The study of how places become centers of manufacturing and commerce reveals a fascinating connection between the environment, technology, and economic growth. By exploring the underlying factors, one can gain insight into the forces that shape the locations of various businesses and the global distribution of production.
In this section, we delve into the main principles that influence the development of economic activities across different regions. From transportation networks to resource availability, various elements come together to determine where industries thrive and how they evolve over time.
To successfully master these concepts, it’s crucial to understand the key models and patterns that guide economic development, as well as the challenges and opportunities posed by both local and global forces. This foundational knowledge not only supports academic success but also helps make sense of the broader impacts of economic activities on society and the environment.
Comprehensive Guide to AP Human Geography

This guide serves as a roadmap for mastering the key concepts related to economic systems, development, and spatial distribution. It emphasizes understanding how various factors such as technology, resources, and infrastructure impact the growth and organization of economic sectors across different regions.
Through this section, students will learn to analyze the intricate relationships between production, location, and global trade. The goal is to equip learners with the tools to identify patterns in economic activities and to assess the challenges posed by varying geographic and environmental conditions.
By focusing on essential models and frameworks, this guide prepares you to tackle complex scenarios and provide well-supported insights into the evolving dynamics of production and commerce around the world.
Understanding Industrial Geography Concepts
The study of economic sectors and their spatial organization reveals how different forces shape the location and development of various types of production activities. It is essential to grasp the key factors that influence where businesses emerge and how they evolve over time, from the availability of raw materials to the accessibility of transportation networks.
To fully understand these dynamics, it is important to focus on several core ideas that govern how industries operate and expand. These include:
- Resource Distribution: The availability of natural resources, such as minerals, water, and energy, plays a crucial role in determining where certain activities can thrive.
- Labor Markets: The availability of skilled labor and cost of wages affect the location decisions of manufacturing plants and service centers.
- Technology: Advances in technology can dramatically alter production processes and influence the geographic spread of certain economic activities.
- Infrastructure: Well-developed transportation and communication systems are vital for industries that rely on the movement of goods and information.
- Environmental and Social Impact: The long-term effects on the environment and surrounding communities also shape decisions on where to establish production hubs.
These fundamental concepts are the foundation for understanding how economic sectors operate in the global market, and how they are affected by a variety of internal and external pressures.
Key Themes in Chapter 11 Review
In this section, we will explore the core topics that define the principles of economic activities, their spatial organization, and the various forces that influence their development. By reviewing these essential themes, you will gain a deeper understanding of how different factors contribute to the growth and distribution of economic sectors around the world.
Factors Influencing Location Decisions
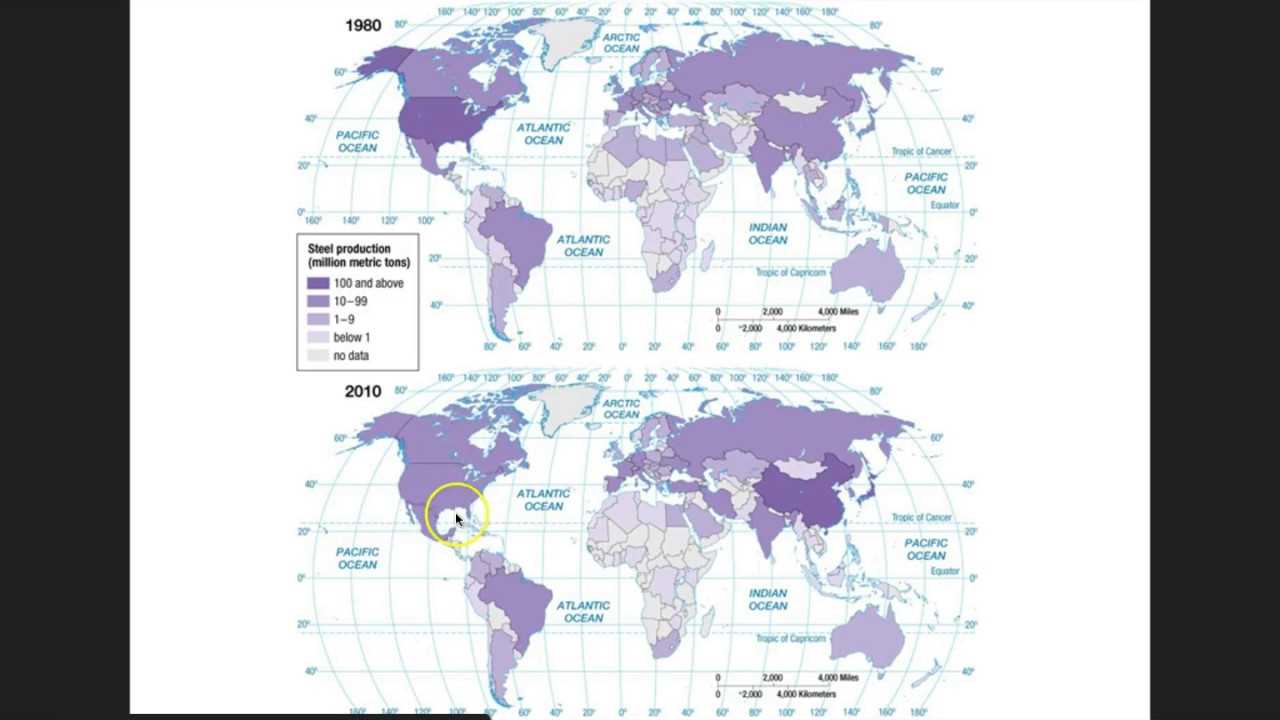
One of the central themes involves understanding the various elements that shape the geographic location of production centers. Factors such as raw material availability, labor costs, and access to markets all play a role in determining where businesses choose to establish their operations. Additionally, the role of transportation infrastructure and energy sources cannot be overlooked, as they are crucial for the movement of goods and services.
Global Patterns and Economic Networks
Another significant theme in this review is the examination of how economic activities are organized on a global scale. Understanding the interconnectedness of different regions through trade routes, financial systems, and supply chains helps explain the global distribution of industries. This theme also covers the shift in production from developed to developing nations, as well as the rise of emerging economies in global commerce.
Importance of Industrialization in Geography
The process of transitioning from agrarian economies to more complex systems of production has played a pivotal role in shaping the development of modern societies. This transformation impacts not only the economy but also the environment, urbanization, and social structures. Understanding the significance of this shift is crucial for grasping the broader patterns of global economic and cultural change.
Impact on Economic Development
Industrialization has fundamentally altered the way resources are utilized and how goods are produced. The spread of manufacturing activities has been linked to economic growth, as it generates jobs, boosts trade, and increases overall productivity. Key aspects of this transformation include:
- Economic Diversification: The shift from agriculture to manufacturing has allowed countries to develop diverse economies, reducing dependency on a single sector.
- Creation of Wealth: By increasing efficiency and scale of production, industrialization leads to the generation of wealth and the expansion of middle-class populations.
- Global Trade Expansion: Mass production enables countries to export goods, contributing to a more interconnected global economy.
Social and Environmental Implications
While industrialization brings economic advantages, it also raises concerns related to environmental sustainability and social changes. Urbanization, for example, results in the rapid growth of cities, altering the social fabric and creating challenges in infrastructure, housing, and public services. The environmental consequences include:
- Resource Depletion: The demand for raw materials leads to the overexploitation of natural resources, resulting in long-term ecological damage.
- Pollution: Industrial activities contribute to air, water, and soil pollution, which impacts both human health and ecosystems.
- Climate Change: The increased use of fossil fuels and emissions from factories have contributed to global warming and changing weather patterns.
Factors Shaping Industrial Location Choices
The decision on where to establish production centers is influenced by a combination of economic, social, and environmental factors. Understanding these determinants is essential for recognizing why certain areas become hubs of activity while others remain underdeveloped. Various considerations guide businesses in choosing optimal locations for their operations.
Key Economic Considerations
Economic factors often play the most significant role in determining the placement of manufacturing operations. These include:
- Availability of Raw Materials: Proximity to essential resources reduces transportation costs and ensures a steady supply of inputs for production.
- Labor Costs and Skills: Access to a skilled workforce or lower labor costs can make certain areas more attractive for businesses.
- Market Access: The nearness to key markets and customers is a driving factor, as it minimizes distribution costs and enhances competitiveness.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Efficient roads, ports, and railways are vital for the movement of goods and minimizing delays in production.
Environmental and Social Influences
Aside from economic aspects, environmental and social conditions also influence industrial location decisions. These factors include:
- Environmental Regulations: Areas with lenient regulations or the ability to adopt more sustainable practices can be more appealing to industries with high environmental impacts.
- Community and Social Impact: Businesses consider the potential social consequences, such as job creation and effects on local communities, when deciding where to locate.
- Government Incentives: Local and national governments may offer tax breaks, subsidies, or other incentives to attract businesses to specific regions.
Test Strategies for Industrial Geography

When preparing for assessments related to the spatial distribution and development of economic sectors, having a clear strategy can greatly improve your performance. By focusing on key concepts and practicing application-based questions, you can strengthen your understanding and tackle any questions with confidence. This section outlines effective strategies to approach exams on topics related to economic organization and production patterns.
Focus on Key Concepts and Models
It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the major theories and models that explain the location of production and commercial centers. Understanding the principles behind concepts such as agglomeration, economies of scale, and comparative advantage will help you quickly identify which model applies to specific scenarios. Key topics to review include:
- Weber’s Least Cost Theory: Focus on the factors that determine optimal locations for production, such as transportation and labor costs.
- Location of Tertiary and Quaternary Sectors: Be aware of the shifting patterns in service industries and high-tech sectors.
- Globalization and Outsourcing: Understand how the movement of production across borders impacts location choices and economic geography.
Practice Application and Case Studies
Many assessments will ask you to apply concepts to real-world examples or case studies. To prepare, practice analyzing regions and countries based on economic data and production characteristics. Consider factors such as resource availability, labor markets, and transportation infrastructure in determining why certain regions become industrial centers. The more examples you work through, the more prepared you will be for application-based questions.
Geographic Models for Industrial Distribution

Various models have been developed to explain how and why certain regions become centers of production, trade, and commerce. These frameworks help to understand the spatial patterns of economic activities and how factors like transportation, resources, and labor influence the organization of production across different locations. By studying these models, one gains insight into the processes that determine the distribution of industries worldwide.
Weber’s Least Cost Theory
One of the foundational models in the study of production locations is Weber’s Least Cost Theory. This model emphasizes the minimization of costs as the primary factor in determining where industries should be located. It considers three main costs:
- Transportation Costs: The costs associated with moving raw materials and finished products to and from production centers.
- Labor Costs: The cost of employing workers, with industries seeking locations where wages are lower and labor is abundant.
- Agglomeration Benefits: The advantages of clustering similar industries together, such as shared infrastructure and reduced operational costs.
The Core-Periphery Model
The Core-Periphery Model explains how economic activities are often concentrated in specific regions, leaving others less developed. In this model, the “core” consists of highly industrialized regions with strong economies, while the “periphery” includes less developed areas that rely on raw material extraction or basic manufacturing. The model helps explain global patterns of development and the uneven distribution of wealth and resources.
Global vs Local Industrial Patterns Explained
The distribution of production centers and manufacturing activities varies significantly depending on whether we consider global or local perspectives. While global patterns reflect widespread economic forces and international connections, local patterns focus on specific regional factors that shape the location and type of production. Understanding these two levels of analysis helps in grasping the complexities of economic organization and the factors that contribute to the spatial distribution of goods and services.
Global Industrial Trends
At the global scale, industrial development is influenced by international trade, technological advancements, and the shifting locations of labor-intensive or capital-intensive industries. Some of the key factors that contribute to global patterns include:
- Global Supply Chains: Industries are increasingly reliant on international networks for sourcing raw materials, manufacturing goods, and distributing products.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Investment from foreign companies into different regions drives the creation of industrial hubs, particularly in developing economies.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in transportation, communication, and manufacturing processes facilitate the growth of industries in various parts of the world, making production more cost-effective and efficient.
Local Influences on Industrial Distribution
On a local scale, industrial activities are shaped by factors such as proximity to natural resources, local labor availability, and the presence of infrastructure. These regional influences play a critical role in determining where industries are concentrated within a particular area. Key factors include:
- Access to Raw Materials: Local availability of essential resources, such as minerals, energy sources, and agricultural products, often dictates where specific types of production occur.
- Labor Market Conditions: Areas with abundant, skilled, or affordable labor often attract industries that rely heavily on human resources.
- Transportation Networks: Regions with developed infrastructure, such as roads, railways, and ports, become focal points for industrial operations due to their ability to facilitate the movement of goods.
Impact of Technology on Industrial Growth
The rapid advancement of technology has had a profound effect on the expansion and efficiency of production processes worldwide. From the introduction of automated machinery to the rise of digital tools for managing supply chains, technological innovations have reshaped how goods are produced, distributed, and consumed. This shift has not only increased the scale of production but has also allowed industries to reduce costs, improve quality, and reach global markets more effectively.
Several key technological developments have played a significant role in boosting industrial growth:
| Technology | Impact on Industrial Growth |
|---|---|
| Automation | Increases production speed, reduces human error, and lowers labor costs. |
| Artificial Intelligence | Enhances decision-making, improves predictive maintenance, and optimizes resource allocation. |
| 3D Printing | Allows for custom manufacturing, reduces waste, and enables on-demand production. |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Improves supply chain efficiency and enables real-time monitoring of equipment and inventory. |
As technology continues to evolve, its influence on industrial operations becomes more pronounced, leading to a more interconnected and efficient global production system. These advances not only contribute to economic growth but also drive the continuous transformation of manufacturing practices across the world.
Role of Transportation in Industrial Development
Transportation plays a crucial role in the growth and expansion of economic sectors by facilitating the movement of raw materials, finished goods, and labor. The efficiency and reliability of transportation networks directly impact production costs, access to markets, and the overall competitiveness of industries. Well-developed transportation infrastructure allows businesses to connect with suppliers and consumers, opening up new opportunities for trade and economic growth.
The development of various transportation modes–such as railroads, highways, ports, and airports–has been essential in determining the locations of manufacturing centers and the distribution of products. Effective transportation systems reduce costs, improve supply chain management, and increase the speed at which goods are brought to market. Furthermore, transportation networks enable the expansion of global trade by linking domestic production with international markets.
Key aspects of transportation that influence industrial development include:
- Cost Efficiency: Reduced transportation costs lower the price of goods and improve access to global markets, allowing industries to scale.
- Speed and Reliability: Fast, dependable transportation ensures timely deliveries and consistent production schedules, leading to higher efficiency.
- Accessibility to Resources: Proximity to transportation hubs facilitates easier access to raw materials, fostering regional industrial growth.
- Market Expansion: Improved transportation allows industries to reach new domestic and international markets, driving economic growth.
Ultimately, the strength of transportation systems not only supports local economies but also influences the broader global economic landscape, shaping how industries grow and evolve over time.
Energy Sources in Industrial Development

The availability and use of energy play a fundamental role in shaping economic activities and determining the location of production facilities. From powering machinery to supporting transportation systems, energy is essential for the functioning of manufacturing processes. The choice of energy sources influences not only the operational costs but also the environmental impact and sustainability of production. Understanding the different energy options and their implications is crucial for analyzing patterns of economic growth and industrial distribution.
Traditional Energy Sources

Historically, the primary energy sources used for industrial activities have been fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. These sources have powered factories, transportation systems, and power plants, driving the expansion of industrialization. Some of the key characteristics of traditional energy sources include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Fossil fuels have traditionally been cheaper and more widely available, making them the preferred energy choice for many industries.
- High Energy Density: Fossil fuels provide a large amount of energy per unit, allowing for high production output.
- Infrastructure Reliance: Industrial systems are often designed around existing fossil fuel infrastructure, making it challenging to transition to alternative sources.
Renewable Energy Sources
As concerns over climate change and environmental sustainability grow, industries are increasingly turning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power. These sources offer more sustainable alternatives with fewer environmental costs. Key benefits of renewable energy include:
- Environmental Impact: Renewable sources produce little to no emissions, helping reduce the carbon footprint of industrial activities.
- Long-Term Availability: Unlike fossil fuels, renewable resources are inexhaustible and can provide a sustainable energy supply for the future.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing innovations in energy storage and efficiency are making renewable energy more viable for large-scale industrial use.
As industries move toward more sustainable energy solutions, the transition from fossil fuels to renewables will continue to shape global economic and industrial landscapes.
Industrialization and Economic Development Link
The relationship between economic progress and the growth of manufacturing and production systems is crucial for understanding how societies evolve. As economies transition from agricultural-based systems to those focused on mass production, the process of industrialization becomes a key driver of change. It brings about shifts in labor, technology, and infrastructure, all of which are foundational for enhancing economic performance and standards of living.
Driving Factors of Economic Growth
Industrialization accelerates the growth of an economy by creating new jobs, boosting productivity, and improving technological innovation. Some of the main ways in which industrial development fosters economic prosperity include:
- Job Creation: The establishment of factories and manufacturing hubs creates a demand for both skilled and unskilled labor, reducing unemployment rates.
- Productivity Enhancement: Advancements in machinery and production methods allow for higher output with fewer resources, driving economic efficiency.
- Technological Advancements: The focus on innovation within industrial sectors leads to the creation of new technologies that improve processes across multiple sectors.
Effects on Global and Regional Economies
The shift towards industrialization also impacts global trade dynamics and regional economic patterns. As nations industrialize, they often become more competitive in international markets, exporting goods and services at scale. Additionally, the process tends to concentrate economic activities in specific regions, creating industrial clusters that become focal points for further growth and development.
Over time, industrialization leads to greater economic interdependence between countries, contributing to globalization and the integration of markets worldwide. These changes often result in improved living standards and better access to goods and services, though they may also present challenges in terms of environmental sustainability and income inequality.
Environmental Concerns in Industrial Processes
The rapid growth of production and manufacturing systems has brought significant economic benefits, but it has also introduced a range of environmental challenges. As factories and production facilities increase in scale, the impact on air, water, and soil quality becomes more pronounced. Understanding the environmental consequences of industrial activities is essential for creating sustainable practices that minimize harm to the planet while maintaining economic output.
Key concerns include pollution, resource depletion, and habitat destruction. These issues not only threaten biodiversity but also contribute to long-term global environmental challenges, such as climate change and ecosystem imbalance. A deeper understanding of how industrial processes influence the environment is crucial for developing effective regulations and technologies that can mitigate these adverse effects.
Air and Water Pollution: Emissions from factories, transportation, and power generation are major contributors to air quality degradation. Harmful pollutants, such as carbon dioxide and particulate matter, contribute to global warming and health issues. Similarly, industrial activities often lead to the contamination of local water sources with chemicals and heavy metals, impacting both aquatic life and human populations dependent on these resources.
Resource Depletion: Intensive industrial activities require vast amounts of raw materials and energy, often leading to the overuse of natural resources. Fossil fuels, minerals, and timber are extracted at rates that far exceed the earth’s ability to regenerate them, raising concerns about the sustainability of such practices in the long term.
Habitat Destruction: Expanding industrial zones and infrastructure developments often result in the destruction of natural habitats, leading to loss of biodiversity. Forests, wetlands, and other ecosystems are increasingly threatened by urban sprawl and the need for space to accommodate growing industries.
While these environmental issues pose significant challenges, advances in green technology, renewable energy, and more efficient production methods offer promising solutions. The integration of sustainable practices into industrial processes is key to reducing negative environmental impacts and ensuring that development occurs in harmony with the natural world.
Historical Evolution of Industrialization
The journey of manufacturing and large-scale production has been one of transformative changes that have reshaped societies across the globe. From humble beginnings, technological innovations, and shifts in economic practices have led to the development of complex production systems. The evolution of these systems has not only influenced the global economy but also drastically altered social, political, and environmental landscapes.
The initial phases of large-scale production were deeply tied to agrarian societies. Early civilizations relied on manual labor, craftwork, and rudimentary tools. However, as societies began to innovate, these methods gradually evolved into more mechanized and organized processes, setting the stage for widespread transformation.
Key Phases of Industrial Evolution
- Pre-Industrial Era: During this period, most production was done by hand in small workshops or by individuals within rural communities. Tools were simple, and labor was predominantly unskilled.
- The First Industrial Revolution: This period, starting in the late 18th century, marked the introduction of machines and new technology, particularly in textiles and steam power. The establishment of factories began to centralize production, dramatically increasing output and efficiency.
- The Second Industrial Revolution: Beginning in the late 19th century, this phase saw advancements in steel production, electricity, and communication technologies. The expansion of railroads and factories led to the growth of urban centers.
- The Third Industrial Revolution: The late 20th century witnessed the rise of automation, computers, and digital technologies, which further transformed manufacturing processes. This era also saw the rise of globalization and the outsourcing of production to various parts of the world.
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution: Currently underway, this revolution is characterized by artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and biotechnology, reshaping production into smarter and more interconnected systems.
Impact of Historical Industrialization
Each phase of industrial evolution brought with it distinct changes in labor patterns, technological advancement, and the distribution of wealth. The shift from agrarian economies to factory-based systems created new job opportunities, though not without significant social disruption. Urbanization, the rise of social classes, and labor movements were some of the key social changes that emerged from this period.
Over time, technological advancements have increasingly transformed traditional industries, leading to more efficient, sustainable, and globally interconnected systems. Understanding the historical evolution of industrialization helps provide insight into the present-day challenges and opportunities facing modern production methods.
Case Studies of Industrial Regions Worldwide
The growth and development of industrial sectors around the world have been shaped by a combination of geography, resources, technological advancements, and economic factors. These regions not only highlight the diverse ways in which production systems have evolved but also reflect the varying impacts these changes have had on local economies, societies, and environments. By examining case studies of industrial regions across different continents, we gain valuable insights into the complex dynamics that influence global manufacturing and economic activities.
Throughout history, several key regions have emerged as powerhouses of production, driven by both local factors such as available resources and external influences such as trade and technological innovations. These areas are not only vital to their own economies but often play a significant role in the global supply chains that connect markets worldwide.
Key Global Industrial Regions
- The Ruhr Valley, Germany: Once the heart of coal and steel production in Europe, this region saw rapid industrialization in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Today, despite deindustrialization, it remains a significant hub for high-tech industries and services.
- The Great Lakes Region, USA and Canada: Known for its vast natural resources and access to the North American market, this area has long been a key site for steel production, automotive manufacturing, and heavy industries. The decline of manufacturing in the latter half of the 20th century has led to a shift toward service-based economies.
- Yangtze River Delta, China: This region is one of the world’s most vibrant and rapidly growing industrial zones, driven by China’s manufacturing boom. The area has become a global center for electronics, textiles, and other consumer goods production, attracting both domestic and international investment.
- Silicon Valley, USA: Known as the tech capital of the world, this region has reshaped global industries by fostering innovation in software, electronics, and information technology. Its emergence as a global leader in high-tech production highlights the shift from traditional heavy industries to knowledge-based economies.
- São Paulo, Brazil: The industrial heart of Brazil, São Paulo, is a key center for automobile manufacturing, machinery, and petrochemicals. Its strategic location and infrastructure make it the main engine of industrial growth in the country.
Challenges and Opportunities
While these regions have experienced remarkable growth, they also face significant challenges such as environmental degradation, labor issues, and the pressures of globalization. In many areas, industries are being restructured to adapt to changing global markets and technological advancements. The shift toward sustainability, the rise of automation, and the increasing demand for cleaner technologies are just some of the factors that are reshaping industrial landscapes.
Understanding these case studies provides valuable lessons for other regions looking to develop their own industrial capacities. By studying the successes and challenges faced by established industrial centers, policymakers and business leaders can better navigate the complexities of the modern industrial economy.
Understanding Major Industrial Sectors
The modern global economy is driven by a wide range of production sectors, each playing a crucial role in shaping the structure of markets, employment, and technological advancements. These sectors are interconnected, often depending on one another to maintain the flow of goods and services across regional and global markets. From heavy manufacturing to technology-driven services, the diversity within industrial sectors is a reflection of evolving consumer demands and innovations.
Each sector within the broader economic system has its unique characteristics, processes, and challenges. Understanding these major sectors is essential for recognizing their influence on economic development, labor markets, and environmental impact. Below is an overview of key sectors that drive the global economy, highlighting their role, scope, and significance.
| Sector | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Sector | This sector involves the extraction and harvesting of natural resources. It includes activities such as mining, agriculture, and fishing. | Agriculture (crops, livestock), Mining (coal, minerals), Fishing, Forestry |
| Secondary Sector | This sector focuses on the transformation of raw materials into finished goods. It includes manufacturing, construction, and production industries. | Automobile Manufacturing, Electronics Production, Textile Factories, Steel Mills |
| Tertiary Sector | The tertiary sector provides services rather than goods. It supports the primary and secondary sectors by providing services such as transportation, retail, and finance. | Retail, Healthcare, Financial Services, Education, Tourism |
| Quaternary Sector | This sector is based on knowledge-based activities. It includes services such as research, technology development, and information management. | Software Development, Scientific Research, Consulting, Information Technology |
| Quinary Sector | The quinary sector involves high-level decision-making, research, and advanced services. It includes roles that require expertise and advanced education. | University Professors, Government Officials, CEOs, Healthcare Specialists |
Each of these sectors plays an essential role in the global economy, influencing everything from local labor markets to international trade dynamics. While traditional sectors such as agriculture and manufacturing remain vital, the rapid growth of knowledge-driven sectors like technology and research is reshaping the global landscape. As economies continue to evolve, understanding the nuances of these sectors will be crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals navigating the future of work and economic development.
Common Mistakes in Chapter 11 Assessments
When preparing for assessments related to economic and spatial patterns of production, there are several common pitfalls that many students encounter. These mistakes can stem from misunderstandings of key concepts, confusion between similar terms, or a failure to fully grasp the underlying principles that govern the location and organization of production. By identifying and addressing these errors, students can improve their understanding and performance in related assessments.
Misunderstanding Key Terminology
One frequent mistake is the confusion between terms that may seem similar but have distinct meanings. For example, students often mix up “agglomeration” and “location factors.” While both are critical to understanding economic clustering, agglomeration refers to the benefits that firms experience by being located near one another, while location factors encompass the broader considerations that influence where businesses decide to establish operations. Properly defining and applying these terms is essential for clear and accurate responses.
Overlooking Regional Variations
Another common error is failing to recognize the importance of regional differences in production processes. Many assessments focus on how economic activities are distributed globally, yet students sometimes overlook how these activities vary within specific regions. For instance, the factors influencing the development of a manufacturing hub in one part of the world may differ significantly from those in another region. Understanding the unique attributes of specific areas is crucial for explaining industrial patterns and growth.
By being mindful of these and other common mistakes, students can enhance their understanding of key concepts and improve their ability to analyze complex economic processes effectively.
How to Excel in Industrial Geography Exams
Achieving top performance in exams that cover economic spatial patterns and production systems requires a strategic approach. It’s not just about memorizing facts, but about understanding the fundamental principles and applying them effectively to different scenarios. Mastering key concepts, recognizing important trends, and practicing with various types of questions are crucial steps in excelling.
1. Understand Core Concepts
Ensure you have a deep understanding of the major factors that shape the location and development of economic activities. This includes:
- Location factors like proximity to resources, labor, and markets
- Economic agglomeration and its role in regional growth
- Key models and theories of production and spatial organization
Once you have a firm grasp on these concepts, apply them to various case studies and real-world examples to reinforce your knowledge.
2. Practice with Past Questions
Familiarizing yourself with past questions is one of the best ways to prepare. Focus on practicing application-based questions, where you are required to analyze and explain specific patterns or trends. Here is an example table of potential questions:
| Question Type | Topic Covered |
|---|---|
| Multiple Choice | Location factors and regional development |
| Short Answer | Economic agglomeration and clustering effects |
| Essay | Comparing industrial development in different regions |
By practicing these types of questions, you’ll develop a clear and organized approach to answering, making it easier to manage your time during the exam.
3. Focus on Key Patterns and Trends
Finally, understanding global patterns, such as the movement of manufacturing to emerging economies, and the role of technology in production processes, is crucial. Recognize how these trends have shaped both developed and developing regions over time.
By staying organized, practicing consistently, and focusing on core concepts and trends, you’ll be well-prepared to excel in exams that evaluate your understanding of economic spatial dynamics and production processes.