
Understanding Business Associations Fundamentals
Key Topics in Business Law for Exams
Common Legal Structures of Business Entities
Essential Questions on Corporate Governance
Examining Partnership Laws in Business

Critical Aspects of Company Formation
Types of Business Contracts to Know

Dispute Resolution Methods in Business
Legal Liabilities in Business Operations
Responsibilities of Business Directors and Officers

Questions on Shareholder Rights and Duties
Legal Procedures for Business Mergers

Business Bankruptcy Law Overview
Corporate Taxation and Legal Implications

Intellectual Property in Business Context

Effective Exam Strategies for Business Law
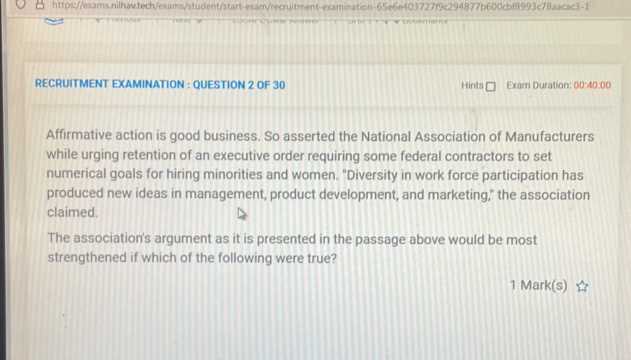
Business Associations Exam Questions and Answers
Mastering the essential concepts related to the formation, management, and legal responsibilities of various corporate entities is crucial for success in any related assessments. To perform well, it’s important to understand the key principles and structures that govern different organizations and their operations. In this section, we’ll focus on the core topics often covered in evaluations, providing a comprehensive overview and helpful insights to guide your preparation.
Understanding Key Legal Structures
One of the primary areas of focus is the range of legal entities that can be established for various business ventures. Whether it’s a partnership, corporation, or limited liability company, each structure has distinct features, benefits, and legal implications. Grasping these differences is essential for addressing case-based problems and theoretical inquiries alike.
Corporate Governance and Responsibilities
The responsibilities of individuals within an organization are another critical topic. From directors and officers to shareholders, each group has specific rights and duties that shape the business’s operations and growth. Understanding these roles will help you address questions related to leadership, liability, and decision-making processes effectively.
Understanding Business Associations Fundamentals
Grasping the core principles behind the creation and operation of legal entities is essential for navigating the complex landscape of commercial law. This section aims to provide a solid foundation in understanding how organizations are structured, how they interact with the legal system, and what responsibilities arise from their operations. A clear comprehension of these basics will significantly enhance your ability to tackle real-world scenarios and theoretical challenges.
At the heart of this subject lies the need to recognize the differences between various organizational models, each with its own set of rules, benefits, and potential drawbacks. Whether it’s through shared ownership, limited liability, or other legal frameworks, these structures dictate how decisions are made and how risk is distributed among participants. Understanding these foundational concepts sets the stage for more complex discussions on governance, legal obligations, and strategic management within different organizational forms.
Key Topics in Business Law for Exams
To succeed in assessments related to the legal aspects of commercial operations, it’s essential to focus on the fundamental areas that shape how entities are formed, governed, and regulated. These areas serve as the backbone for most legal challenges encountered in the field. Understanding these topics provides the necessary foundation to approach practical scenarios, theory-based inquiries, and case studies with confidence.
Among the primary subjects to master are the principles of contract law, liability issues, organizational governance, and the legal frameworks that guide the creation of different organizational models. A clear grasp of topics such as intellectual property rights, dispute resolution, and regulatory compliance is also crucial, as these play a significant role in the daily operations of entities. By concentrating on these core areas, you can navigate the intricacies of legal systems and effectively analyze complex situations that may arise in real-world contexts.
Key Topics in Business Law for Exams
To succeed in assessments related to the legal aspects of commercial operations, it’s essential to focus on the fundamental areas that shape how entities are formed, governed, and regulated. These areas serve as the backbone for most legal challenges encountered in the field. Understanding these topics provides the necessary foundation to approach practical scenarios, theory-based inquiries, and case studies with confidence.
Among the primary subjects to master are the principles of contract law, liability issues, organizational governance, and the legal frameworks that guide the creation of different organizational models. A clear grasp of topics such as intellectual property rights, dispute resolution, and regulatory compliance is also crucial, as these play a significant role in the daily operations of entities. By concentrating on these core areas, you can navigate the intricacies of legal systems and effectively analyze complex situations that may arise in real-world contexts.
Key Topics in Business Law for Exams
To succeed in assessments related to the legal aspects of commercial operations, it’s essential to focus on the fundamental areas that shape how entities are formed, governed, and regulated. These areas serve as the backbone for most legal challenges encountered in the field. Understanding these topics provides the necessary foundation to approach practical scenarios, theory-based inquiries, and case studies with confidence.
Among the primary subjects to master are the principles of contract law, liability issues, organizational governance, and the legal frameworks that guide the creation of different organizational models. A clear grasp of topics such as intellectual property rights, dispute resolution, and regulatory compliance is also crucial, as these play a significant role in the daily operations of entities. By concentrating on these core areas, you can navigate the intricacies of legal systems and effectively analyze complex situations that may arise in real-world contexts.
Common Legal Structures of Business Entities
In the realm of commerce, entities can be structured in various ways, each with its unique features, benefits, and legal implications. These structures determine how ownership is shared, how liability is distributed, and how decision-making processes are managed. Understanding the differences between these models is essential for anyone involved in the creation, operation, or management of an entity.
Corporations and Limited Liability Companies
Corporations and limited liability companies (LLCs) offer the advantage of protecting owners from personal liability. These models separate the entity’s legal identity from that of its owners, ensuring that personal assets are not at risk in the event of financial difficulties or legal disputes. Each model has its own rules regarding taxation, governance, and the distribution of profits.
Partnerships and Sole Proprietorships
Partnerships involve two or more individuals sharing ownership and management responsibilities, while sole proprietorships are owned and operated by a single person. These structures tend to offer more flexibility but come with varying degrees of liability. Understanding the distinctions between general and limited partnerships is crucial for those considering this model.
Essential Questions on Corporate Governance
Corporate governance refers to the systems, principles, and processes by which companies are directed and controlled. The effectiveness of governance structures has a profound impact on the overall performance and legal compliance of an organization. It is crucial for individuals involved in organizational management to understand the key aspects of governance to ensure legal and ethical compliance.
Roles and Responsibilities of Directors
The directors of a company are entrusted with making significant decisions that affect its direction, including financial decisions, strategic planning, and legal compliance. Understanding their legal obligations, including duties of care, loyalty, and good faith, is fundamental for anyone looking to engage in corporate management.
Shareholder Rights and Decision Making
Shareholders play a crucial role in the governance of an entity. Their rights to vote on important matters, such as mergers and the election of directors, are central to the decision-making process. A thorough understanding of shareholder activism, rights to information, and shareholder meetings is vital for those looking to participate in or advise on corporate affairs.
Examining Partnership Laws in Business
Partnerships are one of the oldest forms of business arrangements, offering a structure where two or more individuals come together to share profits, losses, and responsibilities. Partnership laws dictate how these entities are formed, operated, and dissolved, ensuring that all parties are clear about their rights and obligations. This area of law is particularly relevant when addressing issues of liability, dispute resolution, and profit sharing.
Types of Partnerships
There are several types of partnerships, including general partnerships, limited partnerships, and limited liability partnerships. Each type has different rules governing the extent of personal liability for the partners, as well as their rights to control the business and share profits. Understanding these distinctions is essential for anyone considering forming or entering into a partnership.
Key Legal Considerations in Partnerships
Partnership agreements are essential for setting expectations and protecting the interests of all parties involved. These legal documents outline how the partnership will operate, how decisions will be made, and how profits and losses will be shared. It is important for partners to understand the implications of these agreements, including the potential for disputes and how they can be resolved through mediation or legal action.
Critical Aspects of Company Formation
The process of establishing a legal entity involves various steps, each with significant implications for how the organization will operate and be held accountable. It is essential to understand the critical elements of this process, from choosing the right structure to ensuring compliance with legal and financial requirements. These steps not only determine the operational framework but also affect the future growth, liability, and governance of the entity.
Choosing the Right Structure
The first decision in forming an entity is selecting the appropriate structure. The choice impacts taxation, liability, and the management of the company. Common options include corporations, limited liability companies (LLCs), and partnerships. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a structure:
- Liability Protection: Determines whether personal assets will be at risk in the event of financial or legal challenges.
- Tax Implications: Affects how income is taxed, whether at the entity level or passed through to the owners.
- Management Flexibility: Dictates how decisions are made and who has authority to manage the company.
- Ownership Requirements: Defines who can own the entity and whether ownership can be transferred easily.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with local, state, and federal laws is essential when forming any type of entity. It is important to address legal requirements early to avoid future complications. Some of the key compliance areas include:
- Registering with Authorities: Entities must be officially registered with the appropriate government bodies.
- Filing Articles of Incorporation or Organization: These documents lay the foundation for the company’s legal existence and structure.
- Obtaining Necessary Licenses: Depending on the type of entity and industry, specific licenses or permits may be required.
- Operating Agreements: Partnerships and LLCs often require formal agreements outlining the roles, rights, and responsibilities of owners.
Ensuring compliance from the outset helps avoid penalties, taxes, and potential legal disputes later in the company’s lifecycle.
Types of Business Contracts to Know
Contracts form the foundation of many commercial interactions, outlining the terms, obligations, and expectations of the parties involved. Understanding the different types of agreements that may be encountered is crucial for ensuring legal clarity and protecting the interests of all parties. These contracts vary in complexity, from simple sales agreements to intricate partnership and employment arrangements.
Key Types of Agreements
There are several key types of contracts that are commonly used in various commercial settings. Each serves a distinct purpose and offers specific protections. Below are some of the most essential contracts to understand:
- Sales Contracts: These agreements govern the exchange of goods or services, specifying terms such as price, delivery schedule, and payment conditions.
- Employment Contracts: Outline the terms of employment, including job responsibilities, compensation, benefits, and termination clauses.
- Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs): Protect confidential information shared between parties, preventing unauthorized disclosure or use.
- Lease Agreements: Define the terms under which property is leased, including rental amount, duration, and maintenance responsibilities.
- Partnership Agreements: Detail the roles, responsibilities, profit-sharing arrangements, and dispute resolution methods among business partners.
Important Clauses to Consider
When entering into any type of agreement, certain clauses are critical to include for ensuring clear expectations and avoiding future disputes. Some important clauses include:
- Payment Terms: Specifies the amount, method, and schedule of payment to avoid misunderstandings.
- Duration: Defines the time period during which the contract remains in effect.
- Termination Clause: Outlines the conditions under which the contract may be terminated by either party.
- Dispute Resolution: Sets the procedures for resolving conflicts, such as through arbitration or mediation.
- Indemnity Clause: Ensures one party will be compensated for losses or damages resulting from the other party’s actions.
By understanding these contract types and essential clauses, individuals can enter into agreements with greater confidence, knowing their legal rights and obligations are clearly defined and protected.
Dispute Resolution Methods in Business
Disputes are an inevitable part of any commercial activity. Whether it’s a disagreement between partners, a contract issue with a client, or a conflict between employees, addressing these disputes efficiently is essential for maintaining smooth operations. There are several methods to resolve conflicts, each with its own advantages and limitations. Understanding the available options helps in choosing the most effective approach based on the nature of the dispute and the parties involved.
The most common methods for resolving disputes include negotiation, mediation, arbitration, and litigation. Below is a comparison of these methods to help understand their key characteristics:
| Method | Process | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Negotiation | Informal process where parties directly discuss the dispute to reach a mutually acceptable solution. | Cost-effective, flexible, and private. | May not be suitable for complex issues; no guaranteed resolution. |
| Mediation | A neutral third party helps facilitate communication and negotiation between the parties. | Confidential, less formal, encourages cooperation, and can preserve relationships. | Non-binding; may not lead to a resolution. |
| Responsibility | Description | Legal Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Duty of Care | Directors and officers must act with the care that a reasonably prudent person would use in similar circumstances, ensuring decisions are informed and well-considered. | Failure to act with due care may result in claims of negligence or mismanagement. |
| Duty of Loyalty | They must act in the best interests of the company, avoiding conflicts of interest and self-dealing. | Breaching this duty may result in claims of fraud, breach of fiduciary duty, or personal liability. |
| Duty of Obedience | Directors and officers must ensure that the organization complies with its governing documents, as well as applicable laws and regulations. | Non-compliance with laws and regulations can lead to fines, penalties, and reputational damage. |
| Financial Oversight | They are responsible for ensuring the company’s financial statements are accurate and that proper financial controls are in place. | Failure to oversee financial operations properly may lead to corporate fraud charges or shareholder lawsuits. |
| Compliance with Regulations | Directors and officers must ensure the company adheres to industry-specific regulations and labor laws. | Non-compliance could result in regulatory actions, lawsuits, and business shutdowns. |
By understanding these core responsibilities, directors and officers can better navigate the complexities of governance, minimize risks, and contribute to the long-term success of the company. These duties ensure that organizations are managed with integrity, transparency, and in the best interests of all stakeholders involved.
Questions on Shareholder Rights and Duties
Shareholders hold a crucial role in any organization, as they provide the necessary capital and, in return, are entitled to certain rights. These rights, however, come with corresponding duties that ensure the proper functioning of the entity and the protection of all stakeholders involved. Understanding the balance between these rights and obligations is fundamental to maintaining effective governance and ensuring a fair and transparent operational environment.
Key Rights of Shareholders
Shareholders are granted several key rights that enable them to influence the direction of the organization and protect their investments. These rights typically include voting rights, the right to receive dividends, and the right to access company information. Below is a breakdown of common rights shareholders possess:
| Right | Description | Legal Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Voting Rights | Shareholders can vote on significant corporate matters, including electing directors and approving major company policies. | These votes allow shareholders to influence governance and strategic decisions. |
| Right to Dividends | Shareholders are entitled to a portion of the profits, distributed as dividends, based on the number of shares they own. | This right ensures shareholders benefit from the financial success of the entity. |
| Right to Information | Shareholders have the right to access financial statements and other key information about the company’s operations. | Transparency ensures shareholders can make informed decisions and protect their investments. |
Responsibilities of Shareholders

While shareholders have rights, they also carry responsibilities to act in a manner that promotes the long-term success and integrity of the organization. Some of the key duties include acting in good faith, supporting sound governance, and refraining from actions that could harm the company or its stakeholders. Below are some of the key duties that shareholders must uphold:
| Duty | Description | Legal Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Duty of Good Faith | Shareholders are expected to act in the best interest of the organization, avoiding actions that could harm its operations or reputation. | Failure to act in good faith can lead to legal disputes and harm to the company’s standing. |
| Support for Governance | Shareholders should support the governance structure, including electing competent directors and holding them accountable. | Effective governance ensures the company’s operations are transparent and aligned with shareholder interests. |
| Duty to Avoid Conflicts of Interest | Shareholders must avoid situations where their personal interests conflict with the organization’s goals and interests. | Conflicts of interest may lead to legal challenges or loss of trust among stakeholders. |
By understanding both their rights and duties, shareholders can play a vital role in shaping the success of the company, while also ensuring their actions align with broader ethical and legal standards.
Legal Procedures for Business Mergers
Combining two or more entities into a single organization is a complex process that involves a variety of legal steps. These procedures are essential to ensure that the merger complies with all regulatory requirements, protects the interests of shareholders, and minimizes potential legal risks. Properly navigating this process requires careful planning, negotiation, and adherence to relevant laws and regulations.
Initial Steps in the Merger Process
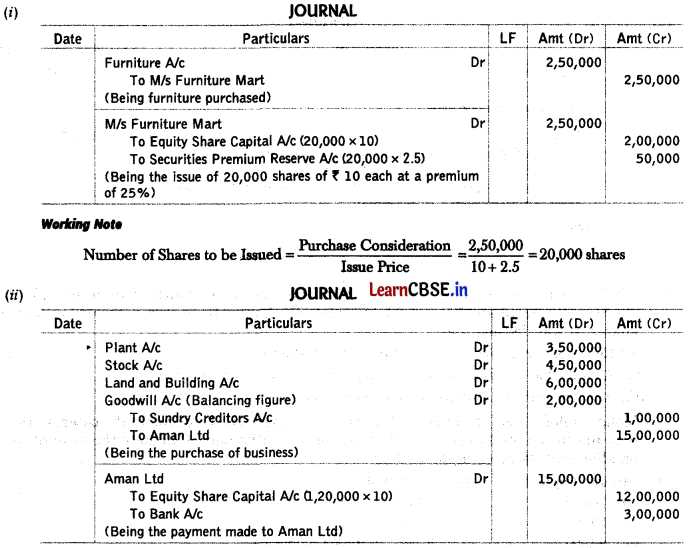
Before proceeding with a merger, both parties must evaluate the potential benefits and challenges. Below are the key preliminary steps involved:
- Due Diligence: Conducting thorough research on the financial, legal, and operational aspects of the other company to assess risks and opportunities.
- Negotiation: Establishing the terms and structure of the merger, including pricing, employee transitions, and integration plans.
- Drafting the Agreement: Preparing a detailed merger agreement that outlines the roles, obligations, and timelines for the merged entity.
- Approval by Stakeholders: Obtaining approval from shareholders, boards of directors, or regulatory authorities, depending on the structure of the merger.
Legal Considerations During the Merger

Several legal issues need to be addressed during the merger process to ensure compliance and smooth integration. These considerations include:
- Antitrust Laws: Mergers that significantly reduce competition may face scrutiny from antitrust authorities. Legal advice is necessary to ensure compliance with competition laws.
- Employment Laws: The merger may involve the transfer of employees or restructuring of teams. Proper legal steps must be taken to comply with labor laws and address employee rights.
- Regulatory Approvals: Depending on the industry, specific regulatory bodies may need to approve the merger, such as financial, healthcare, or telecommunications authorities.
- Intellectual Property: The handling of patents, trademarks, and copyrights must be addressed to ensure ownership and use rights are properly transferred.
Once these legal aspects are resolved, the companies can move forward with finalizing the merger. This includes the transfer of assets, dissolution of the previous entities (if applicable), and the formation of the new organization.
Successfully completing a merger requires strategic planning, legal expertise, and effective negotiation. By addressing all legal requirements, the entities involved can ensure a smooth transition and position themselves for future success in the combined entity.
Business Bankruptcy Law Overview
When an entity faces severe financial distress and is unable to meet its obligations, bankruptcy law provides a structured method for addressing these issues. This legal framework helps companies reorganize their debts or liquidate their assets, depending on the chosen process. It is designed to protect creditors’ rights while allowing the entity to either emerge from financial troubles or dissolve in an orderly fashion. Understanding the fundamental principles of bankruptcy law is essential for any company navigating financial difficulty.
Key Types of Bankruptcy Proceedings
There are different types of bankruptcy filings, each serving a distinct purpose depending on the circumstances. The two most common types are:
- Chapter 7 – Liquidation: In this process, the company’s assets are sold to pay off creditors. Once the assets are liquidated, the remaining debts are typically discharged, and the company is dissolved.
- Chapter 11 – Reorganization: This option allows the company to continue its operations while restructuring its debts. A plan is created to pay creditors over time, often involving negotiations to reduce the overall debt load.
Important Considerations in Bankruptcy Cases
When a company enters bankruptcy, several legal considerations must be addressed to ensure a fair process for all involved parties. Some of these include:
- Creditors’ Rights: Creditors are classified into different categories based on the priority of their claims, which determines the order in which they are paid. Secured creditors typically have the highest priority, followed by unsecured creditors.
- Asset Distribution: In liquidation proceedings, the company’s assets are sold, and the proceeds are distributed to creditors in accordance with the legal priorities established under bankruptcy law.
- Discharge of Debts: Depending on the type of bankruptcy, some or all of the company’s debts may be discharged, releasing the entity from further obligations to creditors.
- Reorganization Plans: In a Chapter 11 case, the company must submit a reorganization plan detailing how it will restructure its debts and operations. This plan must be approved by both the court and the creditors.
While bankruptcy can offer a fresh start or provide a pathway to recovery, it also comes with significant legal, financial, and reputational challenges. Companies must work with experienced legal professionals to navigate these processes effectively, ensuring compliance with applicable laws and the best possible outcome for all stakeholders.
Corporate Taxation and Legal Implications
Taxation plays a critical role in the operations and financial health of any organization. Beyond just meeting regulatory requirements, managing taxes effectively can influence strategic decisions, impact profitability, and shape long-term growth. In addition to tax obligations, entities must also navigate the legal frameworks that govern these taxes, ensuring compliance and avoiding potential penalties. Understanding the intersection of tax laws and corporate operations is essential for minimizing risks and optimizing financial performance.
Types of Corporate Taxation
Corporations are subject to a variety of taxes based on their structure, activities, and location. The main types of taxes they face include:
- Income Tax: Corporations are taxed on their profits, with the rate depending on the country or region. In some jurisdictions, this can be a flat rate, while others implement a progressive system.
- Sales Tax: Many entities are required to collect sales tax on goods and services they provide. This tax is typically passed on to the consumer, though businesses must remit the collected amounts to the relevant tax authorities.
- Payroll Tax: Companies are required to withhold taxes on employee wages and contributions to social security and other benefit programs. These amounts must be submitted to the government on behalf of employees.
- Property Tax: Businesses owning real estate or other taxable assets may be subject to property taxes. These taxes vary by location and are often based on the value of the property.
Legal Implications of Corporate Taxation
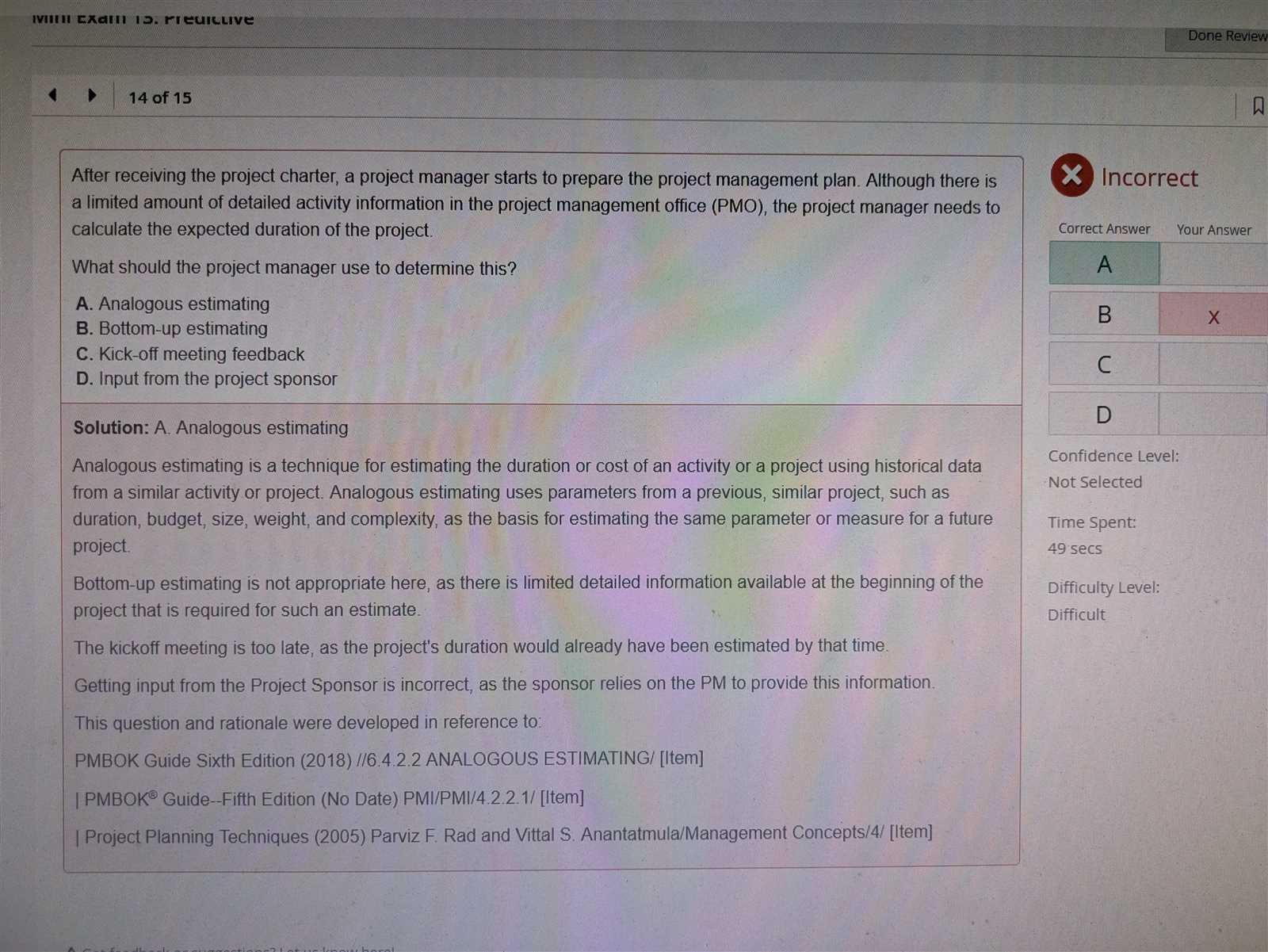
Failure to comply with tax laws can lead to serious legal consequences, including fines, penalties, and even criminal prosecution. Additionally, tax planning and strategies must be carefully aligned with the legal requirements to avoid unlawful practices. Some of the key legal considerations include:
- Tax Evasion vs. Tax Avoidance: While tax avoidance (using legal methods to minimize tax liabilities) is permissible, tax evasion (illegally hiding income or inflating expenses) is a criminal offense. Entities must ensure they adhere to legal methods of reducing their tax burden.
- Transfer Pricing: Multinational companies often face scrutiny over their transfer pricing strategies. This involves the pricing of transactions between subsidiaries, and tax authorities monitor these transactions to ensure they are conducted at arm’s length and not used to shift profits to lower-tax jurisdictions.
- Tax Compliance: Businesses are required to maintain accurate records and file tax returns in a timely manner. Non-compliance can result in interest charges, penalties, and a negative impact on reputation.
- Legal Structures and Tax Liabilities: The legal structure of a corporation–such as whether it operates as a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, or partnership–can impact the taxes owed and the deductions available to the entity.
By understanding the legal landscape surrounding taxation, corporations can better manage their financial obligations, avoid legal risks, and ensure compliance with ever-changing tax laws. Proper tax planning can also contribute to a more efficient allocation of resources and enhance overall profitability.
Intellectual Property in Business Context
In today’s competitive environment, intangible assets like inventions, designs, and branding elements have become central to an entity’s value. These assets are protected by intellectual property laws, which grant exclusive rights to their creators and owners. Securing and managing intellectual property is crucial for maintaining a competitive advantage, fostering innovation, and ensuring that the business’s unique offerings are legally protected from unauthorized use or replication. Understanding the types of protection available and how to enforce these rights is vital for any organization.
Types of Intellectual Property Protections

There are several types of protections that can be applied to intangible assets, each suited to a specific form of innovation or creation. The main categories include:
- Patents: These provide protection for new inventions, granting exclusive rights to the inventor for a set period, typically 20 years. Patents prevent others from making, using, or selling the invention without permission.
- Trademarks: Trademarks protect distinctive symbols, names, logos, or slogans that identify and distinguish products or services in the marketplace. Trademark protection helps build brand identity and prevent consumer confusion.
- Copyrights: Copyrights safeguard original works of authorship, such as books, music, and software. This protection gives the cre
Effective Exam Strategies for Business Law
Successfully tackling tests in law requires not only an understanding of complex concepts but also the ability to apply legal principles in various scenarios. Preparation is key, and strategic studying is crucial to performing well under pressure. By mastering time management, focusing on essential areas, and practicing with sample cases, individuals can improve their ability to recall key information and think critically during the assessment. Developing effective strategies allows for a more organized and confident approach to answering questions accurately and efficiently.
Key Areas to Focus On
Focusing on the most important legal areas can help streamline preparation and ensure that essential knowledge is retained. Some core topics to emphasize include:
- Legal Frameworks: Understanding the fundamental laws that govern various types of legal entities, including structures, liabilities, and governance.
- Contract Law: Focus on the elements of a valid contract, breach scenarios, and remedies, as these are frequently tested in practical scenarios.
- Intellectual Property: Be familiar with the protection mechanisms for inventions, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets, as these often come up in real-world case studies.
- Dispute Resolution: Study the different methods available for resolving legal conflicts, such as arbitration, mediation, and litigation, as well as their advantages and limitations.
Techniques for Success
In addition to knowing the material, utilizing certain strategies during preparation and on the day of the test can enhance performance. Consider the following tips:
- Active Learning: Engage with the material actively by making summaries, creating diagrams, and testing yourself regularly. Rewriting key points in your own words improves retention.
- Practice Under Time Constraints: Simulate real test conditions by completing practice cases within the allotted time frame. This helps to manage time during the actual assessment and reduces anxiety.
- Identify Common Patterns: Recognize recurring themes in past questions or case studies. This allows you to anticipate what areas are likely to be emphasized and how to approach them.
- Focus on Application: Many legal assessments emphasize the ability to apply knowledge to hypothetical scenarios. Practice applying legal principles to different fact patterns, analyzing potential outcomes.
By focusing on the most critical topics and incorporating strategic study techniques, individuals can significantly enhance their ability to succeed in legal assessments. Consistency, practice, and a thorough understanding of key concepts are fundamental for achieving strong results in any legal test.