
Landing a top-tier position in IT requires more than just technical expertise; it demands an understanding of the skills, experience, and problem-solving abilities needed for complex tasks. A professional looking to step into a leadership role in the field must be ready to demonstrate their qualifications and aptitude for handling advanced challenges.
The selection process for such positions often involves a series of in-depth discussions aimed at evaluating the candidate’s knowledge across various technical domains. Employers seek individuals who can not only solve issues but also manage operations, ensure smooth workflow, and innovate within fast-paced environments.
In this guide, we’ll explore the types of topics you can expect, offering practical examples and tips for success. Whether it’s managing infrastructure, troubleshooting, or understanding cutting-edge technology, preparing for these types of discussions will put you in a stronger position to succeed.
Senior Systems Administrator Interview Questions and Answers
In a high-level IT role, professionals are expected to demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of technology, problem-solving abilities, and leadership skills. During the selection process, candidates are often presented with scenarios that test their ability to manage complex systems, ensure security, and troubleshoot effectively under pressure. The ability to address real-world challenges is key to impressing interviewers and securing the position.
Common Topics to Prepare For
Understanding what types of topics are typically covered can help candidates prepare thoroughly. Below are some common areas that employers focus on:
- Network management and troubleshooting
- Infrastructure design and deployment
- Security protocols and risk management
- Server configurations and virtual environments
- Disaster recovery and data backup procedures
Example Scenario-Based Discussions
Many interviews will involve hypothetical situations to gauge your critical thinking and practical application of skills. Here are examples of topics that may come up:
- How would you resolve a sudden network outage affecting all users?
- What steps would you take to secure sensitive data across a multi-site network?
- Describe your approach to handling system updates while minimizing downtime for end-users.
- Explain how you would handle a security breach in a cloud environment.
By focusing on real-world applications and problem-solving approaches, you can showcase your experience and readiness for the challenges presented in such a role.
Essential Skills for Systems Administrators

In IT management, professionals need a broad set of technical and interpersonal skills to effectively manage infrastructure, solve complex issues, and maintain smooth operations. From understanding network protocols to troubleshooting server problems, the range of expertise required is vast. Success in this role depends on a solid foundation in both technical know-how and the ability to collaborate with teams to ensure system stability and security.
Here are some of the core competencies needed for success:
- Networking Knowledge: A deep understanding of network protocols, routers, switches, and firewalls is essential for maintaining secure and efficient communication across systems.
- Server Management: Proficiency in configuring, maintaining, and troubleshooting both physical and virtual servers is crucial to ensure system uptime and reliability.
- Security Expertise: Protecting data and infrastructure from threats requires knowledge of encryption, authentication methods, and secure network configurations.
- Backup and Recovery Planning: Professionals must be skilled in creating and managing backup systems and disaster recovery plans to protect against data loss.
- Automation Skills: Automating repetitive tasks and processes can increase efficiency, so familiarity with scripting languages and automation tools is a valuable asset.
- Problem-Solving Ability: The capacity to quickly analyze issues, troubleshoot effectively, and implement solutions is a critical skill for handling unexpected system failures or disruptions.
- Communication Skills: Clear communication with colleagues, stakeholders, and end-users is essential for resolving issues, explaining solutions, and sharing technical information.
Mastering these abilities helps ensure that professionals can handle the challenges that arise in complex IT environments, from network downtime to security threats, and keep operations running smoothly.
Top Technical Questions for IT Roles
When applying for an advanced position in the technology sector, candidates are often tested on their in-depth understanding of various technical concepts and their ability to solve real-world problems. These discussions typically revolve around key areas such as infrastructure management, security, and troubleshooting. Interviewers aim to assess not only your technical knowledge but also your ability to think critically and handle complex scenarios.
Common Technical Scenarios
During the selection process, candidates may be asked to explain how they would approach particular technical challenges. Here are some common examples:
- How would you address a network outage affecting multiple systems?
- What steps would you take to ensure the security of a cloud environment?
- Explain how you would optimize system performance across a large network.
- Describe your approach to managing user permissions and access rights securely.
Problem-Solving Scenarios
In addition to theoretical questions, employers may present practical problems to see how you apply your knowledge. Examples include:
- How would you restore a server from a backup after a system failure?
- What strategies would you implement to prevent data loss in a high-traffic environment?
- Describe a time when you resolved a critical security breach.
These types of questions help employers gauge your technical expertise and your ability to perform under pressure, ensuring you’re well-equipped to handle the demands of the role.
How to Prepare for the Interview
Preparation is key to succeeding in any selection process. For those applying for a leadership role in IT, it’s crucial to not only have the technical skills but also the ability to communicate effectively and think critically on your feet. Preparing for the process involves reviewing your knowledge, anticipating the challenges you may face, and understanding the company’s needs and culture.
Review Key Technical Areas
Before stepping into the selection process, make sure you’re familiar with the core competencies required for the role. Focus on the following areas:
- Networking protocols and troubleshooting methods
- System configuration, maintenance, and optimization
- Security protocols and risk management strategies
- Backup, recovery, and disaster management procedures
- Cloud infrastructure and virtualization tools
Prepare for Practical Scenarios
In addition to technical expertise, be ready to explain how you’ve handled real-world challenges in the past. Practice answering hypothetical scenarios, such as:
- How would you manage a critical system failure during peak hours?
- What steps would you take to ensure data integrity during a migration?
- How would you mitigate security risks within a multi-cloud environment?
Demonstrating a calm and organized approach to problem-solving will set you apart as a candidate capable of managing complex situations efficiently.
Key Networking Questions You Might Face

In any advanced role focused on IT infrastructure, you will likely encounter questions related to network management and troubleshooting. Employers seek candidates who are not only familiar with network protocols but also capable of resolving connectivity issues and optimizing performance across multiple systems. This section covers some of the fundamental networking topics you should be prepared to discuss in depth.
Common Networking Scenarios
When discussing networking, expect questions that test both your technical understanding and problem-solving abilities. Some examples include:
- How do you troubleshoot a network outage affecting several devices?
- What steps would you take to secure a corporate network from external threats?
- Explain the difference between a switch and a router. When would you use each?
Advanced Networking Concepts
As you progress in your career, you may face more complex inquiries. Employers want to gauge your familiarity with current technologies and your ability to handle large-scale systems. Be prepared for questions such as:
- How do you implement VLANs in a multi-location network?
- What is the role of DNS in network management, and how would you configure it?
- Describe how you would handle network congestion or bottlenecks.
Having a strong understanding of networking principles and the ability to apply them in practical situations will show that you can manage and optimize network infrastructure effectively.
Server Management and Troubleshooting Queries
Effective management of servers is a cornerstone of any IT infrastructure. Being able to maintain server health, monitor performance, and troubleshoot issues quickly is critical to minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity. In this section, we focus on key aspects of server management, including common challenges and strategies for resolving issues efficiently.
Common Server Management Challenges
When discussing server management, you may be asked about various tasks you perform to ensure optimal operation. These might include:
- How do you monitor server performance? Be prepared to discuss tools and metrics used to track CPU usage, memory, disk space, and network traffic.
- What steps do you take when a server is experiencing high load or performance degradation? Show your ability to identify the root cause and resolve issues, such as resource exhaustion or inefficient configurations.
- Explain how you manage patching and updates across multiple servers. Discuss your approach to maintaining security and performance through regular updates without causing disruptions.
Troubleshooting Scenarios
Interviews may include questions that assess how you approach problem-solving when things go wrong. Here are a few examples:
- What is your approach when a server fails to boot up? Outline your troubleshooting process, starting with checking hardware, reviewing logs, and escalating to more advanced diagnostics if necessary.
- How do you address a situation where a critical service is down, affecting users? Highlight your strategy for quickly isolating the problem, communicating with stakeholders, and applying fixes to restore functionality.
- Describe how you would handle a disk failure on a production server. Mention RAID configurations, backup strategies, and your ability to minimize data loss during recovery.
Having a well-rounded knowledge of server management and troubleshooting strategies is essential in ensuring smooth operations and responding to unexpected issues with minimal disruption.
Understanding Virtualization in Systems Admin Jobs
Virtualization has become a fundamental technology in modern IT infrastructure management. It allows for the creation of virtual instances of physical resources, enabling efficient utilization, easier scalability, and improved system management. Professionals in this field are expected to have a solid understanding of virtualization technologies and how they enhance operational efficiency and flexibility.
The Role of Virtualization in IT Management
Virtualization serves several key purposes in an IT environment. It allows for the consolidation of hardware, reducing the number of physical machines needed while maximizing resource usage. Key benefits include:
- Resource Optimization: By running multiple virtual machines on a single physical server, organizations can reduce costs and improve resource allocation.
- Scalability: Virtual environments can be easily scaled up or down based on demand, offering flexibility in managing workloads.
- Isolation: Virtualization allows different applications and systems to run in isolated environments, improving security and minimizing conflicts between processes.
Common Virtualization Technologies
Several tools and platforms dominate the field of virtualization, and familiarity with these technologies is a must for IT professionals. Some of the most widely used include:
- VMware: A leading platform for virtualizing servers and desktops, widely used in data centers for its powerful features and scalability.
- Hyper-V: A Microsoft product that integrates into Windows Server, offering virtualization capabilities for both small and large enterprises.
- VirtualBox: A free, open-source option commonly used for smaller-scale virtual environments or personal use.
Being proficient in these technologies and understanding their impact on system management is essential for professionals who are tasked with managing modern IT infrastructures efficiently and securely.
Common Security Questions for Senior Admins
Security is a critical aspect of any IT infrastructure, especially when managing complex systems. As a professional in a leadership role, you will be expected to have a deep understanding of security practices, protocols, and risk management. Being able to address potential threats, safeguard data, and implement preventative measures are key responsibilities for those in this field.
Handling Security Risks
In your role, you might be asked to explain how you would manage various security risks. Here are some common topics you should be prepared to discuss:
- How would you handle a network breach? Be prepared to outline your incident response process, from initial detection to resolution and post-incident analysis.
- What steps would you take to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive systems? Discuss your approach to implementing strong access controls, including the use of multi-factor authentication and role-based access.
- How do you ensure compliance with security standards? Explain your knowledge of regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and how you implement policies to maintain compliance.
Defending Against External Threats
Another important area is your approach to defending against external attacks, such as malware, phishing, or ransomware. Some potential inquiries could include:
- What is your strategy for defending against phishing attacks? Discuss the use of training, email filtering, and monitoring to reduce the risk of phishing.
- How would you respond to a ransomware attack? Be prepared to describe how you would isolate the infected systems, restore data, and prevent future attacks.
Being able to confidently discuss security protocols, response strategies, and risk management practices will demonstrate your expertise and readiness to protect critical infrastructure and data in any organization.
Database Management Scenarios and Solutions
Managing databases involves ensuring their reliability, performance, and security. Professionals in this field must be able to handle a variety of challenges, from optimizing queries to recovering data in case of failure. In this section, we’ll explore common database management scenarios and discuss effective solutions for resolving them.
Optimizing Database Performance
One of the most common challenges in database management is performance optimization. This can include slow query performance, inefficient indexing, and resource contention. Some typical scenarios might involve:
- What steps would you take to optimize a slow-running query? Discuss approaches such as indexing, query refactoring, and analyzing execution plans.
- How do you handle a database that is using excessive resources? Explain your process for identifying bottlenecks and optimizing system resources.
- What strategies would you employ to scale a database to handle increased traffic? Outline approaches like database partitioning, replication, and load balancing.
Data Recovery and Integrity
Another critical aspect of database management is ensuring data integrity and handling data recovery. Whether it’s recovering from a disaster or ensuring data consistency across multiple nodes, these situations require quick thinking and effective planning. Consider the following examples:
- How would you recover a database after a failure? Discuss backup strategies, point-in-time recovery, and transaction logs.
- What methods do you use to ensure data integrity across a distributed database? Explain approaches like consistency checks, data validation, and replication monitoring.
- How do you handle database corruption? Describe the steps to take when corruption is detected, including the use of repair tools and restoring from backups.
Being prepared for these challenges is essential for maintaining the health and availability of databases, ensuring that they continue to serve the needs of the business while minimizing risks.
Questions About System Monitoring and Performance
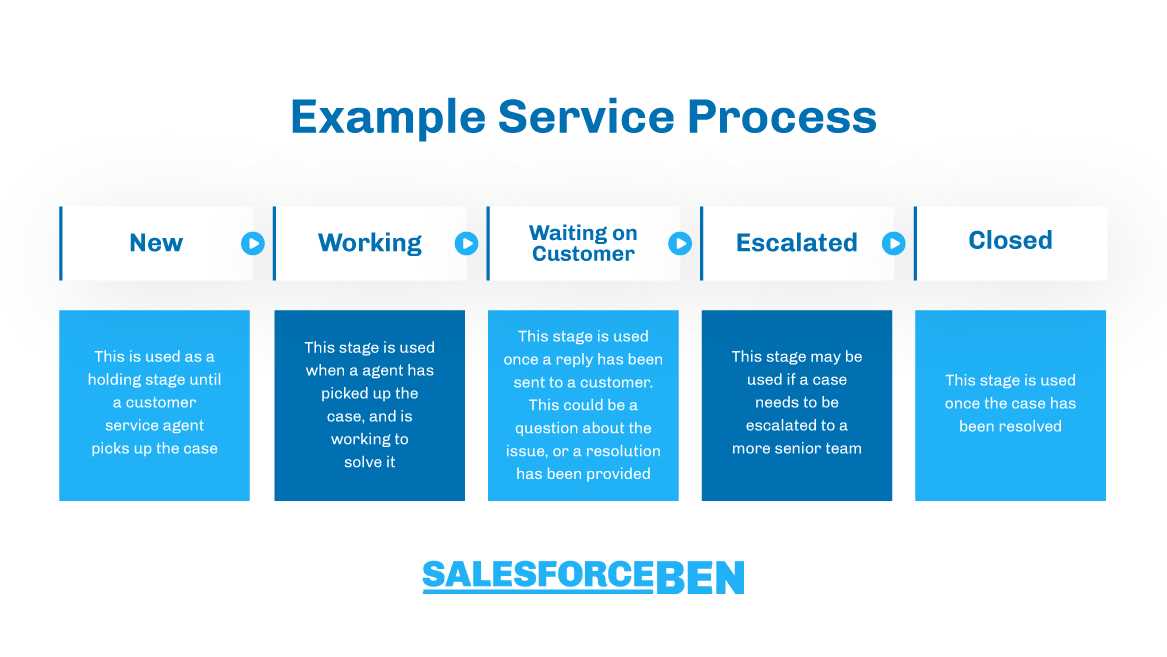
Effective system monitoring and performance management are essential for ensuring the stability and efficiency of IT infrastructure. Professionals in this field need to be able to identify potential issues, optimize performance, and maintain overall system health. In this section, we will explore common inquiries related to monitoring tools, performance metrics, and troubleshooting techniques.
Monitoring Key Metrics
System monitoring involves tracking various metrics to understand the health and performance of IT environments. Below are some common performance indicators and the monitoring tools that professionals might use to keep everything running smoothly:
| Metric | Description | Tools |
|---|---|---|
| CPU Utilization | Tracks the percentage of CPU usage to identify overuse or underuse | Top, Nagios, Zabbix |
| Memory Usage | Monitors the amount of RAM used by applications and processes | VMware vCenter, Prometheus |
| Disk I/O | Measures the rate at which data is read from and written to disk | iostat, Grafana |
| Network Traffic | Monitors the flow of data across the network | Wireshark, NetFlow |
Troubleshooting Performance Issues
When performance issues arise, it’s essential to know how to troubleshoot effectively. Some typical scenarios you may encounter include:
- What steps would you take if the system becomes unresponsive? Discuss the process of isolating the root cause, checking logs, and monitoring resource usage.
- How do you identify which process is consuming excessive resources? Explain the use of tools like `top`, `htop`, or task manager to identify resource hogs.
- What would you do if disk space is running low? Outline how to check disk usage, clean up unnecessary files, and consider extending disk capacity or using compression techniques.
Being proficient in system monitoring, understanding key performance metrics, and knowing how to troubleshoot when things go wrong are vital skills for maintaining a healthy and efficient IT infrastructure.
Understanding Disaster Recovery Protocols
In any IT environment, ensuring that systems are protected against unexpected failures and disasters is crucial. A robust recovery strategy is essential for minimizing downtime, safeguarding data, and ensuring business continuity. This section explores the protocols and strategies involved in disaster recovery, with a focus on their key components and practical application.
Core Components of Disaster Recovery Plans
Disaster recovery planning involves a series of steps to ensure that in the event of an unforeseen issue, critical data and systems can be quickly restored. The following elements are fundamental to any effective recovery plan:
- Backup Strategy: Regular backups of data are essential to avoid loss during system failures. This includes full, incremental, and differential backups.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): The maximum time that can elapse before services must be restored to minimize operational disruption.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): The maximum amount of data loss acceptable, which dictates how frequently backups should be taken.
- Redundancy: The duplication of critical systems and infrastructure, either through hardware, virtual machines, or cloud services, to ensure availability during failures.
Common Recovery Scenarios
Professionals must be prepared for various disaster scenarios and know how to act quickly to restore services. Here are some common situations:
- System Crash: A complete failure of servers or services. The protocol involves restoring data from backups and reconfiguring the systems to resume operations.
- Natural Disasters: Events such as floods, fires, or earthquakes. These require the activation of offsite backups and possibly switching to remote or cloud-based services.
- Cybersecurity Breaches: Attacks like ransomware or data breaches. A recovery plan may include isolating affected systems, restoring from backup, and conducting a security audit.
Understanding these protocols and ensuring that they are tested regularly is key to maintaining system resilience and minimizing the impact of potential disruptions.
Cloud Technologies and Infrastructure Knowledge
Cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern IT operations, providing scalable resources and flexibility for businesses of all sizes. Professionals in IT roles must have a solid understanding of how cloud technologies work, the various deployment models, and how to effectively manage and optimize cloud-based infrastructure. This section delves into essential cloud concepts and infrastructure management techniques that are vital in today’s technology-driven environments.
Key Concepts of Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud environments consist of various components that work together to deliver services to end-users. Some of the most critical concepts include:
- Cloud Deployment Models: These determine how resources are provisioned, including public, private, hybrid, and community clouds.
- Cloud Service Models: The three primary models–Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS)–define the level of control and management a user has over the infrastructure.
- Virtualization: This technology allows multiple virtual instances to run on a single physical machine, enabling greater resource efficiency and scalability.
Cloud Management and Optimization
Efficiently managing cloud resources requires both technical expertise and strategic planning. Key areas of focus include:
- Cost Optimization: Understanding the pricing models of cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud) and how to manage costs through efficient resource allocation and usage.
- Security: Ensuring data protection and compliance with industry standards, such as encryption, firewalls, and identity access management (IAM).
- Performance Monitoring: Using tools to track the performance of cloud-based systems, ensuring they operate at peak efficiency and addressing any issues promptly.
With the ever-increasing reliance on cloud services, proficiency in these areas is essential for anyone working in modern IT roles to effectively manage infrastructure and ensure seamless service delivery.
Backup Strategies for Senior Administrators
Ensuring the integrity and availability of critical data is one of the most important responsibilities in IT management. Having a solid backup strategy in place helps prevent data loss due to unforeseen events such as hardware failure, natural disasters, or cyberattacks. In this section, we explore key methods and best practices for creating an effective backup strategy to ensure business continuity and safeguard data.
Types of Backup Methods
Choosing the right backup method depends on several factors, including the amount of data, recovery objectives, and available resources. Below are common backup strategies that are crucial for protecting data:
| Backup Type | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Full Backup | Involves copying all data to a storage location. Every file is backed up every time. | Easy to restore all data at once. |
| Incremental Backup | Only the data that has changed since the last backup is copied. | Faster backup times and reduced storage space. |
| Differential Backup | Only the data that has changed since the last full backup is copied. | Faster restoration compared to incremental backups, as fewer restore points are required. |
Best Practices for Backup Management
Implementing a backup strategy requires a thoughtful approach. Here are some best practices to ensure data is consistently protected:
- 3-2-1 Rule: Always maintain three copies of your data, two on different storage devices, and one offsite or in the cloud.
- Regular Testing: Periodically test backup restorations to ensure data can be recovered quickly and accurately.
- Encryption: Encrypt backup files to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Automated Scheduling: Automate backup schedules to avoid human error and ensure that backups occur consistently without manual intervention.
By following these strategies, IT professionals can ensure that their data remains secure, recoverable, and available even in the face of unexpected disruptions.
Team Collaboration and Leadership in IT
Effective teamwork and strong leadership are critical components in the success of any IT department. In a rapidly changing technological landscape, collaboration among team members with diverse skills and expertise ensures that complex problems are solved efficiently. A leader who fosters a collaborative environment helps guide the team through challenges, motivates individuals, and aligns everyone towards common goals.
Leadership within IT is not just about technical expertise; it involves communication, empathy, and decision-making. Leaders must be capable of both managing day-to-day tasks and inspiring innovation within the team. Successful leaders also prioritize building strong relationships, fostering trust, and creating an environment where all team members feel valued and empowered to contribute their ideas.
Key Aspects of Effective Teamwork in IT
There are several key factors that make teamwork in the IT industry successful:
- Clear Communication: Ensuring that all team members understand project objectives, deadlines, and expectations promotes smooth collaboration and reduces misunderstandings.
- Adaptability: The ability to adjust to changing requirements and new technologies is vital in maintaining effective teamwork.
- Mutual Respect: Respecting different viewpoints and areas of expertise leads to better decision-making and fosters a positive team dynamic.
Leadership Skills for IT Professionals
Strong leadership in IT requires a unique combination of technical skills and interpersonal abilities:
- Decision-Making: IT leaders must make quick, well-informed decisions under pressure to keep projects on track and resolve issues efficiently.
- Conflict Resolution: Being able to mediate disputes and find solutions that satisfy all parties is essential for maintaining a harmonious work environment.
- Mentoring: Great leaders guide their team members, helping them develop professionally and encouraging them to take on new challenges.
In conclusion, team collaboration and leadership are fundamental to the success of IT departments. Whether through fostering open communication or empowering team members, a leader plays a pivotal role in creating an atmosphere that drives innovation, productivity, and job satisfaction within the team.
Effective Communication in Systems Administration
Clear communication is a cornerstone of success in any technical role, especially when managing complex infrastructure and ensuring the stability of IT environments. In roles where troubleshooting, coordination, and problem resolution are everyday tasks, conveying information effectively can greatly impact the efficiency of operations. Being able to explain technical details to both technical and non-technical stakeholders is a vital skill that enhances workflow, minimizes misunderstandings, and ensures smooth collaboration across teams.
Whether it’s documenting issues, explaining solutions to users, or collaborating with other teams, communication plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of IT operations. Successful professionals in the field are adept at breaking down complex topics, listening actively, and delivering concise messages that drive clarity and understanding.
Key Communication Skills for IT Professionals

Several communication skills are essential for success in technical roles:
- Active Listening: Understanding the problem fully before attempting to solve it is vital. Listening closely to team members, clients, or end-users helps in identifying the root cause of issues and proposing effective solutions.
- Clear Documentation: Writing clear, concise, and detailed documentation ensures that others can follow the steps taken to resolve issues, facilitating troubleshooting and knowledge sharing within the team.
- Technical Simplification: Being able to explain complex technical concepts in a way that non-technical stakeholders can understand is essential, especially when presenting solutions to clients or higher management.
Communication Strategies for Success
To improve communication in a technical environment, consider the following strategies:
- Frequent Updates: Keeping all relevant parties informed with timely updates about progress on tasks or issues ensures that everyone is on the same page and can act accordingly.
- Collaboration Tools: Utilizing the right tools, such as project management platforms and messaging systems, can streamline communication and reduce the risk of miscommunication.
- Feedback Culture: Actively seeking feedback and offering constructive feedback helps improve the quality of communication and overall team performance.
In conclusion, effective communication is essential for successfully managing IT infrastructure and working within teams. Professionals who excel in this area foster collaboration, solve problems more efficiently, and contribute to the overall success of the organization.
Problem-Solving Questions in IT Administration
Problem-solving is at the core of IT roles, where professionals are constantly faced with challenges that require quick thinking and logical solutions. The ability to identify issues, analyze their causes, and implement effective resolutions is essential in maintaining the smooth operation of technology systems. In interviews for such roles, candidates may be asked to demonstrate their approach to solving complex technical problems, showcasing their analytical skills and decision-making process.
When preparing for such scenarios, it’s important to not only focus on technical expertise but also on critical thinking and the ability to remain calm under pressure. The following section outlines common scenarios and key approaches to solving problems in an IT environment.
Approaching Technical Issues
To solve technical problems effectively, IT professionals must approach each situation systematically. Here are some strategies they might use:
- Identifying the Problem: Carefully assessing the issue and gathering relevant information from logs, error messages, or user reports helps clarify the root cause.
- Researching Solutions: After identifying the issue, professionals often consult documentation, forums, or technical resources to determine potential solutions or workarounds.
- Testing and Validating: Before fully implementing a solution, testing it in a controlled environment ensures that it will address the issue without creating new problems.
- Escalation: In cases where the issue is beyond immediate expertise, escalating it to the right department or senior team members ensures that it is resolved efficiently.
Common Problem-Solving Scenarios
IT professionals may encounter a variety of technical problems. Below are some common scenarios they might face:
- Network Connectivity Problems: When users experience network issues, an IT professional must check the hardware connections, verify network configurations, and perform troubleshooting tests to restore connectivity.
- System Crashes or Downtime: Diagnosing the cause of system failures, such as hardware malfunctions, corrupted files, or software conflicts, is crucial to restoring service.
- Security Breaches: Detecting and resolving potential security threats requires a methodical approach to identifying vulnerabilities, closing gaps, and implementing safeguards.
- Software Compatibility Issues: Addressing compatibility between software updates, drivers, or third-party applications requires an in-depth understanding of the environment to find a resolution.
Ultimately, the ability to solve problems efficiently and effectively is a key asset for anyone working in IT. Professionals who are proactive in identifying issues and can find creative solutions to complex challenges are invaluable in maintaining the integrity and security of technology systems.
Current Trends in IT Administration
The field of IT is constantly evolving, driven by new technologies, changing business needs, and emerging security threats. As technology continues to advance, professionals in this area must stay current with the latest trends to ensure that organizations can manage and secure their infrastructure efficiently. Understanding these trends is crucial for adapting to new challenges and improving operational efficiency.
In recent years, several key developments have significantly impacted the way IT operations are carried out. These include the rise of cloud-based services, automation tools, enhanced cybersecurity protocols, and the increasing importance of data management. These trends not only influence how IT professionals approach their daily tasks but also reshape entire organizational structures and strategies.
Key Trends Shaping IT Operations
Below are some of the most important trends currently shaping the landscape of IT management:
- Cloud Adoption: Many businesses are moving their infrastructure to cloud platforms to increase scalability, reduce costs, and improve flexibility. This shift requires IT professionals to have a solid understanding of cloud services, architectures, and security considerations.
- Automation and AI: Automation tools and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming routine administrative tasks, allowing IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. From system updates to resource allocation, AI-driven automation can streamline processes and enhance productivity.
- Cybersecurity Focus: With an increasing number of cyber threats, safeguarding data and systems is more important than ever. The rise of advanced security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and threat detection systems, has become a key area of focus for IT professionals.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The importance of data analytics has grown, as organizations rely on accurate insights to drive decision-making. IT departments are now tasked with ensuring data integrity, managing large datasets, and leveraging analytical tools to optimize business outcomes.
- Remote Work Solutions: The shift to remote and hybrid work environments has changed how IT infrastructures are designed. IT professionals now need to implement secure remote access, collaboration tools, and ensure that systems are accessible and protected from any location.
Preparing for the Future
To stay ahead of the curve, IT professionals must continuously update their skills and knowledge to match the evolving landscape. This includes staying informed about new technologies, gaining expertise in emerging tools, and keeping up with industry best practices. By embracing change and developing a proactive mindset, IT teams can continue to support business goals and adapt to the fast-paced world of technology.
Tips for a Successful Career in IT Operations
Building a thriving career in IT operations requires a blend of technical expertise, continuous learning, and strong interpersonal skills. As technology evolves rapidly, professionals in this field must be adaptable, proactive, and committed to staying updated with industry trends. Below are key strategies that can help individuals succeed and advance in their careers within IT management roles.
Essential Strategies for Career Growth
Here are some proven tips for excelling in this field and progressing to higher-level roles:
- Continuous Learning: Technology is ever-changing, and it’s crucial to stay current with new tools, platforms, and best practices. Invest time in pursuing certifications, attending training sessions, and learning about emerging technologies to remain competitive.
- Networking with Peers: Building a strong professional network can open doors to new opportunities and provide access to valuable insights. Attend conferences, participate in online forums, and engage with colleagues to exchange ideas and experiences.
- Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Strong analytical and troubleshooting abilities are essential for resolving issues quickly and efficiently. Practice critical thinking, learn how to approach problems methodically, and seek out opportunities to solve complex challenges.
- Gain Experience Across Multiple Domains: Having hands-on experience with a variety of technologies, from hardware management to cloud services and security, will make you a well-rounded professional. Explore different aspects of IT operations to build a diverse skill set.
- Effective Communication: While technical knowledge is important, the ability to explain complex concepts clearly to non-technical stakeholders is just as crucial. Strong communication skills foster collaboration and ensure alignment between IT and business objectives.
Table of Important Skills for IT Professionals
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Technical Proficiency | Master key tools and platforms, including operating systems, networking, databases, and cloud services. |
| Analytical Thinking | Ability to troubleshoot issues, identify patterns, and come up with effective solutions quickly. |
| Security Awareness | Understand best practices for protecting sensitive data and preventing breaches in various environments. |
| Collaboration | Work seamlessly with cross-functional teams to ensure smooth operations and effective project outcomes. |
| Adaptability | Stay open to new challenges, technologies, and processes, and be ready to adjust to the evolving demands of the job. |
By focusing on these key strategies and developing a balanced mix of technical expertise and soft skills, professionals can pave the way for long-term success in their careers and open up opportunities for advancement within the IT field.