
Preparing for a comprehensive evaluation in the field of medical imaging requires understanding both theoretical knowledge and practical applications. These assessments test not only your grasp of core concepts but also your ability to apply them in real-life scenarios. The process can seem challenging, but with the right approach, you can confidently tackle any task presented during the evaluation.
In this section, we will explore a variety of essential topics that are frequently covered in evaluations, ranging from the fundamental principles to more advanced techniques. By reviewing common types of tasks and focusing on crucial subject areas, you can enhance your readiness and improve your overall performance. Focusing on clarity and detail will help ensure success when facing these assessments.
Understanding key principles, such as imaging technology, human anatomy, and diagnostic procedures, is critical. Practice and familiarity with common formats will further enable you to quickly identify the correct approaches during any type of evaluation.
Radiography Exam Questions and Answers
When preparing for a professional assessment in the field of medical imaging, it is essential to understand the key topics that are commonly evaluated. Knowing what types of inquiries to expect can significantly enhance your preparation. This section outlines the most frequently covered subjects and provides examples to help you focus your study efforts effectively.
Commonly Tested Topics
- Imaging Techniques: Understanding various imaging methods, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI, is crucial.
- Equipment Operation: Familiarity with how to operate imaging devices and troubleshooting common issues.
- Human Anatomy: Recognizing the structures and systems that are most relevant to diagnostic imaging.
- Safety Protocols: Knowing the safety measures related to exposure and equipment handling.
Sample Tasks to Practice

- Matching: Match the imaging method with its appropriate use case.
- Multiple Choice: Choose the correct answer based on specific technical scenarios.
- Image Interpretation: Analyze an image to identify key features and abnormalities.
- True/False: Determine the accuracy of certain statements related to imaging procedures.
Familiarity with these topics will ensure you’re well-prepared and confident when it’s time to face the assessment. Practicing with these common formats will not only reinforce your knowledge but also help you manage time effectively during the test.
Key Concepts in Radiography Testing
Understanding the fundamental principles behind diagnostic imaging is essential for any professional in this field. Mastery of core concepts allows for accurate assessments and safe practice. The following topics are foundational to both theoretical knowledge and practical application in medical imaging procedures.
Essential Principles
- Image Formation: Knowledge of how images are created using different technologies and the factors that influence image quality.
- Contrast and Density: Understanding how variations in tissue density affect the visibility of anatomical structures.
- Exposure Factors: The role of radiation dose, timing, and intensity in producing clear, accurate images.
- Patient Positioning: Correctly positioning patients to capture the most accurate diagnostic images.
Technological Components
- Imaging Devices: Familiarity with the operation of various diagnostic equipment, including X-ray machines and CT scanners.
- Digital Imaging: The transition from traditional film-based methods to digital techniques and the advantages they offer.
- Quality Control: Regular checks and calibrations to ensure equipment produces optimal results.
By mastering these core concepts, you can approach your tasks with confidence, knowing that you understand the science and technology behind every procedure.
Common Questions in Radiography Exams
When preparing for a professional evaluation in the field of medical imaging, it is important to recognize the types of tasks that frequently appear. These assessments often cover a wide range of topics that require both technical knowledge and practical application. By familiarizing yourself with the common topics and formats, you can better anticipate what will be asked and how to approach each challenge effectively.
Typical Topics Covered
- Imaging Procedures: Identifying the correct technique for various diagnostic scenarios.
- Equipment Handling: Understanding the setup, use, and maintenance of imaging tools.
- Safety Guidelines: Knowing the best practices for protecting both patients and healthcare professionals.
- Image Interpretation: Analyzing images to detect anomalies and assess patient conditions.
Format of the Tasks
- Multiple Choice: Select the correct response based on theoretical knowledge or practical application.
- True or False: Assessing the validity of given statements based on technical principles.
- Practical Scenarios: Analyzing case studies or situations to choose the most appropriate solution.
These areas are commonly tested because they reflect the most important aspects of the profession. By preparing for these types of inquiries, you can feel more confident and capable during the evaluation process.
Understanding Radiographic Imaging Techniques
In the field of medical diagnostics, mastering various imaging methods is crucial for accurate assessment and patient care. These techniques form the foundation of modern healthcare, allowing professionals to visualize internal structures and detect abnormalities. A clear understanding of how each method works, its applications, and limitations is essential for making informed decisions.
Common Imaging Methods
- X-ray: The most widely used technique, particularly effective for detecting bone fractures and certain types of infections.
- CT Scan: A more advanced method that uses multiple X-ray images to create cross-sectional views of the body, useful for detecting tumors and internal bleeding.
- MRI: Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of soft tissues, often employed for brain, spinal cord, and muscle evaluations.
- Ultrasound: Utilizes sound waves to produce images, commonly used for monitoring pregnancy or examining organs like the heart and liver.
Principles Behind Image Creation
- Radiation Use: Understanding how different levels and types of radiation interact with tissues to produce varying image qualities.
- Image Resolution: Factors such as exposure time, sensitivity, and contrast play a role in the clarity and detail of the final image.
- Patient Positioning: Proper alignment of the patient is vital to ensure the most accurate and informative images are captured.
Each imaging technique offers distinct advantages and is selected based on the specific diagnostic needs. By understanding the principles behind these methods, healthcare professionals can make more effective decisions and enhance the quality of care provided.
Types of Radiography Exam Questions
Assessments in the field of medical imaging often present a variety of task types designed to evaluate both theoretical knowledge and practical application. These tasks may test different levels of understanding, from basic principles to more complex diagnostic scenarios. Being familiar with the common formats used in these evaluations can help professionals prepare more effectively and approach each challenge with confidence.
Common Task Formats
- Multiple Choice: These tasks offer several possible answers, with only one correct choice. They are designed to test specific knowledge and comprehension of key concepts.
- True or False: These items assess the understanding of factual statements, requiring individuals to determine if the information is accurate or not.
- Matching: Participants match terms with definitions or images with descriptions. This format evaluates the ability to associate related concepts.
- Case Studies: Real-life scenarios are presented, and participants must apply their knowledge to diagnose or solve the issue described.
Sample Task Comparison
| Task Type | Description | Skills Tested |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Choice | Choose the correct answer from a set of options. | Knowledge recall, decision-making |
| True/False | Determine whether a statement is correct. | Factual accuracy, understanding |
| Matching | Link terms or images to their correct counterparts. | Concept association, recognition |
| Case Study | Analyze a scenario and provide a solution or diagnosis. | Critical thinking, problem-solving |
By understanding the different types of tasks, professionals can better prepare for evaluations, focusing on the specific skills each format is designed to assess.
How to Prepare for Radiography Exams
Preparation for assessments in the field of medical imaging requires a combination of thorough study, practical experience, and strategic planning. To ensure success, it is important to focus on both theoretical knowledge and hands-on skills. This section will outline key steps and tips to help you get ready for your upcoming evaluation, enabling you to approach it with confidence and clarity.
Steps to Effective Preparation
- Review Core Concepts: Go over the fundamental principles, such as imaging techniques, safety protocols, and anatomy relevant to diagnostic procedures.
- Practice with Sample Scenarios: Use practice materials to familiarize yourself with the types of tasks commonly presented in evaluations.
- Study with Peers: Collaborative study groups can help reinforce concepts and offer diverse perspectives on difficult topics.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Identify areas where you may need improvement and dedicate extra time to mastering those concepts.
Study Schedule and Tips
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Start Early | Give yourself enough time to review all key topics, starting well in advance of the assessment date. |
| Set Realistic Goals | Break your study sessions into manageable chunks and focus on one topic at a time to avoid feeling overwhelmed. |
| Use Multiple Resources | Leverage textbooks, online materials, and practical exercises to gain a well-rounded understanding of the subject. |
| Simulate Real Conditions | Take timed practice tests to get used to the pressure and pace of the actual evaluation. |
By following a structured approach and staying consistent with your study routine, you can improve your readiness and feel confident when it’s time to face your evaluation.
Important Radiographic Terminology to Know
In the field of diagnostic imaging, understanding key terminology is essential for clear communication and accurate interpretation of information. Professionals must be familiar with specific terms related to imaging techniques, equipment, and patient care in order to ensure precise diagnoses and effective treatment planning. Below are some of the most important terms you need to know for success in this field.
Key Terms Related to Imaging
- Contrast: A technique used to enhance the visibility of structures or tissues by altering their appearance on an image, often through the use of contrast agents.
- Resolution: The level of detail visible in an image, with higher resolution leading to clearer and more defined visuals.
- Exposure: The amount of radiation applied to create an image, which must be carefully controlled to ensure safety and image quality.
- Field of View: The area captured in the image, which can be adjusted based on the diagnostic requirements.
Terms Related to Patient Care
- Positioning: The placement of the patient to ensure the optimal angle and alignment for imaging purposes.
- Radiation Dose: The amount of radiation the patient is exposed to during imaging procedures, which must be minimized to reduce potential risks.
- Lead Shielding: A protective method used to reduce radiation exposure to non-target areas of the body.
- View: The specific angle or orientation from which an image is captured, such as anterior-posterior (AP) or lateral.
By familiarizing yourself with these essential terms, you can better navigate the technical aspects of imaging procedures, improving both the quality of your work and your ability to communicate effectively with colleagues and patients.
Understanding X-ray Physics for Exams
Mastering the fundamental principles of X-ray technology is essential for anyone preparing for an assessment in the field of medical imaging. A solid understanding of the physics behind this imaging modality enables professionals to perform procedures effectively and interpret results accurately. This section will provide an overview of key concepts and important factors that play a role in the generation and use of X-rays.
Basic Concepts in X-ray Physics
- Electron Interaction: X-rays are produced when high-energy electrons collide with a target material, typically tungsten. This interaction generates both X-rays and heat, which must be managed carefully to avoid equipment damage.
- Radiation Emission: When electrons hit the target, they cause the emission of X-rays. These X-rays travel through the body and are captured on an imaging receptor, creating an image of internal structures.
- Energy and Wavelength: The energy of the X-rays is determined by the acceleration of electrons, which affects the wavelength and penetration power. Higher energy X-rays have shorter wavelengths and can penetrate more dense tissues.
Key Factors in Image Quality
- Exposure Time: The duration the X-ray tube is active affects image clarity. Too much exposure can lead to overexposure, while insufficient exposure may result in unclear images.
- Tube Voltage: The potential difference between the cathode and anode controls the energy of the X-rays. Higher voltage results in more penetrating rays, which are ideal for dense structures like bone.
- Image Contrast: Contrast is influenced by the difference in X-ray absorption between various tissues. Adjusting parameters like exposure time and tube voltage can help achieve the right contrast for diagnostic clarity.
Understanding these concepts is crucial for anyone looking to demonstrate expertise in X-ray technology. By grasping the physical principles behind the process, practitioners can optimize their techniques and produce the highest quality images possible.
Common Mistakes in Radiography Exams
When preparing for assessments in the field of medical imaging, it’s important to be aware of common errors that can hinder your performance. Mistakes during these evaluations often stem from misunderstandings, lack of preparation, or not fully grasping key concepts. Identifying these pitfalls ahead of time can help you avoid them and improve your chances of success.
Technical Errors
- Incorrect Positioning: One of the most frequent mistakes is improper patient positioning, which can lead to unclear or distorted images. Ensuring the correct alignment is critical for accurate diagnostic results.
- Improper Exposure Settings: Using the wrong exposure time or voltage can result in underexposure or overexposure, both of which can affect the clarity and diagnostic value of the images.
- Failure to Adjust for Body Size: Not accounting for the patient’s body size and density can lead to incorrect exposure levels, requiring adjustments in technique to obtain optimal images.
Conceptual Mistakes

- Lack of Understanding of Anatomy: A fundamental knowledge of anatomy is essential for accurately interpreting images. Misidentifying body structures can lead to incorrect conclusions and diagnoses.
- Ignoring Radiation Safety: Not adhering to proper radiation protection protocols can result in unnecessary exposure to both patients and operators. It’s important to always use shielding and apply the ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle.
- Misinterpreting Image Quality: Failing to recognize the importance of image resolution, contrast, and sharpness can lead to overlooking important details that are essential for diagnosis.
By recognizing these common mistakes and taking proactive steps to correct them, you can improve your skills and increase your chances of success in practical assessments. Understanding the technical and conceptual aspects of your work will ultimately lead to better outcomes and a more confident performance.
Effective Study Tips for Radiography Exams

Success in the field of medical imaging relies not only on hands-on experience but also on a strong understanding of theoretical knowledge. Preparing for assessments in this area requires effective study strategies that allow you to retain complex concepts and apply them in practice. Below are some useful tips to help you prepare more efficiently and boost your confidence.
Organize Your Study Routine
- Create a Study Schedule: Break down your study material into manageable sections and allocate specific times to each topic. A structured schedule helps ensure that you cover all necessary areas without feeling overwhelmed.
- Prioritize Key Concepts: Focus on understanding fundamental principles that are often tested. Spend extra time on areas that you find challenging to master, ensuring a comprehensive grasp of the material.
- Take Regular Breaks: Studying for long hours without breaks can lead to fatigue and reduced retention. Schedule short breaks every 30 to 45 minutes to keep your mind fresh and focused.
Use a Variety of Study Resources
- Textbooks and Lecture Notes: Begin with your textbooks and notes from class as primary sources. These materials are typically designed to cover the key content you’ll encounter.
- Practice Scenarios: Work through sample scenarios or practical exercises that simulate real-world situations. This helps reinforce theoretical knowledge and improve problem-solving skills.
- Online Resources: Take advantage of online platforms, such as study guides, forums, and videos, to clarify difficult topics. Many resources provide alternative explanations that may resonate more effectively with you.
Active Study Techniques

- Teach What You Learn: Teaching others is one of the best ways to solidify your own understanding. Explain complex concepts to a peer or even to yourself to reinforce your knowledge.
- Practice with Flashcards: Flashcards are an excellent tool for memorizing key terms, definitions, and procedures. Regularly review them to reinforce important points.
- Group Study: Studying with peers can be beneficial as it provides an opportunity to discuss difficult concepts and learn from each other’s strengths.
By adopting these study techniques, you can build a solid foundation in both theoretical and practical aspects of your profession, ensuring that you’re well-prepared for any assessment that comes your way.
Radiography Equipment and Exam Questions
In the field of medical imaging, mastering the various tools used for capturing images is essential for success. Understanding how these devices function, as well as their specific features, is critical not only for practical use but also for theoretical assessments. Knowledge of equipment will help you answer related inquiries and apply your skills effectively in clinical settings.
Key Imaging Devices
- X-ray Machines: These machines are central to capturing images of the internal structures of the body. Familiarity with their components, such as the tube, control panels, and detectors, is crucial for both operation and theory-based assessments.
- CT Scanners: Computed tomography (CT) machines provide cross-sectional images. Knowing their capabilities, such as slice thickness, rotation time, and reconstruction methods, is important for answering related theoretical questions.
- Ultrasound Devices: These machines use sound waves to produce images of organs and tissues. While not always central to every inquiry, understanding their principles of operation and safety protocols is useful in a range of tests.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI devices use magnetic fields to create detailed images of soft tissues. Understanding how to operate an MRI machine, as well as its limitations and safety considerations, is often included in practical knowledge assessments.
Understanding Image Quality
- Resolution: The sharpness and clarity of an image depend heavily on the resolution settings of the equipment. Knowing how to adjust these settings for optimal quality is a key area for assessment.
- Contrast: This refers to the difference between light and dark areas in an image. Understanding how contrast affects the final image and how to adjust it based on the body part being imaged is an important concept.
- Exposure Time: Adjusting exposure time is vital to prevent overexposure or underexposure of the image. The ability to adjust this setting based on patient characteristics is frequently assessed.
Having a strong understanding of the equipment you work with, along with the theoretical principles that govern their operation, will help you navigate both practical skills and theoretical assessments with confidence. Mastery of these devices ensures that you can effectively respond to inquiries related to imaging procedures and safety standards.
How to Tackle Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple-choice inquiries are a common format used to assess knowledge in many fields. These types of inquiries present a set of possible responses, requiring the test-taker to select the most accurate one. To excel in this format, it’s essential to have a strategic approach, allowing you to effectively navigate through the options and identify the correct answer.
Preparation Strategies
- Know the Material Thoroughly: Familiarity with the key concepts and terminology is crucial. When you’re well-prepared, you’ll recognize key phrases in the options and quickly identify the right response.
- Understand the Question Format: Pay attention to the structure of the inquiry. Many tests use similar phrasing, so practicing with sample exercises helps familiarize you with typical patterns.
- Eliminate Incorrect Choices: Start by removing the obviously wrong options. This increases your chances of selecting the correct one, even if you’re unsure.
Approaching the Questions
- Read All Options Carefully: Even if the first option seems correct, take the time to review all of the possible answers. Sometimes, a better option may be further down the list.
- Look for Keywords: Words like “always,” “never,” “most likely,” or “least” can provide hints about the accuracy of the options. Be cautious with extreme terms as they are often incorrect.
- Trust Your First Instinct: Often, your initial reaction is correct. If you’re unsure, go with your gut feeling, but only after eliminating options that you know are wrong.
By employing these techniques, you can approach each multiple-choice task with confidence. Being organized, prepared, and methodical in your approach ensures that you make the most of your knowledge and tackle these inquiries effectively.
Understanding Radiographic Anatomy in Exams
When preparing for assessments in the field of medical imaging, a solid grasp of human anatomy is essential. A thorough understanding of the body’s structure helps you identify key features and interpret images accurately. It also plays a vital role in answering theoretical inquiries related to image interpretation, positioning, and the anatomy involved in the imaging process.
Key Anatomical Structures to Know
- Bone Structure: Familiarity with the bones’ shapes, sizes, and locations is crucial for recognizing fractures, misalignments, and other abnormalities in images.
- Soft Tissues: The ability to distinguish between various soft tissues, including muscles, organs, and fat, is important for assessing overall image quality and detecting any issues.
- Organs: Understanding the location and orientation of vital organs such as the heart, lungs, and digestive system is necessary for accurate imaging, as well as interpreting the images correctly.
Application of Anatomical Knowledge
- Image Interpretation: Knowing where specific anatomical structures should be positioned helps in recognizing abnormalities and distinguishing between normal variations.
- Positioning Techniques: Correct positioning of the patient relies on knowledge of how the body is structured and how various angles impact the resulting image.
- Pathological Indicators: Understanding normal anatomy allows you to identify deviations and assess potential pathological conditions based on image features.
Mastering anatomical knowledge not only aids in practical application but also enhances your ability to perform well in assessments related to medical imaging. With a clear understanding of the body’s structure, you can accurately answer questions and interpret diagnostic images with confidence.
Practical Radiography Exam Strategies
When preparing for hands-on assessments in the field of medical imaging, a strategic approach can significantly improve your performance. These assessments often test not only your theoretical knowledge but also your ability to apply practical skills in real-life scenarios. To succeed, it is essential to be well-prepared, stay focused, and use effective techniques during the practical portion of the evaluation.
One key strategy is to ensure you are comfortable with the equipment and techniques commonly used in imaging. Understanding the functionality of each device and the proper positioning of patients can save valuable time during the assessment. Equally important is maintaining a calm and methodical approach, as working under pressure can lead to mistakes. Familiarizing yourself with the process beforehand, whether through practice sessions or simulation exercises, will help you feel more confident during the actual task.
Another important consideration is time management. Knowing how long each step in the process should take allows you to avoid rushing through critical actions. Practice creating a routine that incorporates all necessary steps efficiently, from patient preparation to image capture and processing. This can help you complete the task thoroughly and accurately without unnecessary delays.
Finally, remember that attention to detail is crucial. Double-checking your work, such as ensuring proper exposure settings, alignment, and image quality, can make a big difference in your results. Always take a moment to review before finalizing the process to ensure the highest level of accuracy in your work.
Time Management During Radiography Exams
Effective time management is a critical skill when navigating through practical assessments in the medical imaging field. During evaluations, you are often required to perform tasks within a limited time frame while maintaining accuracy and precision. A well-organized approach can help you balance speed with quality, ensuring you complete each task efficiently without compromising performance.
One of the first steps in managing your time effectively is to familiarize yourself with the structure and requirements of the assessment. Knowing the key stages of each procedure and how long they should take allows you to plan ahead and avoid unnecessary delays. Create a mental checklist or routine that helps you stay on track from start to finish, ensuring no steps are skipped or rushed.
Prioritize Tasks
Start by prioritizing the most important steps. For example, patient positioning and equipment calibration are crucial and should be handled first to ensure the quality of the images. Afterward, focus on less time-sensitive tasks such as adjusting exposure settings or processing images. Understanding which actions require immediate attention and which can be completed with less urgency will help you allocate your time wisely.
Practice Under Time Constraints

One of the best ways to improve time management is through regular practice under timed conditions. Simulating real assessment scenarios can help you become accustomed to the pressure and develop a sense of how long each task should take. The more familiar you are with the process, the more confident and efficient you will become during the actual evaluation.
By integrating these strategies, you can optimize your time, reduce stress, and ensure that you meet all the necessary requirements within the allotted time frame.
Radiography Exam Question Formats Explained

Understanding the different types of queries that might appear in assessments is crucial for effective preparation. These assessments often consist of various formats, each designed to test different aspects of knowledge, skills, and reasoning. Knowing the structure of each type of inquiry can help you approach them with confidence and improve your chances of success.
There are several common types of inquiries that candidates can expect. These include multiple-choice, true/false, short-answer, and practical application-based tasks. Each format requires a specific approach to ensure you address the question appropriately and provide the most accurate response possible. Understanding these distinctions can significantly enhance your ability to perform well under assessment conditions.
Multiple Choice Inquiries
Multiple-choice queries are common in these assessments, as they test both recall and recognition. They consist of a question followed by several possible answers, with only one correct option. To tackle these effectively, read each option carefully and eliminate the obviously incorrect ones. Narrowing down your choices increases your chances of selecting the correct answer, even when uncertain.
Practical Application Scenarios
Practical application questions require you to apply theoretical knowledge to real-life situations. These types of queries assess your ability to think critically and use your skills in a clinical environment. Focus on understanding core principles and procedures as they relate to real-world scenarios, and practice applying them in a controlled setting to sharpen your problem-solving skills.
By familiarizing yourself with these various formats, you can prepare more effectively and ensure you are ready for any type of inquiry that may arise during the assessment.
How to Interpret Radiographic Images
Interpreting diagnostic images is a critical skill that requires both technical knowledge and a keen eye for detail. Being able to analyze these images effectively helps in diagnosing conditions and understanding the underlying anatomy. This process involves identifying key features, recognizing abnormalities, and understanding how different tissues and structures appear on the image.
To interpret images accurately, one must develop a systematic approach. This includes knowing how to read images from various angles, understanding the different densities of tissues, and identifying any anomalies that might indicate a pathological condition. Familiarity with the normal appearance of anatomical structures is essential for spotting deviations that may suggest an issue.
Identifying Key Structures
The first step in image interpretation is to recognize the basic anatomical structures. Each image is a representation of body parts such as bones, soft tissues, and organs. By knowing how these structures should look, it becomes easier to spot irregularities. For example, bones should appear white or light, while soft tissues will usually be darker.
Recognizing Abnormalities
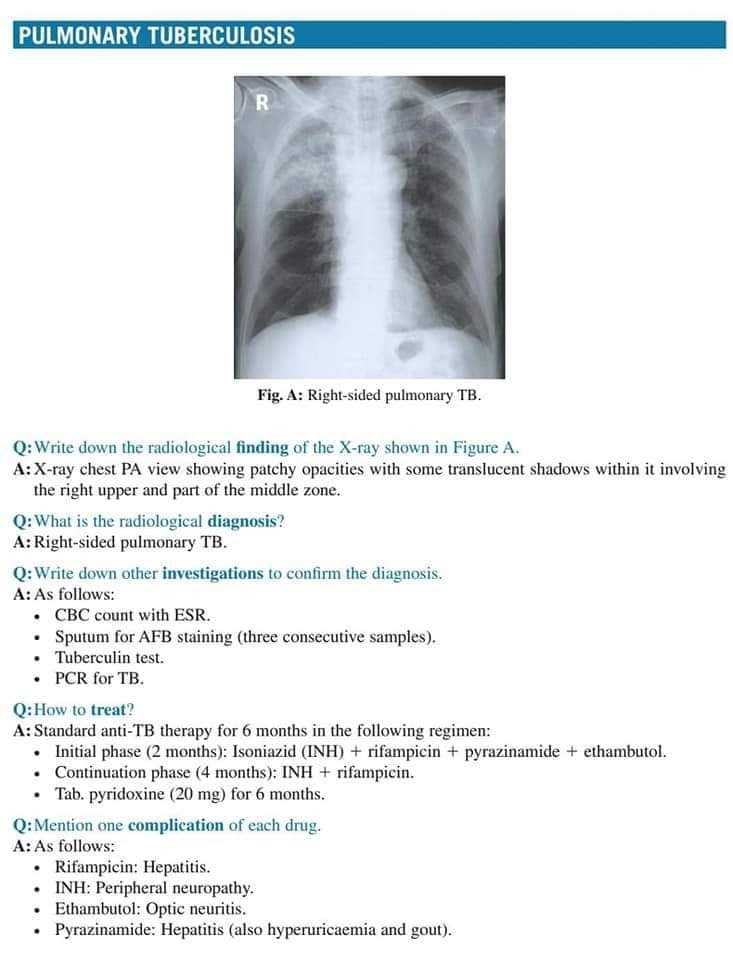
Once the normal structures are identified, the next step is to spot abnormalities. Look for anything that seems out of place, such as unusual shadows, distortions, or unexplained dark or light areas. These can indicate fractures, infections, tumors, or other medical conditions that require further attention.
With consistent practice and a methodical approach, you can improve your ability to interpret these images, ensuring more accurate assessments and better patient care.
Post-Exam Tips for Radiography Students
After completing an assessment, it’s essential to reflect on the experience and implement strategies for continued improvement. The period following an evaluation is a great opportunity to analyze performance, consolidate learning, and focus on areas that may need more attention. This time can be used effectively to enhance future preparation and avoid making the same mistakes again.
Take time to review the material covered, seek feedback, and apply the insights gained to refine your approach. Understanding your strengths and weaknesses allows you to tailor your study methods and develop a more efficient learning routine for future challenges.
Reviewing Performance
After any assessment, it’s helpful to go over the material, especially areas where you felt less confident. Understanding what went well and what didn’t can help you avoid similar challenges in the future. A review should focus on:
- Areas that were challenging or confusing during the assessment
- Questions that seemed tricky or were answered incorrectly
- Techniques that helped improve your performance
Using Feedback to Improve
Feedback from instructors or peers provides valuable insight into your strengths and areas for improvement. Make sure to take notes on constructive criticism and incorporate it into your study plan. The feedback process is an essential tool for growth, as it helps identify gaps in understanding and refine your approach to similar tasks in the future.
Staying Calm and Motivated
Stress and anxiety are natural after an intense period of focus. It’s important to rest and recharge, so that you remain motivated and prepared for the next phase of your learning journey. A balanced routine that includes adequate sleep, exercise, and relaxation will keep you mentally sharp for the next steps in your education.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Reflect on performance | Analyze areas of difficulty and success to improve next time. |
| Review feedback | Use instructor and peer feedback to enhance your knowledge and approach. |
| Take care of yourself | Rest and recharge to maintain motivation and focus. |