Preparation for assessments in this field requires a solid understanding of key principles, methodologies, and techniques used in project assessment. It’s important to not only know the theoretical background but also to be able to apply these concepts in practical situations. This section provides guidance on how to approach such tests effectively, ensuring that you can navigate various challenges with confidence.
To succeed in these evaluations, one must be well-versed in both qualitative and quantitative methods. Knowing how to analyze data, interpret results, and demonstrate your understanding of real-world applications is crucial. This guide will help you focus on the right areas, providing useful insights for tackling different types of tasks that may appear during your preparation.
Monitoring and Evaluation Exam Questions and Answers
When preparing for assessments in this field, it’s crucial to grasp both theoretical foundations and practical applications. A successful approach involves understanding core concepts, learning how to structure your responses, and practicing techniques that demonstrate your proficiency in this area. The following section outlines key strategies and provides examples to help you navigate through potential challenges with ease.
In many cases, tasks will assess your ability to analyze situations, make informed decisions, and present structured solutions. Here are some essential tips to improve your performance:
- Focus on the core principles: Be sure to understand the foundational concepts that guide decision-making in real-world scenarios.
- Practice data interpretation: Be prepared to analyze both qualitative and quantitative information and use it effectively in your responses.
- Structure your responses clearly: Organize your answers logically, starting with the key points and elaborating on them with examples or explanations.
- Prepare for case studies: Many assessments involve real-life case studies that require you to apply your knowledge and skills to specific situations.
By focusing on these areas, you will be able to showcase a deep understanding of the field and perform well in assessments. Remember, preparation is key to demonstrating your competence effectively. The more you practice with different scenarios, the better prepared you will be to tackle challenges confidently.
Key Concepts in Monitoring and Evaluation
Understanding the fundamental principles in this field is essential for assessing the success and impact of projects. These concepts guide the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted, allowing professionals to make informed decisions. A strong grasp of the key ideas behind measurement, assessment, and outcome analysis is crucial for anyone preparing for related assessments.
Some of the core areas to focus on include:
- Indicators: These are measurable factors used to track progress or success over time.
- Data Collection Methods: Understanding how to gather both qualitative and quantitative information is vital for meaningful analysis.
- Outcomes Assessment: The ability to assess the results or effects of an initiative is central to understanding its impact.
- Performance Metrics: These help measure the effectiveness and efficiency of the implemented activities.
By mastering these concepts, you will be able to build a robust framework for assessing programs, identify potential issues early on, and propose effective solutions based on reliable data.
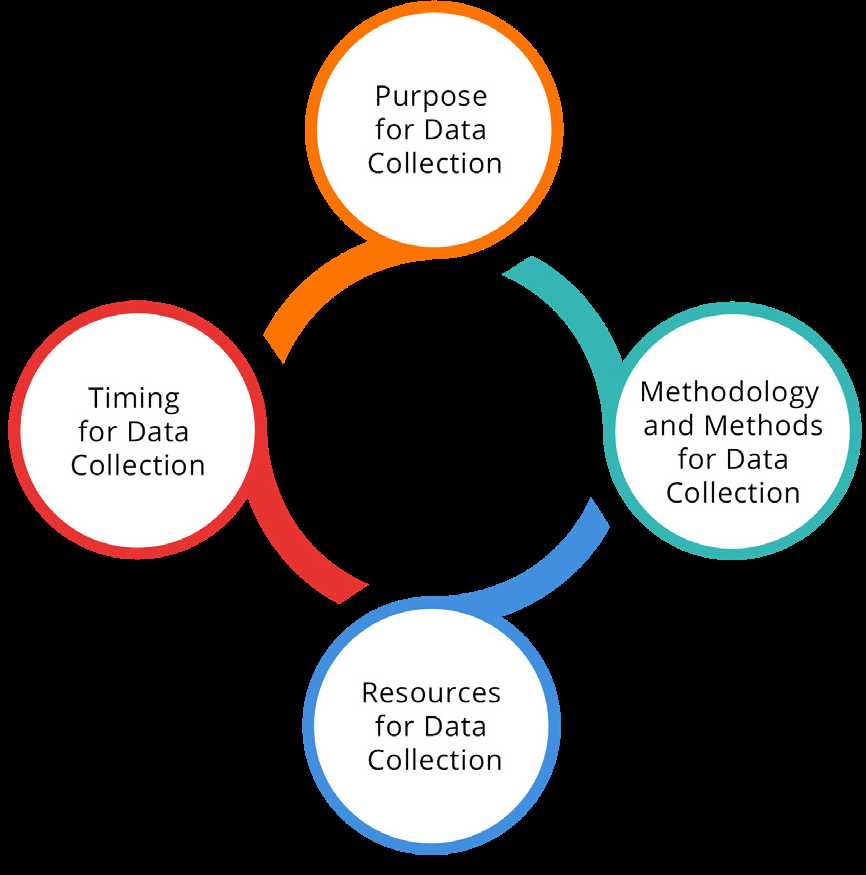
Understanding the Role of Data in Assessments
Data plays a pivotal role in understanding the effectiveness and progress of various projects or programs. It serves as the foundation for making informed decisions and assessing whether objectives are being met. Without accurate and reliable data, it becomes impossible to determine the success or failure of any initiative. The ability to collect, interpret, and utilize data is essential for professionals in this field.
The Importance of Accurate Data Collection
Collecting data in a structured and methodical manner is critical for ensuring its validity. Proper data collection methods allow for a clear understanding of how well a project is performing and where adjustments may be needed. Whether it involves surveys, interviews, or observations, data must be gathered consistently to provide reliable results.
Interpreting Data to Inform Decisions
Once data is collected, the next step is analysis. Interpreting the data correctly is essential to draw meaningful conclusions. By analyzing trends, patterns, and relationships, professionals can gain insights into the effectiveness of strategies and make recommendations for improvement. Effective data interpretation helps turn raw figures into actionable knowledge.
Common Exam Topics in Evaluation Methods
When preparing for assessments in this field, it’s important to understand the various approaches used to measure the success of projects. These methods are essential for identifying whether objectives are achieved and for determining the impact of specific actions. The following topics are frequently addressed in evaluations and are key to demonstrating your understanding of the field.
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Approaches: Understanding the difference between these two methods is crucial for selecting the appropriate one based on the project’s needs.
- Impact Assessment: This involves analyzing the long-term effects of an initiative, beyond just immediate results.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: A method used to compare the outcomes of a project against the resources invested in it.
- Sampling Techniques: These techniques help determine the most representative subset of data for analysis, ensuring validity in results.
- Data Interpretation: The ability to draw conclusions from collected data, turning raw numbers into meaningful insights.
Familiarizing yourself with these topics will help ensure that you can tackle a wide range of scenarios, demonstrating a well-rounded understanding of the field and its methods.
Techniques for Effective Performance Measurement
To accurately assess how well a project or program is performing, it is essential to apply the right techniques that can provide clear, actionable insights. These methods allow professionals to evaluate progress, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that objectives are being met effectively. The following techniques are commonly used to gauge success and measure outcomes.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): KPIs are specific metrics used to track progress towards predefined goals. They provide a clear benchmark for success and help assess if targets are being achieved.
- Benchmarking: This involves compa
How to Analyze Monitoring Results
Effective analysis of results is crucial for understanding the progress of a project or program. This process involves examining collected data to determine whether goals are being met, identifying patterns, and uncovering areas that need attention. By systematically reviewing the information, you can make informed decisions that drive improvements and ensure that objectives are on track.
Steps to Analyze Data Effectively
- Organize the Data: Before diving into analysis, ensure that all collected data is structured and categorized. This step will make it easier to spot trends and correlations.
- Identify Key Metrics: Focus on the most relevant indicators that directly measure success. These may include output, outcome, and impact metrics, depending on the objectives.
- Perform Comparisons: Compare the results to initial targets or benchmarks to assess performance. This helps to gauge whether the project is moving in the right direction.
Methods for Interpreting Results
- Trend Analysis: Look for patterns in the data over time. Identifying trends can provide insights into the sustainability and long-term effectiveness of a project.
- Root Cause Analysis: If performance is falling short, investigate the underlying causes. This approach helps uncover obstacles and challenges that may be hindering progress.
- Data Visualization: Use graphs, charts, or dashboards to present results visually. Visual aids make complex data easier to understand and communicate to stakeholders.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your analysis is thorough, accurate, and actionable, leading to informed decisions that improve project outcomes.
Evaluating Program Outcomes and Impact
Assessing the results and effects of a program is essential to understanding its effectiveness. This process allows stakeholders to determine whether the initiative has met its goals and delivered the expected benefits. By evaluating both short-term and long-term outcomes, one can gain insights into the program’s success and identify areas for improvement. Understanding these results is key to ensuring that future programs are more efficient and impactful.
Key Steps in Assessing Outcomes
- Define Success Criteria: Establish clear, measurable indicators that will help determine whether the program has achieved its intended outcomes.
- Collect Data: Gather relevant data through surveys, interviews, or reports to track progress and measure results against the defined success criteria.
- Analyze Results: Compare actual outcomes with the goals set at the beginning of the program. Identify both the positive outcomes and any challenges faced during implementation.
Understanding the Long-Term Impact
- Sustainability: Assess whether the benefits of the program will last beyond its conclusion. This includes examining the continuation of positive changes and improvements in the target community or area.
- Ripple Effects: Investigate how the program’s outcomes affect other areas or groups. These secondary impacts can be crucial for understanding the broader significance of the initiative.
By focusing on these aspects, one can effectively evaluate a program’s success and ensure that its benefits are not only realized but also sustained over time.
Developing Research Questions for Exams
Creating clear, focused research inquiries is a fundamental step in preparing for assessments. Well-constructed research inquiries guide the investigation process, ensuring that responses address key aspects of the topic. Crafting effective questions is crucial to exploring the depth of the subject matter, and allows for a structured approach to finding relevant information. The following steps outline how to develop research questions that are both insightful and practical for assessments.
Key Considerations for Crafting Research Inquiries
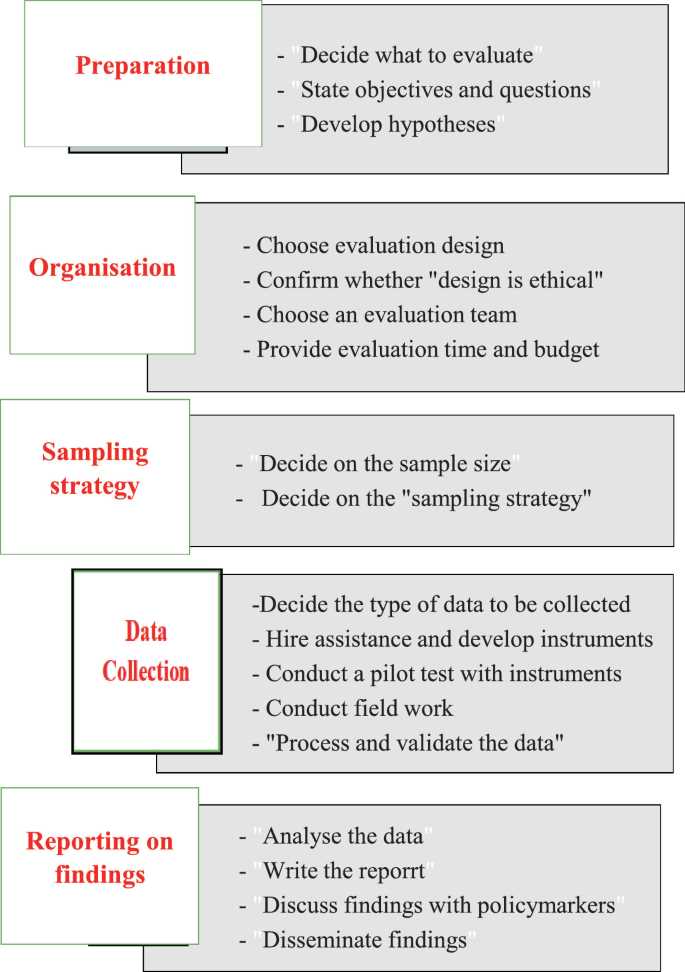
- Define the Scope: Determine the boundaries of your investigation. Clearly define what is to be explored, avoiding overly broad or vague topics.
- Be Specific: The question should target specific aspects of the subject, focusing on one central idea rather than multiple, unrelated concepts.
- Ensure Clarity: Avoid ambiguity in phrasing. The question should be straightforward and easy to understand to facilitate focused research.
- Establish Relevance: Ensure that the inquiry addresses key issues that are central to the subject at hand. The question should contribute to a deeper understanding of the topic.
Types of Research Inquiries
- Descriptive Questions: These seek to explain or describe a phenomenon, providing foundational knowledge and context.
- Analytical Questions: These investigate causes, effects, or relationships between factors, requiring a deeper analysis of the subject.
- Comparative Questions: These examine differences or similarities between concepts, methods, or outcomes, allowing for critical evaluation.
By developing well-thought-out research inquiries, you can ensure that your investigation stays on track, provides meaningful insights, and effectively addresses the core topics being assessed.
Types of Monitoring and Evaluation Tools
To assess the effectiveness and progress of a project, various instruments are used to gather, analyze, and interpret data. These tools help in tracking performance, understanding impacts, and providing evidence for decision-making. By selecting the right tools, stakeholders can ensure they have accurate information for evaluating outcomes and improving future initiatives.
Commonly Used Tools
- Surveys and Questionnaires: These tools collect data from participants, stakeholders, or beneficiaries, often used to measure satisfaction, opinions, or experiences.
- Focus Groups: Small group discussions that allow in-depth exploration of participants’ views on a particular topic or issue.
- Interviews: One-on-one conversations designed to gather detailed information from key stakeholders or experts in the field.
- Observation: Directly watching and recording behavior or conditions in the field to gather qualitative data.
- Case Studies: Detailed examinations of specific instances or outcomes, providing insights into the success or challenges of a project.
Comparison of Tools
Tool Purpose Advantages Challenges Surveys Gather large amounts of quantitative data Can collect data from many people, easy to analyze May not capture in-depth responses, risk of biased answers Focus Groups Gather qualitative insights from a small group In-depth responses, fosters discussion May not represent the larger population, group dynamics can affect results Interviews Collect detailed personal views or experiences Personalized data, allows for follow-up questions Time-consuming, limited sample size Observation Collect real-time data on behavior or conditions Provides authentic insights, captures actual behavior Observer bias, does not explain why behaviors occur Case Studies Provide in-depth analysis of a specific instance Rich, contextual insights, useful for understanding success or failure Not generalizable to all cases, time-intensive Each tool serves a unique purpose, and choosing the right one depends on the goals of the assessment and the type of information needed. Combining multiple tools often leads to a more comprehensive understanding of the situation, helping to inform better decision-making and future planning.
Challenges in Monitoring and Evaluation Exams

When assessing the effectiveness of a program or project, individuals often face several obstacles that can hinder their ability to effectively demonstrate their knowledge or understanding. These challenges can arise from various factors, such as unclear guidelines, complex concepts, or inadequate data. Addressing these issues is crucial to ensure accurate results and a deeper comprehension of the subject matter. The following outlines some of the common difficulties encountered during these assessments.
Common Difficulties in Assessments

- Ambiguous Guidelines: Unclear or poorly defined instructions can make it difficult for individuals to understand exactly what is expected of them, leading to confusion and incomplete responses.
- Complex Concepts: Certain theories or methodologies may be too intricate, requiring advanced knowledge or understanding that may not always be easily grasped by all participants.
- Inadequate Data: In some cases, the lack of comprehensive data or access to critical information can prevent individuals from providing well-supported responses or assessments.
- Time Constraints: Tight time limits can add pressure, leading to rushed answers that may lack depth or clarity, especially when tackling complex or multi-part questions.
- Subjectivity in Scoring: Without clear criteria, grading can become subjective, which may affect the fairness and consistency of the evaluation process.
Strategies to Overcome These Challenges
- Clarify Guidelines: Ensuring that instructions are detailed and precise can help eliminate confusion, allowing for more focused and accurate responses.
- Simplify Concepts: Breaking down complex theories or methodologies into digestible parts can make them more accessible, especially for those with less experience in the field.
- Ensure Sufficient Data: Providing access to comprehensive and relevant data beforehand can help individuals make informed decisions and develop well-supported arguments.
- Manage Time Effectively: Practice under time constraints and prioritizing questions can help improve time management, reducing the pressure on individuals during assessments.
- Use Objective Scoring: Establishing clear, standardized criteria for grading can help maintain fairness and consistency in the evaluation process.
By addressing these challenges, participants can better navigate assessments and demonstrate a deeper understanding of the subject, leading to more accurate and meaningful evaluations of their knowledge and skills.
Tips for Answering Evaluation Questions
Responding to assessments that focus on the effectiveness and impact of a program or initiative requires more than just recall of facts. It’s important to approach each prompt methodically and provide well-structured, evidence-based responses. The following strategies will help enhance your ability to provide clear, relevant, and insightful replies, demonstrating a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Key Strategies for Crafting Strong Responses
- Understand the Prompt: Carefully read each prompt to fully grasp what is being asked. Break down complex tasks into smaller components to ensure all parts are addressed.
- Provide Clear Structure: Organize your response logically. Begin with an introduction, followed by your main points, and conclude with a strong summary that ties everything together.
- Use Evidence: Support your statements with data, examples, or case studies. This will strengthen your argument and demonstrate a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Be Concise: Avoid unnecessary jargon or overly long explanations. Stick to the point while ensuring that your response covers all necessary aspects.
- Stay Objective: Provide a balanced view. If discussing the shortcomings of a program, also highlight any positive outcomes or strengths to present a well-rounded perspective.
Helpful Tips for Effective Responses

Tip Benefit Read Instructions Carefully Ensures you are responding to exactly what is being asked, avoiding unnecessary tangents. Stay Focused on Key Points Helps prevent your response from becoming too broad or off-topic, making your argument stronger. Include Data or Examples Supports your ideas with evidence, increasing credibility and demonstrating critical thinking. Review Your Response Allow time to check for clarity, grammar, and relevance, ensuring your answer is clear and well-presented. By following these strategies and tips, you can improve your ability to respond thoughtfully and comprehensively, effectively demonstrating your knowledge and understanding in assessments.
Preparing for Practical Monitoring Scenarios
When preparing for assessments involving real-world situations, it’s important to focus on understanding the key elements of program implementation and performance analysis. Practical scenarios test your ability to apply theoretical knowledge to real challenges. These exercises often require critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and the ability to make informed decisions based on available data. Preparing for such situations involves understanding the context, identifying key indicators, and knowing how to assess the effectiveness of different interventions.
Steps for Effective Preparation

- Understand the Context: Familiarize yourself with the specific environment in which the scenario takes place. Consider the objectives of the program and the challenges faced by stakeholders involved.
- Identify Key Metrics: Know the key performance indicators (KPIs) that are most relevant to the situation. These metrics will help you assess whether the desired outcomes are being achieved.
- Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Practice identifying potential challenges and thinking through solutions. Consider different strategies for improving performance and addressing issues in real time.
- Analyze Data Effectively: Learn how to interpret data quickly and accurately. Being able to draw insights from quantitative and qualitative information is crucial for making informed decisions.
- Scenario-Based Practice: Engage in practice scenarios that simulate real-world conditions. This helps you build confidence and improve your ability to respond to unexpected challenges during the actual assessment.
Techniques for Enhancing Decision-Making
- Use a Structured Approach: Follow a step-by-step method for analyzing the scenario. This could include identifying the problem, gathering relevant data, assessing options, and selecting the best course of action.
- Consider Stakeholder Perspectives: Understand the different viewpoints and needs of those involved in the program, as this will help you make more balanced and effective decisions.
- Be Adaptable: Be prepared to adjust your approach based on new information or changing circumstances. Flexibility is key when responding to dynamic situations.
By focusing on these key areas, you can develop a more comprehensive understanding of practical scenarios and improve your ability to address real-world challenges effectively. Whether it’s handling a crisis or optimizing program performance, being well-prepared is essential for success.
Structuring Your Responses in Evaluations
When addressing assessment prompts, it’s essential to present your thoughts in a clear, organized manner. A well-structured response not only conveys your understanding but also demonstrates your ability to apply concepts effectively. Whether responding to theoretical or practical inquiries, following a logical flow helps ensure your points are communicated concisely and persuasively. Structure is the key to making your responses impactful and aligned with the expectations of evaluators.
Key Elements of a Well-Structured Response
- Introduction: Start by briefly summarizing the question or problem at hand. This gives the reader a context for your response and sets the stage for your analysis.
- Thorough Analysis: Dive into the core of the issue. Provide clear explanations, support your points with evidence or examples, and consider the different dimensions of the topic. Ensure that each point you make logically follows from the previous one.
- Conclusion: Summarize your key findings and provide a clear conclusion. If appropriate, offer recommendations or next steps based on the analysis you’ve presented. Keep the conclusion concise but impactful.
Effective Techniques for Clarity and Precision
- Use Clear Language: Avoid jargon or overly complex terms that might confuse the reader. Use simple, direct language to explain your points.
- Provide Evidence: Where possible, support your arguments with data, examples, or theoretical frameworks. This strengthens your response and adds credibility to your points.
- Stay Focused: Ensure each paragraph serves a clear purpose and contributes to your overall argument. Avoid going off-topic or including unnecessary information.
- Be Concise: While it’s important to provide thorough explanations, avoid over-elaborating. Stick to the most relevant details and keep your responses concise yet informative.
By structuring your responses in a logical, clear, and evidence-backed manner, you improve both the quality and impact of your submissions. A well-organized answer not only demonstrates your understanding but also helps evaluators follow your reasoning more easily.
Reviewing Case Studies for Exam Success
Case studies are valuable tools for deepening your understanding of complex topics and preparing for assessments. By analyzing real-world scenarios, you can apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations, strengthening your problem-solving abilities. Reviewing case studies allows you to identify key issues, assess strategies, and understand the outcomes of different approaches. This process enhances critical thinking, helping you to be more prepared for tackling similar scenarios in your assessments.
Why Case Studies Are Crucial for Preparation
Case studies provide insight into how theoretical concepts are applied in real-life situations. They offer a practical context for learning, demonstrating how concepts function outside of the classroom. Understanding the context, challenges, and solutions in these studies enables you to think critically about how to approach similar questions in an assessment. The detailed analysis helps to bridge the gap between theory and practice, making your responses more grounded and relevant.
Key Steps to Review Case Studies Effectively
- Identify the Core Problem: Begin by understanding the central issue of the case study. What is the main challenge or question being addressed? Clarifying this helps you focus your analysis on the most critical aspects.
- Analyze the Approach: Pay attention to the methods used to tackle the problem. How were different solutions explored? What strategies were employed, and how effective were they?
- Evaluate the Outcome: Assess the success or failure of the solutions. Were the results in line with the goals? Understanding what worked and what didn’t helps you learn from both positive and negative outcomes.
- Draw Connections: Relate the case study to concepts you’ve learned. How do the findings align with theories, frameworks, or models discussed in your studies? This reinforces the practical application of theoretical knowledge.
- Practice Answering Based on Case Studies: After reviewing, practice responding to questions based on the case. This will help you improve your ability to present your thoughts clearly and concisely during the assessment.
Regularly reviewing case studies helps you think critically and apply your knowledge more effectively. The more familiar you are with different cases, the more prepared you’ll be for the variety of scenarios you may encounter in assessments.
Understanding Qualitative and Quantitative Methods
Different research approaches offer unique insights into various problems, each suited to different types of questions and objectives. Some methods focus on gathering numerical data to identify trends and relationships, while others focus on in-depth exploration of experiences and perspectives. By combining both approaches, researchers can gain a well-rounded understanding of the subject matter, enhancing the robustness of their findings.
Qualitative Methods
Qualitative techniques are designed to explore complex phenomena through detailed observation, interviews, and analysis of text-based or visual data. This approach is used to gather non-numerical data, emphasizing the depth of understanding and the nuances of human experience. It’s particularly useful in contexts where the goal is to explore perceptions, motivations, behaviors, or social contexts in greater detail. Common methods include:
- Interviews: Structured or unstructured conversations that allow for deep insights into participants’ thoughts and experiences.
- Focus Groups: Discussions among a group of people guided by a facilitator to explore diverse opinions or reactions.
- Case Studies: In-depth examination of a single instance or event to explore its complexities and outcomes.
Quantitative Methods
In contrast, quantitative approaches focus on gathering numerical data that can be analyzed statistically. These methods help identify patterns, correlations, and generalizable trends across larger populations. Quantitative research is useful when the goal is to measure the extent of a phenomenon or test hypotheses based on predefined variables. Common techniques in this category include:
- Surveys: Questionnaires designed to collect standardized data from large numbers of respondents.
- Experiments: Controlled studies designed to test the effects of specific variables on an outcome.
- Statistical Analysis: The use of various mathematical tools to analyze numerical data, identify patterns, and test hypotheses.
By understanding and applying both qualitative and quantitative methods, researchers can draw on the strengths of each to produce comprehensive findings that address both the “what” and the “why” of the research question.
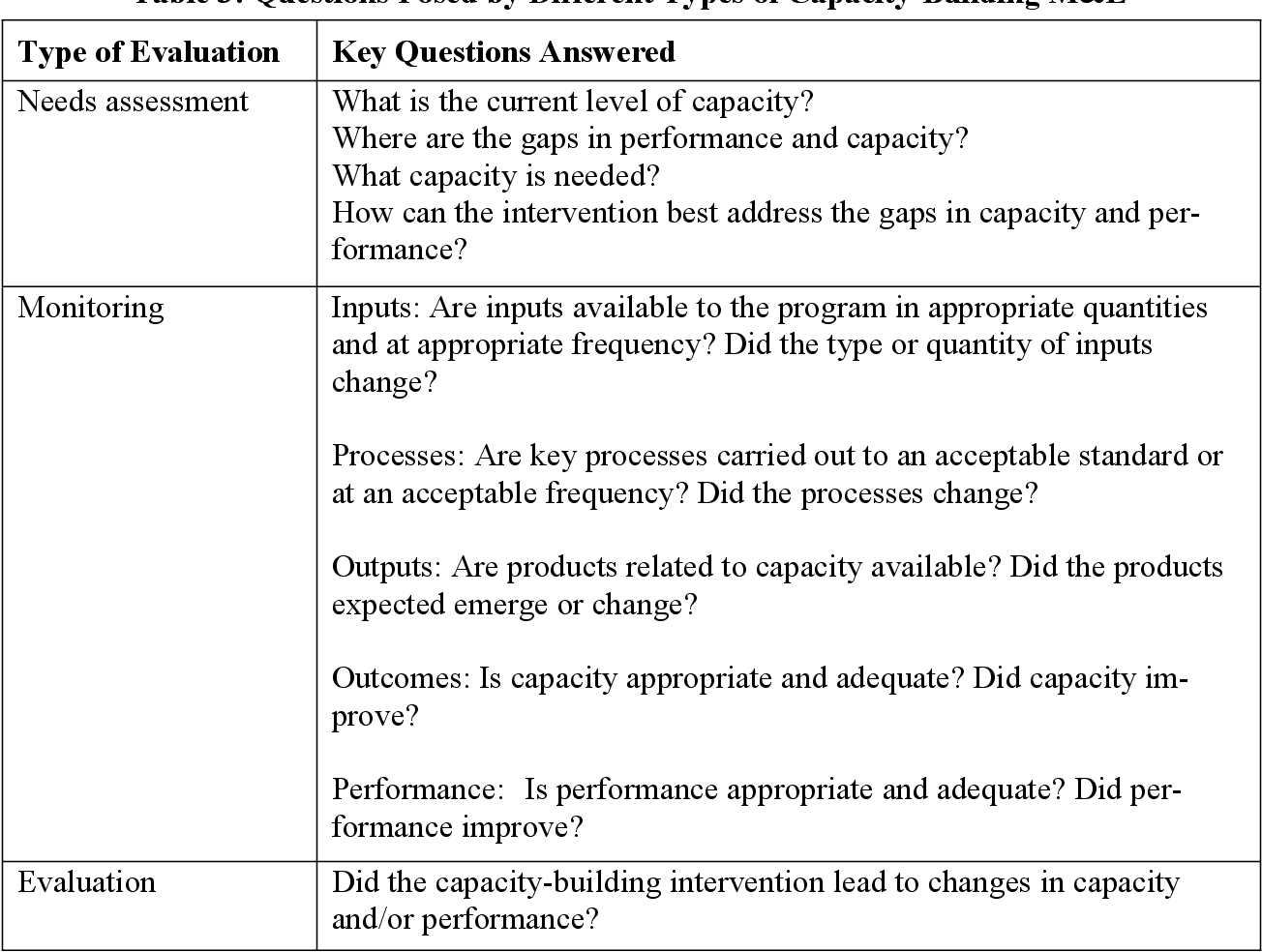
Important Theories in Evaluation Practices

Several foundational theories have shaped the way we assess and interpret programs, projects, and policies. These frameworks guide how practitioners approach the process of gathering data, measuring success, and determining impact. By understanding these theories, one can gain a deeper understanding of the methods used to assess effectiveness, efficiency, and relevance across various domains.
The following table outlines some of the most influential theories that inform the approaches used in the field:
Theory Description Key Focus Utilization-Focused Theory Focuses on using evaluation results to improve decision-making and enhance program effectiveness. This theory emphasizes stakeholder engagement and practical application. Practicality, Stakeholder Engagement Goal-Based Theory Assesses the success of a program based on the degree to which it achieves pre-established objectives. It provides a clear framework for defining measurable goals. Goal Achievement, Measurability Participatory Theory Engages program stakeholders in the evaluation process to ensure that the evaluation reflects their perspectives and needs. It values inclusion and collaboration. Stakeholder Participation, Collaboration Realist Theory Focuses on understanding how programs work in particular contexts. It seeks to explore the mechanisms and conditions that produce desired outcomes. Context, Mechanisms, Outcomes These theories serve as important guidelines for designing effective assessments, ensuring that the processes not only generate meaningful data but also contribute to the broader goals of improving practices, policies, and strategies.
Exam Strategies for Monitoring Professionals
Achieving success in assessments requires more than just knowledge of concepts and theories. It involves strategic preparation, time management, and the ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations. Professionals working in assessment-related fields must adopt effective strategies to ensure they can showcase their skills and expertise during an evaluation process.
The following list outlines several effective strategies that can enhance your performance in these assessments:
- Understand Key Concepts: Review essential ideas related to program assessment, success metrics, and impact measurement. Be prepared to explain these concepts clearly and concisely.
- Familiarize Yourself with Common Frameworks: Knowing various frameworks and methodologies allows you to approach problems from different angles, giving you an edge when addressing scenarios or case studies.
- Practice with Sample Scenarios: Work through mock exercises that mimic real-world situations. This will help you become more comfortable applying theoretical knowledge in practical settings.
- Time Management: Allocate sufficient time to each section of the assessment. Make sure to manage your time wisely, so you can thoroughly address each part of the task.
- Focus on Clarity: When presenting your thoughts, ensure clarity in your responses. Structure your answers logically, starting with a clear statement followed by supporting arguments or evidence.
- Reflect on Past Experiences: Relate your own experiences with programs or projects when responding to questions. Drawing from practical examples can help reinforce your understanding and demonstrate application.
- Stay Updated: Keep up to date with the latest trends, tools, and techniques in the field of program assessment. This knowledge can help you provide modern, relevant insights during the assessment.
By combining these strategies with a strong knowledge base, you can approach your next assessment with confidence and demonstrate your expertise in the field effectively.
Final Thoughts on Exam Preparation
Preparing for assessments in the field of program evaluation and impact analysis requires a strategic approach, combining theoretical knowledge with practical application. Success in these types of evaluations comes from mastering core concepts, understanding different methodologies, and honing problem-solving skills that can be applied to real-world scenarios. The final stage of preparation is about reinforcing your knowledge, fine-tuning your strategies, and staying confident in your ability to showcase your skills during the evaluation process.
Here are some essential elements to focus on as you finalize your preparation:
- Review Core Concepts: Ensure you have a solid understanding of the fundamental principles of program assessment, including different types of frameworks and metrics for measuring success.
- Practice Problem Solving: Test your ability to solve problems and work through case studies, applying theories to practical situations. This will help you think critically and act decisively during the evaluation.
- Time Management: Use practice sessions to improve your time management skills. The ability to allocate time effectively to each task is crucial to demonstrating your depth of understanding without feeling rushed.
- Use Real-World Examples: Draw upon personal experience or case studies you’ve encountered to demonstrate how you can apply theoretical knowledge to practical challenges.
- Stay Calm and Focused: Stress and anxiety can detract from your performance. Approaching the evaluation with calmness, confidence, and clarity will help you think clearly and articulate your responses effectively.
In conclusion, preparation is the key to success. Focus on refining your knowledge, practicing real-world applications, and developing strategies to address any challenges that may arise. With the right preparation, you’ll be ready to demonstrate your expertise and perform confidently during the assessment.