
When it comes to saving the lives of children during emergencies, a deep understanding of pediatric care principles is essential. The certification process for advanced care in these situations requires individuals to demonstrate a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical skills. The key to success in this evaluation lies in grasping critical concepts, applying them effectively, and mastering essential procedures for rapid response.
Participants are assessed on their ability to manage various scenarios, including sudden cardiac arrest and respiratory failure, using a well-established framework. This includes the correct application of medications, interpretation of vital signs, and collaboration within a medical team. Mastering these techniques ensures that healthcare providers can deliver the best possible outcomes in high-stress environments, where time is often the most critical factor.
Preparation for this certification involves not only studying the material but also developing a practical understanding of how to implement life-saving techniques swiftly and accurately. By reviewing core concepts, familiarizing yourself with the tools and equipment, and practicing under realistic conditions, you can confidently approach any situation where a child’s life is at risk.
Comprehensive Overview of the PALS Test
The certification process for advanced pediatric care requires individuals to demonstrate their ability to manage critical situations involving children. This comprehensive evaluation examines knowledge and proficiency in handling life-threatening conditions, with an emphasis on effective intervention and teamwork. It is designed to ensure that healthcare providers are well-prepared to act swiftly and efficiently in high-pressure emergencies.
The evaluation covers a wide range of scenarios, from sudden cardiac arrest to respiratory failure, and requires mastery of both medical procedures and the correct use of specialized equipment. Candidates must also understand how to assess and prioritize different emergencies, applying appropriate treatments in real-time to stabilize the patient. Throughout the process, candidates are expected to show strong decision-making skills and an understanding of pediatric-specific care protocols.
Ultimately, this certification ensures that healthcare professionals are equipped with the essential skills needed to save lives and provide the highest standard of care in pediatric emergencies. Proper preparation involves not only theoretical study but also hands-on practice in realistic emergency settings. This combination of knowledge and practical experience is crucial for anyone seeking to excel in pediatric critical care.
Key Concepts in Pediatric Advanced Life Support
Effective management of critically ill children involves several core principles that healthcare providers must understand and apply in emergency situations. These concepts are designed to help practitioners recognize the severity of a child’s condition quickly, prioritize life-saving interventions, and execute them accurately. The key to success lies in a deep understanding of both the physiological differences in children and the appropriate medical responses in urgent scenarios.
Vital Sign Assessment and Interpretation
One of the first steps in pediatric emergency care is the assessment of vital signs. This includes measuring heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation. Recognizing normal and abnormal values for children at different ages allows medical professionals to identify signs of distress early and determine the necessary interventions.
| Age Group | Normal Heart Rate | Normal Respiratory Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Infants (0-12 months) | 100-160 bpm | 30-60 breaths per minute |
| Children (1-10 years) | 70-120 bpm | 20-30 breaths per minute |
| Adolescents (11+ years) | 60-100 bpm | 12-20 breaths per minute |
Airway Management and Breathing Support
Maintaining an open airway is critical in any emergency, especially in pediatric patients. Health professionals must be able to recognize signs of obstruction or respiratory distress and take the necessary steps to ensure proper ventilation. This can involve techniques such as suctioning, positioning, or providing supplemental oxygen. In some cases, advanced airway management may be required, including the use of intubation or other invasive methods to secure the airway and ensure adequate oxygenation.
By mastering these foundational concepts, healthcare providers are better equipped to handle pediatric emergencies efficiently, improving the chances of a positive outcome in life-threatening situations.
Understanding Scenarios in PALS Training
In pediatric emergency care, the ability to respond effectively in real-world situations is essential. Training scenarios are designed to simulate various critical conditions that healthcare providers may encounter while treating children in urgent care settings. These scenarios help individuals practice and refine their skills, ensuring that they can provide timely and appropriate interventions in life-threatening situations.
Each scenario presents a unique challenge, requiring participants to assess the situation, recognize the severity of the condition, and apply the correct medical procedures. These exercises test both knowledge and decision-making under pressure, emphasizing the importance of fast, precise actions in critical moments.
| Scenario Type | Key Skills Tested | Common Interventions |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac Arrest | CPR, Defibrillation | Chest compressions, Defibrillation, Medication administration |
| Respiratory Failure | Airway management, Oxygenation | Intubation, Positive pressure ventilation, Suctioning |
| Shock | Fluid resuscitation, Vasopressors | IV fluids, Medications, Monitoring vital signs |
By practicing these scenarios, healthcare professionals gain confidence in their abilities, improving their preparedness for real-life emergencies. These simulated situations ensure that caregivers can act decisively and competently when faced with life-threatening conditions involving children.
Essential Skills for PALS Certification
To succeed in the certification process for pediatric advanced life support, healthcare providers must acquire a comprehensive set of skills that encompass both theoretical knowledge and hands-on abilities. These skills are crucial for responding to emergencies involving children, where prompt and effective action can be the difference between life and death. Mastery of these techniques ensures that providers can manage critical situations efficiently and confidently.
Core Skills Required for Certification
The following skills are fundamental to performing well during the certification process and in real-world pediatric emergencies:
- Advanced Airway Management: Knowing how to secure and maintain a clear airway in pediatric patients is essential. This includes techniques such as endotracheal intubation and advanced ventilation methods.
- CPR and Chest Compressions: Properly performing CPR, including effective chest compressions, is a critical skill in cases of cardiac arrest.
- Medication Administration: Understanding the dosages, indications, and routes for medications in pediatric care is vital for stabilizing patients.
- Recognition of Cardiac Rhythms: Ability to interpret different heart rhythms and respond with the appropriate intervention is an essential skill in managing cardiac emergencies.
- Team Coordination: Collaborating with other healthcare providers and coordinating efforts during an emergency situation is crucial for the best patient outcomes.
Practical Application in Emergency Scenarios
Beyond theoretical knowledge, healthcare professionals must demonstrate these skills in practice through simulated emergency situations. Effective decision-making and fast, accurate interventions are essential in saving lives. The ability to remain calm under pressure, assess the patient’s condition quickly, and make critical decisions is an indispensable part of the certification process.
By refining these skills through training and practice, healthcare providers can enhance their ability to respond to pediatric emergencies, ensuring that they are prepared for any situation that may arise in a real-life setting.
Effective Strategies for Mastering PALS
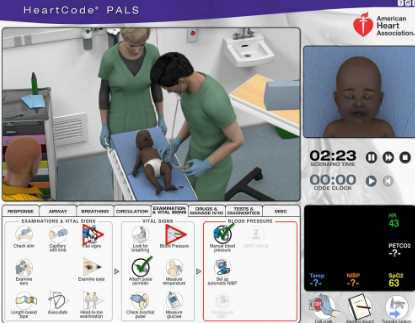
To successfully master pediatric advanced life support, healthcare providers need to adopt a focused and structured approach to learning. This involves a combination of theoretical understanding, hands-on practice, and the ability to think critically in high-pressure situations. Implementing effective strategies during preparation can make a significant difference in one’s ability to perform well in a certification setting and in real-world emergencies.
One of the most important strategies is to break down the material into manageable sections. Focusing on specific topics, such as airway management, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and medication administration, allows individuals to gradually build their competence in each area. Reviewing key concepts and common emergency scenarios frequently helps reinforce learning and improve retention.
- Active Learning: Engage with the material by practicing hands-on techniques, reviewing case studies, and simulating emergency situations to improve your practical skills.
- Group Study: Collaborate with colleagues or peers to discuss complex topics and share insights, which helps deepen understanding and identify areas for improvement.
- Regular Practice: Repeated practice is essential for mastering life-saving skills, such as chest compressions, medication dosages, and the correct use of medical equipment.
- Time Management: Develop strategies for managing time during emergencies by practicing simulations under time constraints. This will help improve speed and efficiency in real-life scenarios.
- Use of Visual Aids: Incorporate diagrams, charts, and videos into your study routine to visualize important concepts, such as cardiac rhythms and airway techniques.
In addition to these strategies, it is crucial to stay updated with the latest guidelines and recommendations. Being aware of the most current practices and protocols will help ensure that providers are well-prepared for any situation they may encounter during certification or clinical practice.
By using these approaches, healthcare professionals can enhance their ability to perform well under pressure, improve patient outcomes, and confidently manage pediatric emergencies.
Common Challenges in PALS Evaluations
During the evaluation process for pediatric advanced care, healthcare providers often face a variety of challenges that test both their knowledge and practical skills. These difficulties can arise from the complexity of pediatric emergencies, the need for quick decision-making, and the pressure of performing under time constraints. Identifying and understanding these challenges is essential for effective preparation and successful performance during the assessment.
Complexity of Pediatric Emergencies
Pediatric emergencies can differ significantly from adult cases due to the unique physiological characteristics of children. The following challenges are commonly encountered:
- Age-Related Variations: Children of different ages require different care approaches. Understanding age-specific parameters, such as normal vital signs, is crucial for accurate assessment and intervention.
- Recognition of Early Symptoms: Many serious conditions in children, such as respiratory distress or shock, may not present with obvious symptoms initially, making early recognition challenging.
- Limited Communication: Children may be unable to verbalize their symptoms, making it harder for healthcare providers to assess their condition. This requires professionals to rely on observation and clinical judgment.
Decision-Making Under Pressure
Another significant challenge during pediatric care evaluations is the pressure of making quick decisions in high-stress situations. Common obstacles in this area include:
- Time Constraints: In emergency scenarios, every second counts. Professionals must make rapid, accurate decisions, which can be difficult under pressure.
- Managing Multiple Tasks Simultaneously: Often, providers must manage several critical interventions at once, such as administering medications, securing airways, and coordinating with a team, all while maintaining focus and efficiency.
- Emotional Stress: Pediatric emergencies can be particularly emotionally challenging, especially when dealing with young patients. This can impact a provider’s ability to think clearly and act decisively.
Recognizing these common challenges and actively preparing for them can help healthcare providers navigate the complexities of pediatric emergency care more effectively. Mastery of essential skills, along with practice in simulated scenarios, is crucial for overcoming these obstacles and achieving success during the evaluation process.
Important Medications for Pediatric Emergencies

In pediatric emergency care, the use of specific medications is crucial for stabilizing and treating children in critical conditions. These medications are tailored to the unique physiological needs of young patients, and understanding their proper administration, dosages, and indications is essential for healthcare providers. Timely and accurate medication administration can significantly improve the outcome of an emergency situation.
Common Medications Used in Pediatric Emergencies
Several medications are frequently used in managing pediatric emergencies, each serving specific purposes depending on the condition being treated. Below are some of the most commonly used drugs:
- Epinephrine: Used in cases of severe allergic reactions, anaphylaxis, and cardiac arrest, this medication helps stimulate the heart and improve circulation.
- Atropine: Given for bradycardia (slow heart rate), atropine helps increase heart rate by blocking parasympathetic nervous system activity.
- Amiodarone: This antiarrhythmic drug is often used in cases of life-threatening arrhythmias such as ventricular fibrillation or tachycardia.
- Diazepam: Used for seizure management, especially in children with prolonged seizures, this medication helps stop or prevent seizures from worsening.
- Albuterol: A bronchodilator commonly used for treating wheezing or asthma-related respiratory distress, it opens the airways and eases breathing.
Medication Dosage and Administration
Proper dosing of medications in pediatric emergencies is critical, as children’s bodies react differently to drugs compared to adults. Healthcare providers must carefully calculate doses based on the child’s weight and age. Over- or under-dosing can lead to serious complications, so accuracy is paramount in emergency care settings.
By having a thorough understanding of these medications and their appropriate uses, healthcare professionals can provide more effective care during pediatric emergencies, improving patient outcomes and saving lives.
How to Interpret Cardiac Rhythms Accurately
Accurately interpreting cardiac rhythms is an essential skill in pediatric advanced care, as it allows healthcare providers to identify and respond appropriately to life-threatening heart conditions. Understanding the different types of heart rhythms, their causes, and their implications is crucial for making timely and effective decisions in emergency situations. This ability can significantly impact patient outcomes, especially when rapid interventions are required.
Key Steps for Accurate Cardiac Rhythm Interpretation
To interpret cardiac rhythms accurately, healthcare providers should follow a systematic approach that includes the following steps:
- Identify the Rhythm: Begin by observing the rhythm’s regularity. Determine whether the heart rate is regular or irregular, and assess the rate (fast, slow, or normal).
- Measure the P-R Interval: The P-R interval helps to assess if the electrical conduction is normal or delayed. A prolonged interval may indicate a conduction block.
- Examine the QRS Complex: This represents ventricular depolarization. Check for its width and morphology. A wide QRS complex may indicate a conduction abnormality.
- Evaluate the ST Segment: The ST segment can indicate myocardial ischemia or infarction. An elevated or depressed ST segment should raise suspicion for these conditions.
Common Cardiac Rhythms to Recognize
Some of the most important rhythms to identify include:
- Normal Sinus Rhythm: Characterized by a regular rhythm with a heart rate of 60-100 beats per minute, this is the normal rhythm in a healthy heart.
- Bradycardia: A heart rate below 60 beats per minute, which can lead to reduced blood flow and oxygen delivery if not treated promptly.
- Tachycardia: A heart rate above 100 beats per minute, which can be caused by fever, hypovolemia, or other factors and may require immediate treatment.
- Ventricular Fibrillation: A life-threatening arrhythmia that causes erratic electrical activity in the ventricles, leading to a loss of effective circulation.
By carefully following these steps and understanding the various rhythms, healthcare professionals can ensure they are making the correct interventions at the right time, ultimately improving patient survival rates during cardiac emergencies.
Best Practices for Team-Based Resuscitation
Effective resuscitation requires coordinated teamwork and clear communication. When responding to a critical situation, having a well-organized and efficient team can make all the difference in ensuring the best possible outcome for the patient. Best practices in team-based resuscitation focus on clear roles, continuous collaboration, and maintaining a calm and systematic approach to emergency care.
Key Principles for Successful Team-Based Resuscitation
To maximize the effectiveness of a resuscitation team, consider the following practices:
- Clear Role Assignments: Each team member should have a clearly defined role, such as airway management, medication administration, or monitoring vital signs. This minimizes confusion and ensures tasks are completed efficiently.
- Effective Communication: Constant, concise communication is essential. Team members should report updates on patient status, interventions, and any changes in condition to ensure everyone is on the same page.
- Practice and Simulation: Regular training and simulation of emergency scenarios allow team members to practice their roles in a high-pressure environment, improving coordination and reaction time during real emergencies.
- Maintain a Calm Environment: Remaining calm under pressure is crucial. A composed approach from the team leader and members helps reduce stress and supports better decision-making during resuscitation efforts.
Effective Team Coordination in Critical Moments
Coordinating actions in high-stress situations is essential to avoid confusion and ensure efficient resuscitation. Here are some tips to enhance coordination:
- Regular Check-ins: Regularly checking in with team members ensures that no aspect of the resuscitation is overlooked and that everyone is progressing with their tasks.
- Prioritize Critical Interventions: In emergencies, focus on life-saving interventions first. The team should prioritize tasks like establishing an airway, restoring circulation, and managing respiratory issues.
- Reevaluate Frequently: Continuous evaluation of the patient’s condition is necessary to adjust interventions as needed. This ensures the team adapts to changes in the patient’s status quickly.
By adhering to these best practices, resuscitation teams can improve their efficiency, reduce the likelihood of errors, and ultimately increase the chances of a positive outcome for the patient during life-threatening situations.
Top Resources for PALS Preparation
Preparing for pediatric advanced life support certification requires access to high-quality resources that cover both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. With the right tools, healthcare providers can enhance their understanding of emergency procedures, improve clinical decision-making, and refine their hands-on abilities. This section highlights some of the most effective materials and platforms available to aid in preparation for critical care scenarios involving children.
Recommended Study Materials
Several types of resources can help learners grasp the essential concepts of pediatric emergency care. These include books, online courses, and practice scenarios that simulate real-life situations:
- Official Guidelines and Protocols: Reviewing the latest guidelines from reliable organizations helps ensure that practice aligns with the most current standards in pediatric care.
- Comprehensive Textbooks: Books focusing on pediatric resuscitation and emergency care often provide detailed explanations of protocols, medications, and equipment used in critical situations.
- Online Courses and Webinars: Interactive courses allow learners to engage with the material at their own pace. Many online platforms also provide quizzes and certifications to test knowledge and progress.
- Case Study Collections: Real-world case studies help learners apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills in emergency contexts.
Practical Training Tools

Hands-on experience is crucial for mastering life-saving techniques. The following tools provide opportunities for practice and simulation:
- Simulation Software: Many platforms offer virtual simulations of emergency scenarios that require rapid decision-making, reinforcing the knowledge learned through textbooks and lectures.
- Manikins and Simulators: Using high-fidelity manikins during practice sessions allows healthcare providers to simulate real-life interventions, such as CPR, airway management, and medication administration.
- Practice Exams: Mock exams designed to replicate the real certification tests help familiarize learners with the format and types of questions they will encounter, improving confidence and performance.
By utilizing a combination of these resources, individuals can build a strong foundation in pediatric emergency care, ensuring they are well-prepared for both certification and real-world practice.
Latest Updates in PALS Guidelines
Staying up-to-date with the most recent revisions in emergency care protocols is crucial for healthcare professionals. As new research and clinical experiences shape the field, guidelines are regularly updated to reflect the latest evidence-based practices. This section covers the most recent changes in pediatric advanced life support protocols, focusing on key updates that improve patient outcomes in critical care scenarios.
Changes in Resuscitation Protocols
One of the most important updates in pediatric emergency care involves modifications to resuscitation protocols. These changes help streamline treatment procedures, ensuring that healthcare providers can respond more effectively during a crisis.
- Updated Airway Management Techniques: New recommendations focus on minimizing intubation attempts and promoting early intervention with non-invasive methods such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP).
- Revised Dosage for Medications: Recent guidelines suggest adjustments in medication dosages for children in different weight categories, enhancing the precision of pharmacological interventions.
- Compression-Only CPR: Recent studies support the use of compression-only CPR in pediatric cases, reducing the emphasis on ventilation during certain emergency situations, and focusing on chest compressions to improve circulation.
Enhanced Focus on Team Coordination

Effective communication and team coordination have become even more crucial in managing pediatric emergencies. The latest revisions emphasize role clarity and structured communication during resuscitation efforts to reduce delays and errors.
- Clearer Role Assignments: Each team member now has more defined responsibilities, which reduces confusion and accelerates decision-making during critical moments.
- Structured Communication Systems: The use of standardized communication methods, such as closed-loop communication, ensures that all team members are aligned during resuscitation efforts.
By incorporating these updated guidelines, healthcare providers can deliver more effective, timely, and accurate care, leading to better outcomes for pediatric patients in emergencies.
Critical Thinking in Life-Threatening Situations
In high-pressure emergencies, the ability to think critically can mean the difference between life and death. Healthcare providers must quickly assess complex situations, prioritize actions, and make decisions based on available information, all while managing their own stress and maintaining a clear focus. This section explores the importance of critical thinking in urgent care scenarios and provides strategies for improving decision-making under pressure.
Key Elements of Critical Thinking in Emergencies
Critical thinking involves several key skills that are essential when dealing with life-threatening conditions. These elements help healthcare professionals make informed and timely decisions in the most chaotic environments.
- Prioritization: In emergencies, it’s vital to assess the severity of each issue and address the most critical needs first. This ensures that life-saving interventions are not delayed.
- Rapid Information Processing: Emergency situations often provide limited information, so healthcare providers must process and evaluate data quickly, making use of available tools and knowledge.
- Flexibility: Circumstances in critical care can change rapidly. Providers must be adaptable, willing to adjust their approach based on new information or a change in the patient’s condition.
- Decisiveness: Timely decision-making is crucial, even when there is uncertainty. Healthcare providers must make informed choices quickly and without hesitation to avoid delays in care.
Strategies for Improving Critical Thinking
Critical thinking skills can be developed and refined with consistent practice and specific techniques. The following strategies help healthcare professionals enhance their ability to think critically in high-stress situations:
- Scenario-Based Training: Regularly practicing with real-life scenarios, such as simulation-based training, allows healthcare providers to hone their problem-solving skills and prepare for the unexpected.
- Collaboration and Team Input: Engaging with other team members for input or second opinions can provide valuable perspectives, helping to prevent errors and improve overall decision-making.
- Reflection: After an emergency response, taking time to reflect on the decisions made and their outcomes can help identify areas for improvement and strengthen future responses.
By focusing on these critical thinking elements and strategies, healthcare professionals can improve their ability to act quickly and effectively in life-threatening situations, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of errors.
Step-by-Step Approach to Pediatric Care
Providing effective care for young patients requires a structured, methodical approach, especially in emergency situations. Each step in the process must be carefully considered to ensure that the child receives the best possible outcome. This section outlines a comprehensive, step-by-step framework that healthcare professionals can follow to manage pediatric care, from initial assessment to advanced interventions.
Initial Assessment and Stabilization
The first step in managing any pediatric emergency is to perform a rapid assessment to determine the child’s condition. This involves evaluating their airway, breathing, circulation, and overall responsiveness to ensure immediate stabilization. Proper assessment during this phase is essential for guiding subsequent decisions and interventions.
- Check Airway: Ensure that the child’s airway is clear and open. If necessary, perform maneuvers to establish or maintain airway patency.
- Evaluate Breathing: Assess the child’s breathing rate and quality. Administer oxygen if the child is hypoxic or in respiratory distress.
- Assess Circulation: Check pulse, capillary refill, and blood pressure to assess circulatory status. Begin fluid resuscitation or medication if required.
Advanced Care and Monitoring
Once stabilization has been achieved, advanced care should be provided as necessary, based on the child’s specific condition. This may involve advanced airway management, the use of medications, or other targeted interventions. Continuous monitoring throughout this phase is crucial to detect any changes in the child’s status and to modify the care plan accordingly.
- Medications: Administer appropriate medications based on the child’s condition, including those to stabilize heart rate, control seizures, or treat infections.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Use monitoring devices to keep track of vital signs, such as oxygen saturation, heart rate, and blood pressure, to guide further treatment.
- Prepare for Transport: If the child’s condition does not improve or requires specialized care, prepare for transport to a higher-level care facility while maintaining the established interventions.
By following a step-by-step approach, healthcare providers can ensure that pediatric patients receive timely and effective care, minimizing the risk of complications and improving outcomes.
Vital Signs Monitoring Techniques
Accurate monitoring of vital signs is a fundamental aspect of patient care, especially in critical situations. It allows healthcare providers to assess the patient’s immediate status, detect potential complications, and guide treatment decisions. This section explores essential techniques for monitoring vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature, and the tools used to measure them effectively.
Heart Rate Monitoring
Heart rate is a key indicator of cardiovascular health and overall well-being. Monitoring heart rate provides insight into the patient’s circulatory system, identifying signs of distress or instability.
- Pulse Palpation: Manual assessment of pulse at various sites, such as the radial or carotid artery, provides a quick estimate of heart rate and rhythm.
- ECG Monitoring: Continuous electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring allows for more detailed analysis of the heart’s electrical activity, detecting arrhythmias and abnormal rhythms.
- Pulse Oximetry: This non-invasive method helps estimate heart rate along with oxygen saturation levels, providing valuable information in respiratory or circulatory emergencies.
Blood Pressure Measurement

Blood pressure provides essential data on the patient’s vascular health. Accurate monitoring of blood pressure is crucial for detecting signs of shock, hypertension, or other cardiovascular conditions.
- Auscultatory Method: Using a stethoscope and sphygmomanometer, this method allows the healthcare provider to measure both systolic and diastolic pressure accurately.
- Oscillometric Devices: Automated blood pressure cuffs can quickly provide readings, especially useful in emergency settings where time is critical.
Respiratory Rate Assessment
Respiratory rate is a vital indicator of respiratory function. Monitoring breathing patterns and rates can help detect distress, hypoxia, or respiratory failure.
- Visual Observation: Counting the number of breaths per minute by observing chest movement is a basic method, especially when using pulse oximeters or other monitoring tools.
- Capnography: This advanced technique involves measuring the concentration of carbon dioxide in exhaled air, providing insights into respiratory efficiency and the effectiveness of ventilation.
Temperature Measurement
Body temperature reflects metabolic activity and can be a critical parameter for detecting infection, inflammation, or heat-related illnesses.
- Thermometers: Standard devices like digital thermometers or infrared thermometers are used for quick and accurate readings, especially in pediatric or emergency settings.
- Invasive Temperature Monitoring: In some cases, such as during intensive care, internal temperature probes may be used for continuous monitoring.
By employing these techniques, healthcare professionals can ensure comprehensive and accurate monitoring of vital signs, which is crucial for making informed clinical decisions and providing optimal care to patients in critical conditions.
How to Handle High-Stress Situations
In high-pressure scenarios, the ability to stay calm and think clearly is essential for providing effective care. Whether in an emergency room, on the field, or during a life-threatening event, healthcare providers must manage stress efficiently to make critical decisions. This section outlines techniques for maintaining composure, managing stress, and ensuring optimal performance in demanding situations.
Key Techniques for Stress Management
Managing stress in emergencies requires a combination of preparation, mental clarity, and practical strategies. By employing the following techniques, healthcare professionals can navigate high-stress situations more effectively.
- Focus on the Present: Concentrate on the immediate tasks at hand rather than worrying about what might happen next. This helps reduce anxiety and ensures that attention is directed where it’s needed most.
- Use Breathing Exercises: Deep, slow breathing can activate the body’s relaxation response, lowering heart rate and reducing the feeling of being overwhelmed.
- Stay Organized: Having a clear, structured approach to emergency care helps reduce confusion and improves efficiency. Ensure that you follow established protocols and prioritize tasks logically.
- Trust Your Training: Rely on the skills and knowledge gained through training and practice. Confidence in your abilities helps reduce self-doubt and enhances decision-making under pressure.
Team Coordination and Support
Handling high-stress situations is not done alone. Effective team coordination is key to ensuring that all aspects of patient care are addressed quickly and efficiently.
- Clear Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with your team. This ensures that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities, minimizing confusion during critical moments.
- Delegate Tasks: Distribute responsibilities according to team members’ strengths and expertise. Delegating tasks can help prevent burnout and ensure that important actions are completed in a timely manner.
- Provide Support to Colleagues: Offer encouragement and assistance to fellow team members. A supportive environment helps reduce collective stress and improves team morale.
By incorporating these strategies, healthcare providers can better handle the pressures of high-stress situations, improving both their own well-being and the quality of care provided to patients in critical conditions.
Effective Use of Medical Equipment in PALS
In emergency situations, having the right medical equipment and knowing how to use it effectively is crucial for providing life-saving care. The proper application of tools such as airway management devices, defibrillators, and monitoring equipment can make the difference between life and death. This section explores the essential medical devices used in pediatric care and outlines best practices for their effective use in high-pressure situations.
Essential Medical Equipment for Pediatric Care
There are several key pieces of medical equipment that are vital for managing pediatric emergencies. These devices should be used with precision and care to ensure the best possible outcomes for young patients.
- Airway Management Devices: Devices like endotracheal tubes, laryngeal masks, and bag-valve masks are crucial for maintaining an open airway. Proper training is required to ensure these tools are used effectively in situations where the patient’s breathing is compromised.
- Defibrillators: Automated external defibrillators (AEDs) and manual defibrillators are used to restore normal heart rhythm in cases of severe arrhythmias. Knowledge of proper defibrillation protocols is vital for ensuring successful outcomes.
- Intravenous Access Tools: Catheters, needles, and intravenous lines are essential for administering fluids, medications, and blood products. Quick and accurate placement of these devices is crucial, particularly in pediatric patients where vein access can be challenging.
Best Practices for Using Medical Equipment

While having the right equipment is important, knowing how to use it effectively under pressure is equally crucial. Here are some best practices for using medical devices during pediatric emergencies:
- Familiarity with Devices: Ensure that all team members are thoroughly trained in the proper use of each piece of equipment. Regular drills and simulations help increase familiarity and improve response time in real situations.
- Proper Sizing and Adjustments: Pediatric patients require specialized equipment designed for their size and age. Always check that the device is appropriately sized and adjusted for the child to avoid complications.
- Quick and Efficient Setup: In critical moments, time is of the essence. Practice setting up and deploying equipment quickly and accurately to minimize delays in care.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of the equipment during use. For example, checking the placement of an endotracheal tube or verifying the heart rhythm after defibrillation ensures that interventions are working as intended.
By mastering the use of medical equipment, healthcare providers can improve their ability to respond effectively to pediatric emergencies, ensuring that every patient receives the best possible care when every second counts.
Differences Between PALS and BLS Training
Training in life-saving techniques is critical for healthcare professionals, and two of the most widely recognized programs are designed to teach how to manage emergencies involving children and adults. While both programs share the goal of providing critical care in emergency situations, they differ significantly in terms of their approach, the age groups they focus on, and the complexity of the skills they teach. This section will explore the key differences between the two programs, focusing on their scope, techniques, and application in clinical settings.
Key Focus Areas

The primary distinction between the two programs lies in their focus. While both aim to teach basic and advanced techniques for resuscitation, they differ in the complexity of the procedures and the patient populations they address.
- Pediatric vs. Adult Care: PALS training is specifically geared toward managing pediatric emergencies, whereas BLS is more general and includes care for both children and adults. The skills taught in PALS focus on the unique physiological needs of children, which differ significantly from those of adults.
- Basic Life Support vs. Advanced Care: BLS focuses on fundamental life-saving techniques such as CPR, airway management, and defibrillation. PALS goes beyond these basics to cover more advanced interventions, including drug administration, advanced airway management, and using equipment like pediatric defibrillators.
- Scenario Complexity: PALS training typically involves more complex scenarios, including various arrhythmias, shock, and respiratory failure in children. BLS, on the other hand, covers more straightforward cases like choking, cardiac arrest, and basic airway management.
Skills Taught in Each Program

While there is some overlap in the skills taught in both programs, PALS focuses more on specific pediatric needs, whereas BLS provides essential skills that can be applied across all age groups.
- Airway Management: Both BLS and PALS emphasize the importance of maintaining an open airway. However, PALS includes more advanced techniques such as intubation and the use of pediatric-specific airway equipment, whereas BLS focuses on simpler methods such as using a bag-valve mask or performing the Heimlich maneuver.
- CPR Protocols: Both programs cover CPR, but PALS includes specific modifications for infants and children, such as adjusting compression depth and rate, whereas BLS covers CPR techniques for both adults and children in a more generalized way.
- Drug Administration: PALS training teaches the safe administration of medications, including dosages specific to pediatric patients, a skill that is not covered in basic BLS courses.
Understanding the distinctions between these two types of training is essential for healthcare providers to ensure they are properly prepared to handle emergencies for both pediatric and adult patients. By tailoring interventions to the patient’s age and condition, professionals can offer the most effective care during critical situations.
Building Confidence for Real-Life Emergencies
Handling emergency situations requires not only technical knowledge but also the confidence to act decisively under pressure. In high-stress scenarios, healthcare professionals must be able to apply their skills effectively and quickly. Building this confidence takes practice, preparation, and a solid understanding of the protocols for managing critical situations. This section will explore strategies to enhance confidence when faced with life-threatening emergencies, ensuring that professionals are ready to respond when every second counts.
Key Strategies to Build Confidence
Confidence in managing emergencies can be built through consistent practice and exposure to realistic scenarios. Below are some of the key strategies to help improve performance in real-life situations:
- Regular Simulation Training: Participating in regular hands-on simulations is one of the most effective ways to develop confidence. Simulated emergencies allow professionals to practice their skills in a controlled environment, making them more prepared to handle actual emergencies.
- Mastering Key Procedures: Focusing on mastering critical procedures such as CPR, airway management, and medication administration will help ensure that professionals feel confident in their ability to respond to various emergencies.
- Peer Support and Teamwork: Working alongside colleagues during training exercises fosters collaboration and support. Team-based simulations help professionals feel more confident in their ability to rely on others and contribute effectively in high-pressure situations.
Creating a Positive Mindset

Developing a positive mindset is essential for building confidence, as it helps individuals overcome self-doubt and stay focused during emergencies. Here are a few ways to cultivate a positive attitude:
- Visualization: Visualizing oneself successfully handling an emergency can help boost confidence and reduce anxiety. Repeating this mental exercise can create a sense of familiarity and preparedness.
- Continuous Learning: Staying updated on the latest protocols and guidelines through ongoing education helps reinforce knowledge, contributing to a sense of competence and readiness.
- Reflection and Feedback: After participating in training exercises, taking time to reflect on performance and seek feedback can help individuals identify areas for improvement and gain a clearer understanding of their strengths.
Comparison of Confidence-Building Techniques

Here is a comparison of different techniques used to build confidence in emergency scenarios:
| Technique | Effectiveness | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Simulation Training | High | Regular practice |
| Mastering Key Procedures | High | Consistent review |
| Peer Support | Moderate | During training exercises |
| Visualization | Moderate | Ongoing mental practice |
| Continuous Learning | High | Ongoing education |
Building confidence for real-life emergencies is an ongoing process that requires practice, a positive mindset, and continuous learning. By mastering key techniques, working as part of a team, and staying up-to-date with the latest practices, professionals can approach emergencies with the confidence and competence needed to provide the best possible care.