucial for improving readability. Focus on sentence clarity and conciseness to avoid misinterpretation of the intended meaning.
By addressing these common mistakes and sharpening your understanding of language mechanics, you can approach each section with more confidence and accuracy.
Effective Time Management Strategies
Time management is a crucial skill when preparing for any timed evaluation, as it ensures that you can complete all sections with enough time to review your answers. Effective management not only involves allocating time to each question but also staying calm and focused throughout the entire process. By adopting certain strategies, you can maximize your efficiency and performance under time constraints.
Setting time limits for each section is one of the most effective ways to ensure you stay on track. For instance, decide in advance how long you will spend on each question, and be disciplined about moving on when time is up. This prevents getting stuck on any one question and allows you to allocate time more wisely across the whole assessment.
Prioritize easier questions first, tackling the ones you feel most confident about. This not only boosts your confidence but also ensures that you’re not wasting time on questions that are unnecessarily difficult. After completing the easier questions, return to the more challenging ones with the remaining time.
With practice, you’ll develop a natural rhythm for managing your time effectively, allowing you to perform at your best and avoid unnecessary stress.
How to Approach Sentence Correction

Correcting sentences requires a keen understanding of grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure. The key to mastering this skill is to approach each sentence with a clear strategy, focusing on both clarity and correctness. By breaking down the sentence into its components and identifying potential issues, you can make effective revisions that enhance the overall readability.
Start by identifying common errors such as subject-verb agreement, misplaced modifiers, or incorrect use of punctuation. Once you’ve identified these, think about the structure of the sentence–does it flow logically? Are the ideas presented in a clear and concise manner? Focusing on these elements first will help you address the most obvious issues.
Next, evaluate each correction option carefully. Often, there will be multiple choices that seem correct, but the best option will improve the overall clarity and flow of the sentence. Pay attention to the tone and style of the sentence, and choose the option that maintains or enhances its effectiveness without introducing unnecessary complexity.
By practicing this methodical approach, you will become more proficient at quickly identifying and correcting sentence-level issues, ultimately improving your performance on similar tasks.
Mastering Grammar Rules for ACT
Grammar rules are the foundation of clear and effective writing. A strong command of these rules is essential for success in language-based assessments. By focusing on key grammar concepts, you can quickly identify errors in sentences and choose the correct corrections. Mastering these rules will not only help you in exams but will also enhance your writing skills for various contexts.
Key Grammar Concepts to Focus On
- Subject-Verb Agreement: Ensure that subjects and verbs match in number and person.
- Pronoun Usage: Use pronouns correctly to avoid confusion and maintain clarity.
- Modifiers: Place modifiers next to the word they are modifying to avoid ambiguity.
- Parallel Structure: Maintain consistent patterns in lists, comparisons, and phrases for clarity.
- Punctuation: Master the correct use of commas, semicolons, and other punctuation marks to structure sentences properly.
Effective Ways to Practice Grammar
- Study grammar rules regularly to build a solid understanding of key concepts.
- Review common error types and practice identifying them in sample sentences.
- Use grammar exercises to reinforce your knowledge and test your ability to apply the rules in context.
By committing to consistent grammar practice and focusing on these essential rules, you will become more confident in your ability to identify and correct errors quickly and accurately.
Understanding Punctuation Questions
Punctuation plays a crucial role in conveying meaning and ensuring the clarity of written communication. Understanding how to use punctuation marks effectively is essential for making sentences readable and precise. In assessments that test language skills, punctuation questions evaluate your ability to correctly apply these marks to improve sentence structure and avoid confusion.
Common Punctuation Marks and Their Usage
- Commas: Used to separate items in a list, after introductory phrases, or to set off non-essential information.
- Semicolons: Connect closely related independent clauses or separate items in a complex list.
- Colons: Introduce lists, explanations, or further elaboration of a preceding clause.
- Apostrophes: Indicate possession or form contractions.
Approaching Punctuation Questions

When faced with punctuation questions, always focus on sentence clarity. Pay attention to the relationship between ideas in a sentence and use punctuation marks to create logical pauses and separations. Review the passage carefully to determine where punctuation is either missing or misused. The correct choice should make the sentence easier to read without altering its intended meaning.
Commonly Tested Vocabulary
Having a strong vocabulary is essential for understanding and interpreting written material effectively. Vocabulary questions often test your ability to comprehend words in context and recognize their meanings. A well-rounded vocabulary allows you to quickly identify the right word choices, which can significantly improve your performance in language-based assessments.
Key Categories of Vocabulary to Focus On

- Academic Terms: Words commonly used in formal writing or discussions, such as “analyze,” “synthesize,” and “evaluate.”
- Contextual Clues: Words that require you to infer their meaning based on the surrounding text, such as “ambiguous,” “contemporary,” and “imminent.”
- Synonyms and Antonyms: Understanding words that are similar or opposite in meaning, like “ardent” and “passionate” or “hostile” and “friendly.”
- Transitional Words: Words that help guide the flow of writing, such as “however,” “therefore,” and “consequently.”
Effective Strategies for Expanding Vocabulary
- Read regularly to expose yourself to new words and phrases used in different contexts.
- Use flashcards to reinforce word meanings and improve retention.
- Engage in active learning by practicing the use of new words in sentences and conversations.
By familiarizing yourself with commonly tested vocabulary and using strategies to reinforce these words, you can increase your comprehension and improve your ability to identify the most appropriate word choices in any given context.
How to Tackle Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension challenges your ability to understand and analyze written material. To perform well, it’s crucial to not only grasp the main ideas but also pay attention to subtle details and inferences. Developing a strategic approach to reading and answering questions can greatly enhance your performance in this section.
Key Strategies for Success
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Skim the Passage First | Quickly scan the text to get a sense of the main ideas and structure before diving into the questions. |
| Highlight Key Information | As you read, mark key points, such as the main argument, important facts, or quotes that support the text’s themes. |
| Understand Question Types | Familiarize yourself with the types of questions typically asked, such as main idea, detail, inference, or vocabulary in context. |
| Return to the Passage | After reading the question, refer back to the passage to locate the relevant information before choosing your answer. |
Effective Practice Techniques
Regular practice with varied reading materials can sharpen your comprehension skills. Engage with different genres, such as articles, essays, and literary works, to improve both speed and understanding. Testing yourself with sample questions will help you refine your ability to identify key ideas quickly and accurately.
Identifying Word Choice Errors
Choosing the right word is essential for clear and effective communication. Incorrect word usage can change the meaning of a sentence or make it difficult to understand. In language assessments, identifying and correcting word choice errors is a critical skill, as it ensures that sentences are both grammatically correct and contextually appropriate.
Common Types of Word Choice Mistakes
- Misused Synonyms: Using a word that seems similar but doesn’t fit the context. For example, confusing “affect” with “effect” or “accept” with “except.”
- Incorrect Tone: Words that do not match the formal or informal tone of the sentence. For example, using “cool” in a formal essay instead of “interesting” or “impressive.”
- Redundancy: Using unnecessary words that repeat the same meaning, such as “each and every” or “absolutely essential.”
- Vague or Ambiguous Terms: Words that are too general or unclear for the context, such as “things” or “stuff,” which lack specificity.
How to Avoid Word Choice Errors

To avoid word choice mistakes, always read through sentences carefully and think about the meaning each word conveys. Pay attention to context, as some words may have different meanings depending on the situation. When in doubt, refer to a dictionary or thesaurus to ensure you’re selecting the most accurate word for the sentence.
Recognizing Sentence Structure Issues
Proper sentence structure is essential for clear and effective communication. When sentences are poorly constructed, they can confuse the reader and obscure the intended message. Identifying issues with sentence structure allows for more precise and fluent writing, ensuring ideas are expressed logically and coherently.
Common Sentence Structure Problems

- Run-on Sentences: These occur when two or more independent clauses are incorrectly joined without proper punctuation or conjunctions, making the sentence overly long and confusing.
- Fragments: Sentence fragments are incomplete thoughts or clauses that lack a subject or verb, which results in an abrupt or unfinished statement.
- Comma Splices: This happens when two independent clauses are joined with just a comma, without the necessary conjunction or semicolon, leading to a grammatically incorrect sentence.
- Misplaced Modifiers: Modifiers placed incorrectly can lead to confusion about which word or phrase they are modifying, creating ambiguity or absurd meanings.
How to Correct Sentence Structure Issues

To avoid sentence structure problems, it’s important to focus on clarity and simplicity. Always check if your sentence includes both a subject and a verb, and make sure each clause is properly connected. Break long, complex ideas into shorter sentences when needed, and ensure modifiers are placed next to the words they modify for better precision.
Understanding Modifier Placement
Modifiers are words, phrases, or clauses that provide additional information about other elements in a sentence. Proper placement of modifiers is crucial for clarity, as incorrect positioning can lead to confusion or unintended meanings. When modifiers are placed incorrectly, they can distort the sentence or make it difficult to understand the intended message.
To avoid errors, it’s essential to position modifiers as close as possible to the word they are meant to describe. Misplaced modifiers can create ambiguity, causing the reader to misinterpret the subject or action being described. Careful attention to modifier placement ensures that the sentence communicates the intended information clearly and accurately.
How to Practice for ACT English

Improving language skills for assessments requires strategic and consistent preparation. To excel in a language section, it’s important to engage in exercises that focus on grammar, sentence structure, and effective communication. Building these skills through targeted activities will enhance performance and ensure readiness for various types of questions.
Effective Preparation Techniques
- Focused Grammar Exercises: Spend time revising essential rules like subject-verb agreement, punctuation, and modifier placement. This will help to spot and correct errors quickly.
- Sentence Construction Practice: Regularly work on writing and revising sentences. Focus on varying sentence length and complexity to improve clarity and coherence.
- Reading and Analysis: Read different types of written content such as articles and essays. Analyze sentence structures and identify errors or areas that can be improved.
Tracking Your Progress

Tracking your improvement is vital to understanding where you stand and where to focus further efforts. Use practice sets or mock exercises to gauge your proficiency. Take note of mistakes and revisit specific concepts that need attention.
| Practice Area | Frequency | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Grammar Review | 3 times a week | Grammar books, online quizzes |
| Sentence Construction | 2 times a week | Writing exercises, worksheets |
| Reading Analysis | Daily | Books, news articles, essays |
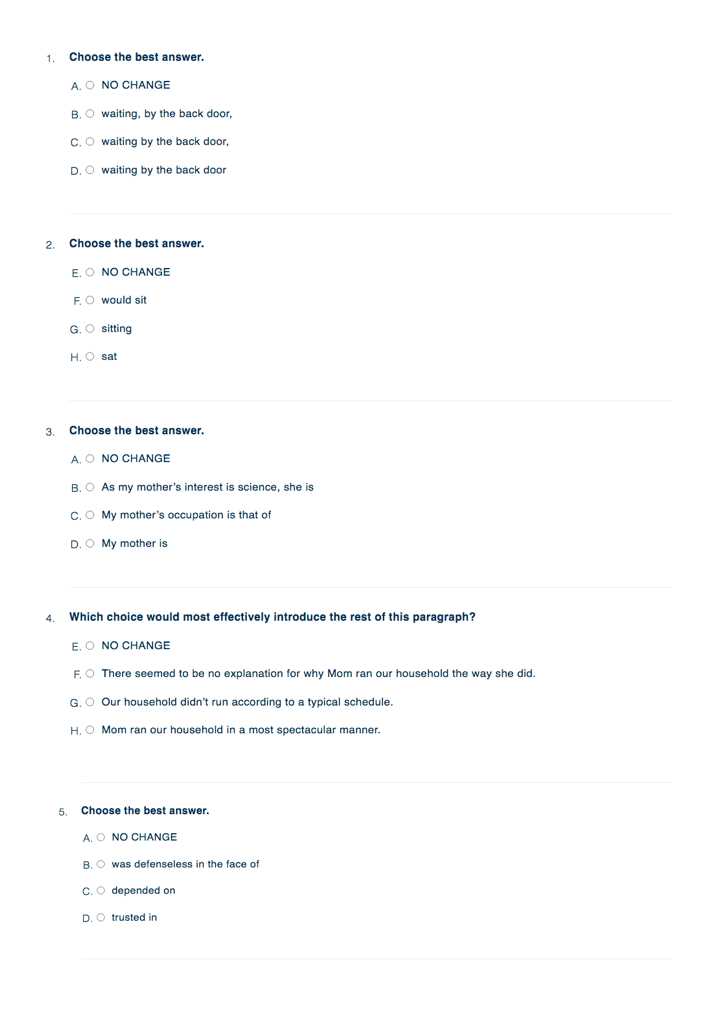
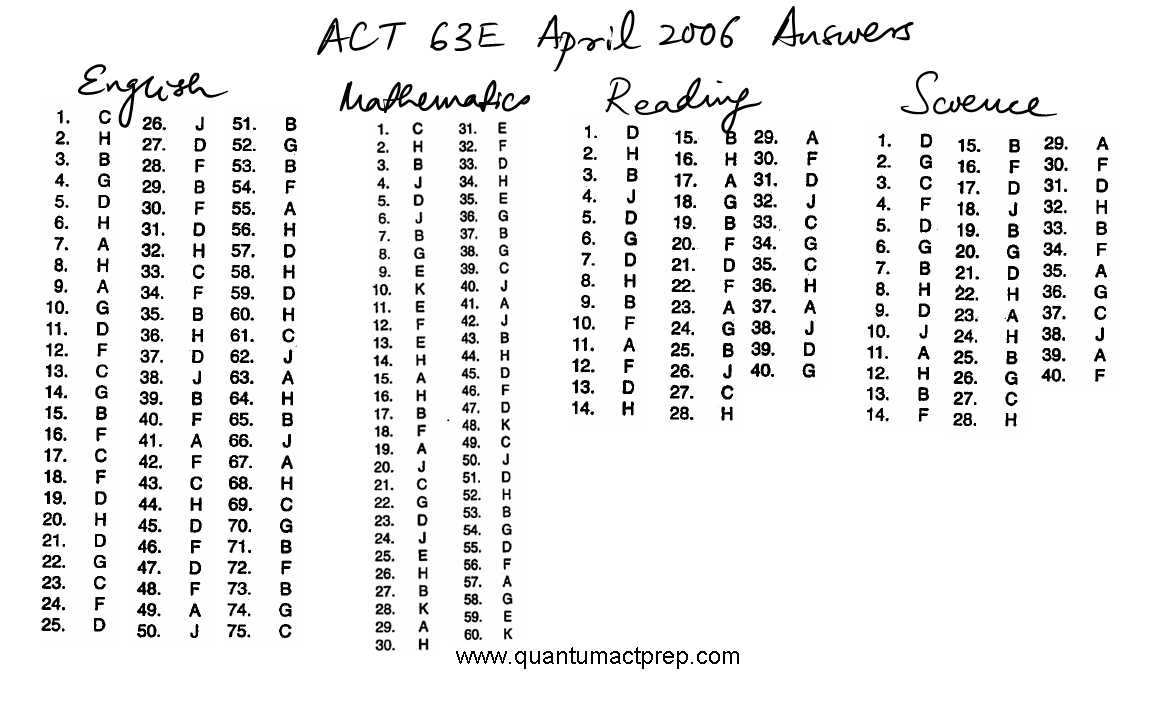
Detailed Review of Test 2 Answers
Reviewing responses thoroughly is essential to understanding strengths and areas that need improvement. A careful analysis of incorrect selections can help identify patterns of mistakes, whether they are related to specific concepts, question types, or misinterpretation of instructions. By breaking down the reasoning behind each choice, one can better prepare for future assessments.
Identifying Key Areas for Improvement
In many cases, errors arise from a lack of attention to detail or misunderstanding of the underlying concepts. Whether the issue lies with grammar rules, sentence structure, or comprehension, pinpointing the exact cause of an error allows for targeted practice and enhanced performance. Focus on reviewing:
- Grammar Errors: Errors related to subject-verb agreement, punctuation, and modifiers are common in many responses.
- Sentence Clarity: Misinterpretation of complex sentence structures often leads to choosing incorrect responses.
- Comprehension Mistakes: Inadequate understanding of the context can result in missing key details.
Strategies for Correcting Mistakes

Once errors have been identified, it’s important to implement strategies to improve. Some effective methods include:
- Active Revision: Regularly revise key concepts and practice with different exercises to reinforce correct usage.
- Mock Sessions: Simulate test conditions with time limits to build familiarity and improve response time.
- Post-Assessment Reflection: After each exercise, reflect on mistakes made and seek to understand why the wrong choice was made, addressing the root cause of the error.
Breaking Down Each Test Question
To truly grasp the concepts being tested, it’s crucial to analyze each question in detail. Breaking down the structure, context, and reasoning behind every query helps improve understanding and enhances overall performance. By evaluating each component, you can identify common traps and improve your ability to make quick, accurate decisions under pressure.
Understanding the Question Format
Many questions are designed to test not just knowledge but the ability to interpret information quickly. These often include tricky wording, making it easy to misread. Understanding how questions are structured helps to pinpoint the key information you need to focus on. Pay attention to:
- Keywords: Identify key terms or phrases that direct the answer.
- Context: Ensure you fully understand the context before jumping to conclusions.
- Choice Distractors: Recognize options that are designed to mislead or test specific knowledge.
Analyzing Incorrect Selections
When reviewing wrong answers, focus on why a particular choice was tempting but ultimately incorrect. By understanding the mistake, you can learn how to avoid making similar errors in the future. Key steps include:
- Recognize the Misstep: Did you misinterpret the question? Were you distracted by a seemingly logical but incorrect option?
- Evaluate the Correct Answer: Understand why the correct response works, and how it aligns with the rules or concepts being tested.
- Apply the Lesson: Practice with similar questions to reinforce correct thinking and reduce mistakes.
Commonly Misunderstood Concepts
There are several concepts that frequently cause confusion for many individuals preparing for this type of assessment. These topics often appear straightforward at first glance, but they are layered with nuances that can easily lead to mistakes. Understanding these common pitfalls and the logic behind them is essential for improving both comprehension and performance.
Subject-Verb Agreement Challenges
One of the most common areas of confusion is subject-verb agreement. While this rule seems simple, it can become tricky when sentences involve collective nouns, compound subjects, or complex sentence structures. A few points to remember include:
- Singular vs. Plural: Ensure that the subject and verb agree in number. For example, “The team is ready” versus “The teams are ready.”
- Compound Subjects: With compound subjects joined by “and,” use a plural verb. However, when combined with “or,” the verb must agree with the subject closest to it.
- Indefinite Pronouns: Words like “everyone” or “each” are singular and require a singular verb.
Pronoun-Antecedent Agreement
Another frequently misunderstood area involves ensuring that pronouns agree with their antecedents in both number and gender. Many test-takers incorrectly match plural pronouns with singular antecedents or fail to ensure that the gender is consistent. Key points include:
- Gender Agreement: Make sure the pronoun matches the gender of the noun it refers to.
- Number Agreement: If the antecedent is singular, the pronoun must also be singular, and the same applies to plural antecedents.
- Ambiguity: Avoid unclear pronoun references that can make the meaning of the sentence ambiguous. It is essential that the pronoun clearly refers to a specific noun.
Final Thoughts on Improving Your Score
Achieving a higher score in any assessment requires consistent effort, effective strategies, and a solid understanding of the subject matter. While there are no shortcuts to success, there are numerous techniques and approaches that can significantly enhance your performance. In this section, we will focus on key strategies that can help you improve your results and approach the evaluation with confidence.
Effective Study Techniques
Developing a study routine that focuses on both strengths and weaknesses is essential. Here are some valuable study methods to consider:
- Active Learning: Engage with the material actively by taking notes, summarizing key concepts, and teaching the material to others. This helps reinforce learning and improves retention.
- Targeted Practice: Focus on the areas where you struggle the most. By identifying weak spots, you can allocate more time to mastering specific concepts.
- Timed Drills: Practice under timed conditions to simulate the actual assessment environment. This helps improve both speed and accuracy when answering questions.
Mindset and Preparation
Your mindset plays a crucial role in performing well. Approaching the preparation with the right attitude can make a significant difference. Consider the following tips:
- Stay Positive: A positive mindset can help reduce anxiety and keep you motivated. Confidence in your abilities goes a long way in improving performance.
- Practice Consistently: Regular, consistent practice is more effective than cramming at the last minute. Set aside time each day to review and practice.
- Take Breaks: Avoid burnout by incorporating regular breaks into your study schedule. Rest is crucial for maintaining focus and long-term retention.