
When preparing for a professional certification in environmental science, a thorough understanding of key concepts and principles is crucial. Mastery of essential topics not only boosts confidence but also enhances the ability to apply knowledge effectively in real-world situations. Comprehensive preparation involves reviewing various subjects, from ecosystem dynamics to land management strategies, ensuring a well-rounded grasp of the field.
Practical insights gained from studying critical areas help candidates tackle a wide range of challenges they may face in the certification process. By focusing on core themes and testing their proficiency through targeted exercises, individuals can develop a clear understanding of how different elements interconnect within natural systems.
Success lies in the ability to combine theory with practical application. Candidates must be prepared to demonstrate their knowledge across multiple domains, answering not only theoretical inquiries but also problem-solving tasks that require in-depth analysis. This preparation is key for standing out in any professional setting related to environmental management.
Essential Forestry Exam Preparation Tips
Effective preparation is the key to mastering any certification in environmental science. Focusing on the right areas and utilizing the best resources can significantly increase your chances of success. Here are some essential tips to guide you through the process:
- Understand Key Concepts: Before diving into specific topics, ensure you have a strong grasp of the core principles that underpin the field. Focus on the fundamental processes that govern ecosystems, resource management, and sustainability practices.
- Practice with Real-Life Scenarios: Apply your knowledge to realistic situations. Use case studies and examples to understand how theoretical concepts translate into practical solutions. This approach will help you think critically during assessments.
- Time Management: Allocate sufficient time to each subject area. Avoid cramming and create a study schedule that allows for regular review sessions. Prioritize the topics that are most challenging or complex.
Another important aspect is the preparation of study materials. Having access to quality resources ensures that you are learning from the best information available. Seek textbooks, online platforms, and practice exercises that cover the most commonly tested material. Some additional tips include:
- Use Flashcards: Create or find flashcards for key terms and definitions. This method helps reinforce your memory and makes it easier to recall information during the assessment.
- Join Study Groups: Engaging with peers can help clarify complex topics. Group discussions allow for different perspectives and shared knowledge that might improve your understanding.
- Take Practice Tests: Simulate test conditions by practicing under timed constraints. This helps improve your ability to work under pressure and ensures you’re familiar with the format of the questions.
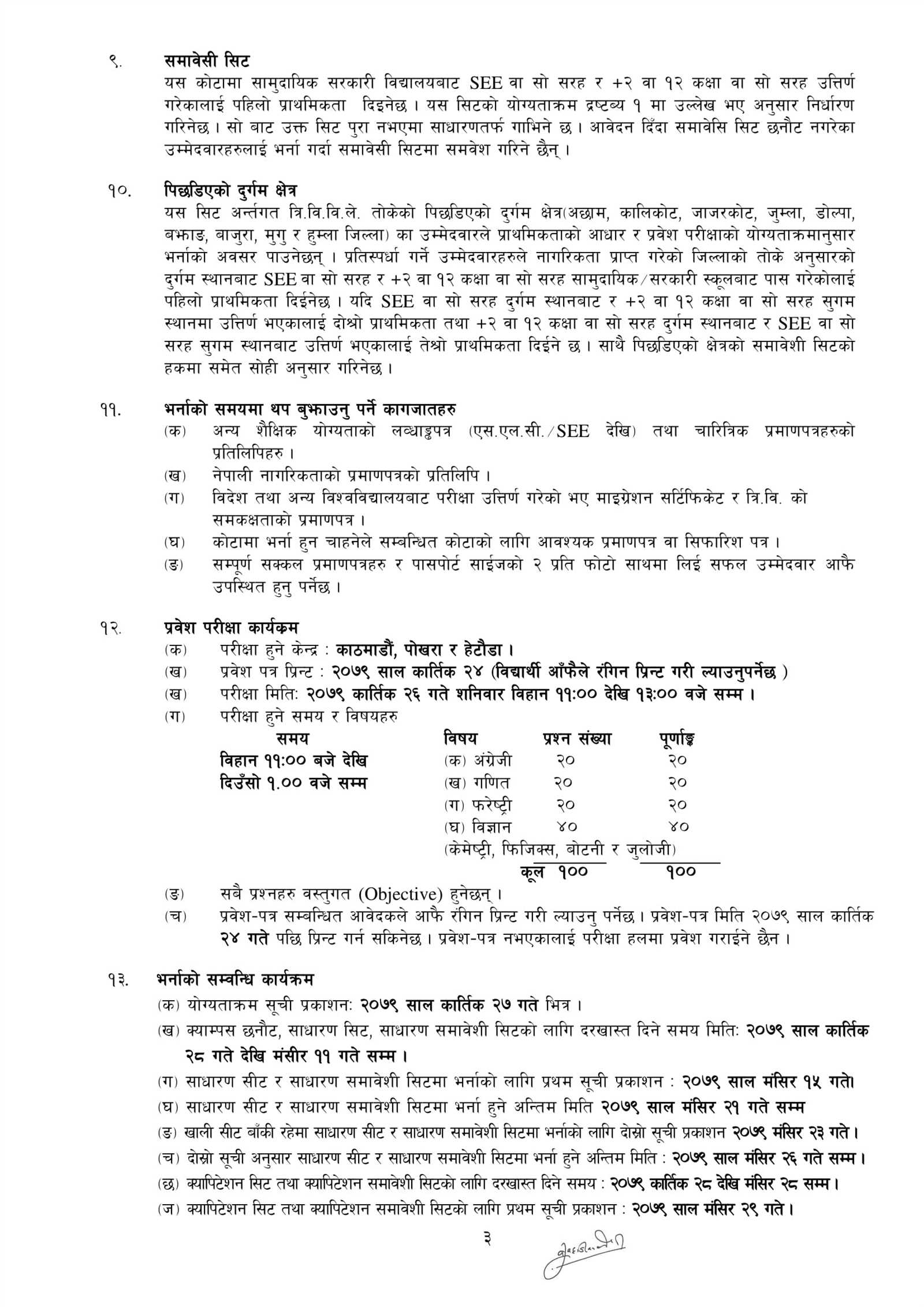
By following these strategies, you’ll be able to approach the certification process with confidence and preparedness, ready to tackle any challenge that comes your way.
Key Topics for Forestry Certification Exams
To succeed in professional assessments within environmental science, it’s crucial to focus on the most important topics. A strong foundation in the essential areas will not only help you answer a variety of inquiries but also prepare you for real-world challenges. Below are the key areas that you should prioritize during your preparation:
Core Concepts to Master

- Ecology and Ecosystem Functioning: Understanding the balance within natural systems is fundamental. Study how organisms interact with their environment, focusing on energy flows, nutrient cycles, and biodiversity.
- Resource Management: Focus on methods used to sustainably manage natural resources. This includes forest growth, water conservation, and the ethical management of renewable resources.
- Environmental Laws and Policies: Familiarize yourself with local, national, and international environmental regulations. Knowing the legal framework for managing land and resources is essential for professionals in the field.
Practical Skills and Knowledge
- Soil Science: An understanding of soil types, their properties, and their role in supporting plant life is crucial for anyone involved in environmental management.
- Plant Identification: Knowledge of plant species, both native and invasive, is necessary for land and vegetation management. Learn to identify key species and understand their roles in ecosystem health.
- Wildlife Conservation: Learn about habitat preservation, species protection, and conservation techniques. This knowledge is vital for ensuring biodiversity in managed environments.
Focusing on these topics will ensure you are well-prepared for any challenge you may face in your professional certification. By mastering the core principles and practical applications, you’ll gain the confidence needed to excel in your field.
Common Questions Asked in Forestry Exams

During assessments in environmental management, candidates are often tested on a range of topics that cover theoretical knowledge and practical skills. The most common inquiries focus on key principles that define sustainable land use, resource conservation, and ecosystem dynamics. Understanding the type of content frequently covered can help you prepare more effectively for your evaluation.
Key Areas of Focus

- What are the primary factors affecting forest health? Questions may explore the causes of disease, pests, and environmental stressors that impact ecosystems. Be prepared to identify the effects of these factors on biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
- How can natural resources be managed sustainably? Expect inquiries on techniques that promote long-term ecological balance. This could include topics such as crop rotation, reforestation, and water conservation practices.
- What is the role of different plant species in the ecosystem? Some questions may test your knowledge of plant identification and their ecological functions. These include their role in soil preservation, air quality, and supporting wildlife habitats.
Practical Scenarios

- How would you manage a forest area facing drought? Inquiries like this assess problem-solving abilities. You may need to suggest practical solutions, including watering strategies, native plant preservation, or soil treatment methods.
- What measures would you take to prevent soil erosion? Prepare for questions that ask you to address issues related to soil conservation, focusing on techniques such as terracing, mulching, or planting ground cover.
- Describe how climate change impacts forest ecosystems. Knowledge of how shifting temperatures and changing precipitation patterns affect biodiversity and forest regeneration is often tested.
By familiarizing yourself with these common inquiries, you can develop a well-rounded approach to your study and gain confidence in your ability to address similar scenarios during your evaluation.
Understanding Forest Ecology for Exams
A deep understanding of ecological principles is essential for anyone preparing for assessments in environmental science. Grasping the intricacies of how forest ecosystems function is critical for making informed decisions about land management, conservation, and restoration. Key concepts include energy flow, nutrient cycling, and species interactions within forest environments. The more you understand these processes, the better prepared you will be for tackling related topics in your evaluations.
Forest ecosystems are complex and involve various interactions between biotic and abiotic components. To help visualize these relationships, consider the following table that outlines some fundamental ecological processes:
| Ecological Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Flow | The movement of energy through the food chain, starting from the sun and passing through producers, consumers, and decomposers. |
| Nutrient Cycling | The process by which nutrients like nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus are recycled within the ecosystem through soil, water, plants, and animals. |
| Species Interactions | The relationships between different organisms, including predation, competition, symbiosis, and mutualism, that shape ecosystem dynamics. |
| Succession | The natural process by which ecosystems change and develop over time, from bare land to a mature forest. |
By mastering these key principles, you will be better equipped to apply your knowledge to real-world scenarios. Whether it’s identifying the causes of ecosystem disruption or suggesting methods for restoring balance, a strong foundation in forest ecology is essential for success in environmental assessments.
Forest Management Strategies Explained
Effective management of woodland areas is crucial for maintaining ecological balance, promoting sustainability, and ensuring the long-term health of natural resources. There are various strategies employed to achieve these goals, ranging from conservation efforts to controlled harvesting techniques. Understanding these strategies is essential for professionals looking to manage natural spaces responsibly while also addressing human needs.
Sustainable Harvesting Methods
One of the primary strategies in land stewardship is sustainable harvesting. This approach ensures that trees and plants are harvested in a way that minimizes environmental impact and allows for natural regeneration. Key techniques include:
- Selective Cutting: A method where only certain trees are removed based on size, age, or species, allowing the rest of the forest to remain intact.
- Clear-Cutting with Reforestation: A more intensive approach where all trees are removed from a specific area, followed by active replanting to restore the ecosystem.
- Agroforestry: Integrating tree planting with agricultural practices, providing both environmental and economic benefits.
Conservation and Restoration Techniques
Preserving biodiversity and restoring damaged ecosystems are also essential components of forest management. These strategies help mitigate the effects of human activity and climate change, fostering healthier environments. Key techniques include:
- Invasive Species Control: Removing or controlling non-native species that threaten the natural balance of the ecosystem.
- Forest Restoration: Replanting native species and addressing soil erosion or water quality issues to help restore degraded land to its original state.
- Wildlife Habitat Preservation: Creating or maintaining spaces that support wildlife populations, ensuring they thrive within their natural environment.
By adopting these strategies, land managers can enhance forest resilience, support local wildlife, and provide a sustainable supply of resources for future generations. Balancing ecological health with human needs remains a core principle of effective management.
What to Expect in Forestry Tests
Preparing for assessments in land management and environmental sciences requires understanding the format and focus of the evaluation. These tests typically cover a broad range of topics that assess both theoretical knowledge and practical application in areas such as ecosystem health, resource management, and conservation practices. Knowing what to expect can help you better focus your preparation efforts.
Test Structure and Format
In these assessments, the format usually consists of multiple-choice questions, short-answer inquiries, and practical scenarios. Here’s an overview of what you might encounter:
| Test Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Multiple-Choice | These questions assess your ability to recall facts and understand key concepts. Topics can range from ecosystem processes to resource conservation methods. |
| Short-Answer | Test your ability to articulate knowledge and explain concepts in detail. You may be asked to describe specific management techniques or the effects of environmental changes. |
| Practical Scenarios | Evaluate how you apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations. For example, you might be asked how to address an ecological disturbance or manage a specific area. |
Key Areas of Focus
During these tests, you can expect to cover the following topics:
- Ecosystem Dynamics: Understanding the relationships between different organisms and their environment.
- Resource Management Techniques: Knowledge of sustainable land use and conservation practices.
- Environmental Laws and Policies: Familiarity with local and global regulations regarding natural resource management.
- Practical Problem Solving: Applying concepts to real-life situations and proposing effective solutions.
By familiarizing yourself with the test structure and the main areas of focus, you’ll be well-prepared for the challenges ahead. A balanced study approach will help you feel confident in both recalling information and applying it in practical scenarios.
How to Study for Forestry Exams

Effective preparation for assessments in environmental management and conservation requires a structured approach. By understanding the key topics, developing strong study habits, and utilizing a variety of resources, you can improve your performance and feel confident going into your evaluation. Here are some essential tips to help you succeed in your studies.
Organize Your Study Materials
Start by gathering all the materials you need, such as textbooks, notes, and study guides. Organizing your resources helps you focus on the most important concepts. Consider the following steps:
- Review Course Outline: Ensure that you are familiar with the topics covered and identify any areas that require additional focus.
- Break Down Study Topics: Divide the material into manageable sections, and set specific goals for each study session.
- Highlight Key Concepts: Focus on definitions, important processes, and practical applications.
Utilize Active Learning Techniques
Instead of passively reading through the material, engage with it actively to reinforce your understanding. Here are some effective techniques:
- Practice with Flashcards: Create flashcards to test your memory of key terms, definitions, and concepts.
- Take Practice Quizzes: Practice answering hypothetical scenarios and multiple-choice questions to test your knowledge and application skills.
- Teach What You Learn: Explaining complex topics to others can help solidify your understanding and identify areas that need further clarification.
Join Study Groups
Collaborating with others can enhance your learning experience. Study groups allow you to share insights, ask questions, and discuss challenging concepts. Consider these tips:
- Share Resources: Exchange study materials and discuss topics that you may have missed or misunderstood.
- Hold Practice Sessions: Simulate test conditions and quiz each other on key topics.
- Learn from Peers: Take advantage of the diverse perspectives and strategies other students bring to the group.
Review Regularly
Consistent review is crucial to retaining information. Instead of cramming the night before, make sure to:
- Set a Study Schedule: Plan your study time in advance and stick to it. Consistent, shorter study sessions are more effective than long, irregular ones.
- Revise Before Bed: Reviewing material before you sleep helps with memory consolidation.
- Test Yourself: Regularly quiz yourself to gauge your progress and adjust your study plan accordingly.
By following these study strategies, you will increase your chances of performing well in the assessment. Remember, preparation is key–stay organized, stay focused, and keep practicing to ensure you are ready to apply your knowledge when it matters most.
Forestry Terminology You Must Know
Understanding the specialized terms used in land management and environmental sciences is essential for success in this field. Whether you’re preparing for assessments or looking to deepen your knowledge, familiarizing yourself with key terminology will help you better grasp the concepts and processes involved. Below are some important terms and their meanings that you should be well-versed in.
Key Terms Related to Ecosystem and Land Management
These terms are critical when discussing the health of ecosystems and the practices used to maintain natural habitats:
- Regeneration: The process of renewal and regrowth in a forest or land area, often through natural seeding or active planting.
- Carbon Sequestration: The capture and storage of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in vegetation and soil to mitigate climate change.
- Succession: The natural sequence of changes in an ecosystem over time, such as from bare land to a mature forest.
- Habitat Fragmentation: The breaking up of a continuous habitat into smaller, isolated sections, often due to human activity.
Resource Management and Conservation Terms
Understanding how natural resources are managed and conserved is key in this discipline. Below are terms used in these contexts:
- Sustainable Harvesting: The practice of removing resources, such as timber or plants, in a way that does not deplete them for future generations.
- Selective Cutting: A harvesting technique where only mature or specific trees are removed, leaving the forest intact.
- Conservation Easement: A legal agreement that permanently limits the use of land in order to protect its natural resources.
- Invasive Species: Non-native organisms that threaten the biodiversity of an ecosystem by outcompeting or harming native species.
Being familiar with these terms not only helps in technical assessments but also allows you to engage more effectively in discussions related to land management and environmental protection. A strong grasp of terminology ensures clearer communication and better decision-making in this field.
Test Your Knowledge with Practice Questions
One of the most effective ways to assess your readiness for a certification or evaluation in environmental management is by practicing with relevant scenarios. By engaging in simulated tasks and challenges, you can gauge your understanding and identify areas that need further attention. Below, we provide a set of practice scenarios designed to help you test your knowledge and refine your skills.
These exercises are crafted to help you apply theoretical concepts to practical situations, enhancing both your recall and critical thinking. Challenge yourself by attempting these exercises and checking your answers to see where you need improvement.
Scenario 1: Resource Management
Scenario: A forest area has been impacted by a wildfire. The ecosystem is struggling to regenerate. What are the first steps you would take to support the recovery process?
- Identify the affected species and assess their health.
- Implement soil stabilization techniques to prevent erosion.
- Consider planting native species to accelerate natural regeneration.
- Monitor the site regularly to track progress and adjust as needed.
Scenario 2: Invasive Species Control
Scenario: You have discovered a non-native plant species that is overtaking a local habitat and threatening native vegetation. What would you do to address the issue?
- Conduct a survey to determine the extent of the infestation.
- Develop a management plan to remove the invasive species.
- Replant native species to restore the balance of the ecosystem.
- Work with local authorities to prevent further spread of the invasive species.
By practicing with scenarios like these, you will improve your ability to think critically and make informed decisions in real-world situations. These exercises not only help solidify your knowledge but also boost your confidence in applying what you’ve learned.
Time Management During Forestry Exams
Effective time management is crucial when preparing for assessments in environmental science and resource management. Being able to allocate your time wisely allows you to complete each section with adequate focus and minimizes the risk of rushing through important tasks. In this section, we’ll explore strategies that help you manage your time efficiently during tests.
Setting Priorities and Allocating Time
Start by reviewing the structure of the test to understand how much time is allotted for each section. Prioritize your time based on the difficulty level of each task and the weight of the questions. Here are some strategies for time allocation:
| Task | Time Allocation | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Choice Questions | 20-30% of total time | These are usually quicker and easier to complete, so they should be tackled first. |
| Short Answer Questions | 30-40% of total time | These require more thought and detail, so allocate more time for these tasks. |
| Essay or Case Study | 30-40% of total time | Ensure ample time for structuring and providing detailed responses with examples. |
Tips for Staying on Track

To ensure that you stick to your time limits, use the following strategies:
- Use a timer: Keep track of time throughout the test to ensure you’re moving at a steady pace.
- Don’t linger on difficult tasks: If a question is taking too long, move on and come back to it later.
- Read instructions carefully: Misunderstanding instructions can lead to wasted time. Always read the task description thoroughly before answering.
- Stay calm: Rushing through a test can lead to mistakes. Stay calm and focus on completing one section at a time.
By using these strategies, you’ll be better equipped to manage your time efficiently, ensuring that you have enough time to address all sections without unnecessary stress.
Essential Forestry Laws and Regulations
Understanding the legal framework that governs land use, resource management, and environmental protection is crucial for anyone involved in the management of natural habitats. These laws and regulations are designed to ensure sustainable practices, protect biodiversity, and maintain ecological balance. In this section, we will cover key legislation and guidelines that impact the management of forests and other natural resources.
Familiarity with these rules is essential for responsible decision-making, ensuring that landowners, managers, and professionals comply with environmental standards and contribute to the long-term health of ecosystems. Below, we outline some of the most important laws and regulations to consider:
- National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA): This law mandates environmental assessments for major projects that could significantly impact ecosystems, requiring analysis and mitigation of potential environmental harm.
- Endangered Species Act (ESA): The ESA provides protection for species at risk of extinction, requiring management plans that minimize harm to these species and their habitats.
- Clean Water Act (CWA): This regulation focuses on protecting water resources from pollution and encourages the management of wetlands and riparian zones to safeguard water quality.
- Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA): The RCRA governs the disposal of hazardous waste, ensuring that substances harmful to the environment are handled responsibly and safely.
- Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) Certification: Though not a law, FSC certification sets standards for responsible forest management, promoting sustainable logging practices and ensuring the protection of biodiversity.
Compliance with these laws helps mitigate negative impacts on the environment, promotes sustainable land-use practices, and ensures that natural resources are protected for future generations. Understanding these regulations is not just a requirement, but a key component in responsible land management and conservation efforts.
Best Resources for Forestry Exam Prep
Preparing for assessments in natural resource management and land conservation can be a daunting task, but utilizing the right materials can make all the difference. With a wide range of study aids available, it’s essential to choose those that best align with the topics covered and the exam format. In this section, we will highlight some of the most effective tools and resources to help you succeed in your preparation.
Books and Study Guides

Books specifically tailored to land management and environmental science are invaluable for grasping complex concepts and providing in-depth knowledge. Look for comprehensive study guides that cover a wide range of topics. These resources are often written by experts in the field and include practice exercises, sample case studies, and quizzes to help reinforce your learning.
- The Land Manager’s Handbook: A detailed resource covering sustainable land management practices, environmental policies, and more.
- Environmental Science for Land Management: A guide that breaks down key environmental principles with examples and practice questions.
- National Resources Management Handbook: A thorough text on ecosystem management and conservation strategies, with useful study tips and test prep sections.
Online Platforms and Courses

Online courses and digital platforms offer flexible study options, allowing you to learn at your own pace and access interactive content. These platforms often feature videos, quizzes, and discussion forums where you can engage with instructors and fellow students.
- Coursera – Environmental Management Courses: Online courses that cover fundamental concepts in environmental science and land management with hands-on practice.
- Udemy – Land Conservation Certification: A course designed to prepare learners for assessments related to natural resource management with practical applications.
- Quizlet – Study Flashcards: A mobile-friendly platform for creating custom flashcards and quizzes based on your study material.
Incorporating these resources into your study plan will help you gain a deeper understanding of key topics and improve your performance in the assessment process. From in-depth textbooks to interactive online platforms, these tools provide a comprehensive approach to preparing for your land management and conservation evaluation.
Forest Conservation Topics for Exams
When preparing for assessments related to natural resource management and habitat preservation, it’s essential to focus on key areas of forest conservation. These topics encompass the fundamental concepts, strategies, and practices aimed at maintaining healthy ecosystems and sustainable land use. Understanding these subjects not only helps in passing evaluations but also fosters a deeper appreciation for environmental stewardship and sustainability.
Below are some crucial areas to concentrate on for a comprehensive understanding of forest conservation:
- Deforestation and Its Impact: Understanding the causes, consequences, and solutions to deforestation, including its effects on biodiversity, carbon cycles, and soil health.
- Sustainable Forest Management: The principles and practices involved in managing forests for long-term ecological, economic, and social benefits, balancing conservation with resource use.
- Forest Restoration Techniques: Methods for rehabilitating degraded forests, including replanting, soil erosion control, and restoring ecological functions.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Strategies to protect plant and animal species within forest ecosystems, focusing on the importance of preserving genetic diversity and ecosystem services.
- Forest Policy and Legislation: Key laws and regulations that govern forest use, including international agreements, local regulations, and national policies aimed at conservation and sustainable land management.
- Climate Change and Forests: The role of forests in mitigating climate change, including their ability to sequester carbon, and the impact of climate change on forest health.
- Wildlife Habitat Preservation: Techniques for managing forest habitats to support wildlife, focusing on habitat restoration, corridor preservation, and species management.
These topics are integral to understanding the complexities of managing forest ecosystems and ensuring their sustainability for future generations. Mastery of these concepts will not only enhance your preparation for assessments but also provide you with the knowledge to contribute to meaningful conservation efforts worldwide.
Understanding Forest Health and Disease
Maintaining the vitality of forest ecosystems is crucial for ensuring their longevity and ecological balance. Various factors, both natural and human-induced, can impact the health of trees and other plant species. Understanding the signs of illness and damage in forests is essential for preventing widespread devastation and implementing effective management practices.
Healthy forests are fundamental to biodiversity, air quality, and water regulation. However, disease outbreaks, pest infestations, and environmental stressors such as climate change can all pose significant threats. Early detection and intervention are key to preserving forest integrity and preventing irreversible damage.
Common Threats to Forest Health
- Pathogens: Fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases can weaken trees, leading to defoliation, dieback, and, in severe cases, death. Notable examples include root rot and blight.
- Pests: Insects like bark beetles, aphids, and moths can infest trees, damaging the bark, leaves, and branches. These pests often introduce diseases or stress trees, making them more susceptible to other threats.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can stress trees, making them more vulnerable to disease and pest attacks. Extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, can also exacerbate the situation.
Preventive Measures and Solutions
- Monitoring: Regular surveys and health assessments help detect early signs of stress, pests, or disease in trees.
- Quarantine and Control: Limiting the spread of harmful pests and pathogens through quarantine measures and controlled treatments can prevent widespread damage.
- Reforestation and Restoration: Replanting trees and restoring damaged habitats helps promote healthy, diverse ecosystems that are more resilient to future threats.
By focusing on forest health and disease management, we can protect these vital ecosystems from further degradation and ensure their continued contribution to the environment. Understanding these issues is crucial for anyone involved in conservation and resource management.
Effective Study Strategies for Forestry
When preparing for assessments in environmental management and ecosystem care, developing a strategic study plan is essential for success. Effective learning techniques help retain critical information, understand complex concepts, and perform well under pressure. In this section, we explore methods to enhance your study efficiency and maximize results.
Mastering the key areas of forest management, conservation, and ecological principles requires focus and discipline. It’s important to use a variety of study approaches to build a solid foundation and stay engaged throughout the preparation process. Whether you’re tackling theoretical concepts or practical skills, these strategies will guide you toward comprehensive knowledge and confidence.
Active Learning Techniques

- Concept Mapping: Visualizing relationships between different topics helps reinforce connections and makes it easier to recall information during evaluations.
- Practice Problems: Working through case studies, practice scenarios, or mock assessments enables you to apply theoretical knowledge in practical contexts.
- Group Study: Collaborating with peers allows for diverse perspectives and facilitates discussion on complex topics, improving overall understanding.
Time Management Tips
- Set Clear Goals: Break down the material into smaller, manageable chunks and set daily or weekly goals to stay on track.
- Prioritize Weak Areas: Focus on topics that are challenging or less familiar, giving them more time and attention to ensure full comprehension.
- Regular Breaks: Schedule breaks to avoid burnout and keep your mind fresh, allowing you to absorb more information effectively.
Adopting these study techniques will ensure that you approach your learning with a structured plan and targeted strategies. The combination of active learning and time management will enhance your preparation, ensuring you’re well-equipped for any challenge that arises in your field.
Certification Preparation Tips and Tricks
Successfully completing a professional assessment in the field of natural resource management requires more than just knowledge–it demands strategy, focus, and preparation. This section will provide useful strategies to help you approach your assessment with confidence, making sure you’re ready for any challenge that may come your way.
Whether you’re preparing for a written or practical assessment, there are several methods that can improve your chances of success. By incorporating these tips into your study routine, you can streamline your preparation process, reduce anxiety, and increase your efficiency when faced with difficult tasks.
Planning Your Study Routine

- Start Early: Give yourself plenty of time to cover all topics thoroughly. Starting early reduces the stress of last-minute cramming and allows time for review.
- Understand the Format: Familiarize yourself with the structure of the assessment, whether it includes multiple-choice, short-answer, or practical components, to help you focus your preparation.
- Break It Down: Split your study materials into smaller sections and tackle one at a time, avoiding overwhelm while ensuring complete coverage of the subject matter.
Test-Taking Strategies
- Read Instructions Carefully: Before starting, ensure you fully understand the instructions for each section to avoid errors that may cost valuable points.
- Time Management: Allocate a specific amount of time to each question or task and stick to it. Don’t spend too much time on any single item.
- Stay Calm and Focused: During the assessment, try to remain calm and collected. If you don’t know the answer to a question immediately, move on and return to it later.
By implementing these planning techniques and test-taking strategies, you’ll be better prepared to handle the challenges ahead. With focus and determination, you’ll be well-equipped to succeed in your certification process.