
In this section, we explore essential principles that shape the framework of a nation’s governing system. By examining foundational elements, we can better understand how power is distributed and how different branches interact with each other. These concepts are crucial for anyone looking to grasp the core ideas behind the legal structure and rights within the country.
Fundamental rights, governance mechanisms, and the relationship between citizens and their leaders are core topics covered here. We will discuss how these ideas are applied practically and how they affect day-to-day life. This exploration also includes the rules and regulations that ensure balance and fairness in society.
Understanding these concepts prepares individuals for assessments or discussions related to political science. It equips you with the necessary tools to analyze, interpret, and apply knowledge related to governmental structures and legal systems effectively.
Understanding Key Principles in Government Framework
This section dives into critical concepts that form the foundation of a nation’s governing structure. It focuses on the key elements that define how power is distributed, how laws are interpreted, and how different institutions within the government work together to maintain order and protect citizens’ rights.
By exploring important aspects like individual freedoms, legal protections, and the structure of decision-making bodies, this part provides a deeper understanding of how these principles influence daily life. It covers the mechanisms that ensure balance and fairness, and how these principles are applied in various scenarios.
These insights are not only valuable for gaining a clearer view of how government functions but also serve as essential knowledge for anyone preparing for evaluations in political studies or legal frameworks. Understanding these concepts allows for more informed discussions and a better grasp of how laws and rights are upheld within a society.
Overview of Key Topics
This section highlights essential themes that play a crucial role in understanding how governance operates and how rights and responsibilities are structured. It covers fundamental principles that serve as the backbone for legal frameworks and political systems, exploring how laws are applied and interpreted in various contexts. Key discussions focus on the relationship between citizens and governmental bodies, as well as the mechanisms that maintain balance within the system.
Core Principles of Governance
Separation of powers is a central theme, explaining how different branches of government operate independently while ensuring mutual oversight. This principle is vital to preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful and to maintaining fairness across all levels of governance.
Rights and Legal Protections
Individual freedoms and protections are another key area of focus. These legal rights safeguard citizens’ personal liberties and ensure that justice is applied equally to all. This section also discusses the process of amending laws to reflect changing societal needs.
Understanding the Preamble
The opening statement of any foundational document plays a crucial role in establishing the principles upon which the entire framework is built. It serves as a guiding introduction, outlining the core values and goals that the legal system seeks to uphold. By analyzing this part, we can gain insights into the intentions behind the creation of laws and the overall structure of governance.
Key Principles in the Preamble
Within the opening lines, several important concepts are emphasized, such as justice, liberty, and the general welfare. These principles are designed to ensure that the legal and governmental systems serve the people and are accountable to their needs. Understanding these ideas helps clarify the purpose of the system and its foundational commitments.
Purpose of the Preamble
The main function of this introductory section is to set the tone for the entire legal framework. It defines the aspirations of the document and acts as a declaration of intent, ensuring that the system is aligned with specific values and goals. These guiding principles often serve as a standard for evaluating the effectiveness of governance over time.
| Key Concept | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Justice | Ensuring fairness and equality for all citizens under the law. |
| Liberty | Protecting individual freedoms and personal rights. |
| Welfare | Promoting the well-being and prosperity of all individuals in society. |
Important Clauses in Chapter 3
This section delves into significant provisions that define the structure and operation of the legal system. These clauses outline the essential rules that govern how power is distributed, how rights are protected, and how laws are implemented. Each clause plays a pivotal role in shaping the framework of governance and ensuring a fair and just system for all citizens.
By examining these clauses, we gain a better understanding of the core principles behind the functioning of government institutions. They serve as a foundation for interpreting laws and ensuring that actions taken by the state align with the broader goals of equality, justice, and liberty.
Some of the most important clauses focus on the division of powers, individual rights, and the responsibilities of governmental bodies. These sections also provide a mechanism for resolving conflicts and adapting to changing circumstances, ensuring that the system remains dynamic and responsive.
How the Bill of Rights Relates
This section explores the essential role that a specific set of legal protections plays in safeguarding individual freedoms and limiting government power. These provisions directly address the need for protecting personal rights and ensuring that any actions by authorities align with fundamental principles of justice. They serve as a crucial safeguard against abuses of power and a reminder of the rights that all citizens are entitled to.
Key Provisions and Their Impact
These legal protections focus on a variety of important issues, from freedom of speech to the right to a fair trial. By outlining specific freedoms, they guarantee that certain actions by government bodies cannot infringe upon citizens’ personal rights. Understanding how these rights are applied is vital for anyone looking to interpret or engage with the legal system.
- Freedom of speech: Protects individuals’ ability to express their opinions without government interference.
- Right to assembly: Ensures that citizens can gather and protest peacefully without fear of retaliation.
- Right to a fair trial: Guarantees that individuals accused of crimes will receive a fair and impartial hearing.
- Protection against self-incrimination: Prevents individuals from being forced to testify against themselves in legal matters.
Relation to Modern Legal Interpretations
The principles outlined in these protections continue to shape legal discussions and interpretations today. They serve as a baseline for assessing whether actions taken by government bodies adhere to the fundamental rights of individuals. These clauses not only apply in the context of historical events but are essential in ensuring ongoing fairness and equality under the law.
The Role of Judicial Review
This section examines the critical function of judicial oversight in maintaining the balance of power within a governing system. It involves the ability of courts to assess the legality of actions taken by other branches of government, ensuring that all decisions comply with established laws and principles. This process acts as a check on governmental power and is essential for preserving the integrity of the legal system.
Judicial review plays a significant role in upholding fundamental rights and ensuring that laws do not violate established protections. By reviewing the actions of legislative and executive branches, courts serve as a safeguard against potential overreach or unconstitutional actions. It ensures that no branch of government exceeds its authority or acts outside its given scope.
Through this process, courts have the power to strike down laws or executive actions that are deemed inconsistent with higher legal principles. This mechanism ensures that all decisions align with core values such as justice, fairness, and equality, reinforcing the rule of law within society.
Separation of Powers Explained
This section explores the division of authority among various branches of government to ensure that no single entity holds excessive power. By clearly outlining the distinct roles and responsibilities of different governing bodies, this principle prevents any one branch from becoming too dominant and allows for checks and balances across the system.
The separation of powers serves as a fundamental structure, promoting accountability and transparency. It guarantees that each branch has its own specific functions, ensuring that decisions are made collaboratively and within the scope of the law.
Key Branches and Their Roles
- Legislative Branch: Responsible for creating laws and overseeing the implementation of policy.
- Executive Branch: Enforces laws and manages the day-to-day operations of government.
- Judicial Branch: Interprets laws and ensures that they are applied consistently and fairly.
Importance of Balance
By maintaining this balance, the system prevents the abuse of power and ensures that each branch can function independently while still holding the others accountable. This structure is essential for preserving democratic principles and protecting individual freedoms within society.
Federalism and Its Application
This section examines the division of power between central and regional authorities, ensuring that both levels of government operate within their defined roles. The system is designed to balance governance between national and local jurisdictions, allowing for more localized decision-making while maintaining unity across the entire country.
Federalism plays a crucial role in ensuring that local needs are addressed effectively while also preserving national cohesion. By granting certain powers to states or provinces and reserving others for the national government, this system allows for flexibility and adaptation to diverse regional conditions without undermining the overall framework.
Through this framework, both levels of government share responsibilities for things like law enforcement, education, and infrastructure, while also having distinct areas of authority. Understanding how federalism is applied helps clarify how various issues are managed and resolved in both local and national contexts.
The Impact of Constitutional Amendments
In this section, we explore how modifications to foundational legal documents can reshape the framework of governance and affect the rights and responsibilities of citizens. Amendments serve as a mechanism for adapting laws to changing societal needs and ensuring that the legal system remains relevant over time. These changes reflect the evolving values and priorities of a nation.
Key Effects of Amendments
Amendments often address gaps or clarify principles in existing laws, providing greater protections or altering the balance of power. They can enhance individual freedoms, refine governmental authority, and address unforeseen challenges that arise over time.
- Expanding Rights: Amendments may extend civil liberties, such as voting rights or freedom of speech, to more citizens.
- Shaping Governance: Changes can impact the structure and function of government, altering the relationship between national and local authorities.
- Addressing Social Issues: They can address pressing social or economic issues, such as equality or welfare, by aligning legal frameworks with contemporary values.
Challenges and Benefits
While amendments offer a way to improve the legal system, they can also present challenges. The process of making changes can be lengthy and contentious, requiring widespread consensus. However, their long-term benefits include a more responsive and adaptable system that reflects the collective will of the people.
Key Supreme Court Cases Discussed
This section focuses on landmark judicial rulings that have significantly shaped the legal landscape. These cases have had profound implications on the interpretation of laws, individual rights, and the distribution of power among government branches. They serve as essential examples of how judicial review functions in practice and how courts interpret foundational principles in contemporary contexts.
Each case reflects a pivotal moment in legal history, where the highest court’s decision influenced societal norms, clarified legal ambiguities, and often set precedents that guide future rulings. Understanding these cases is crucial for grasping the dynamic nature of the legal system and how it adapts to new challenges.
Example of Key Cases:
- Marbury v. Madison: Established the principle of judicial review, allowing courts to invalidate unconstitutional laws.
- Brown v. Board of Education: Ruled that racial segregation in public schools was unconstitutional, marking a turning point in civil rights.
- Roe v. Wade: Recognized a woman’s constitutional right to choose an abortion, addressing privacy and reproductive rights.
These cases not only reflect important legal shifts but also demonstrate how the judiciary influences public policy and societal change over time. They continue to serve as key references for legal professionals and scholars, shaping ongoing debates and legal reforms.
Understanding Checks and Balances
This section explains the system designed to prevent any single branch of government from becoming too powerful. By distributing authority across multiple branches, each with its own set of responsibilities, this system ensures that power is not concentrated in one place. It promotes accountability and helps maintain the balance of governance.
Checks and balances involve a series of mechanisms where each branch has the ability to limit the actions of the others. This interdependence prevents abuses of power and encourages cooperation between legislative, executive, and judicial bodies.
How It Works
- Legislative Branch: Has the power to create laws but can be checked by the executive, which can veto legislation. The judiciary can also rule laws unconstitutional.
- Executive Branch: Enforces laws and has the authority to appoint judges, but its actions can be checked by the legislature through impeachment or budget control.
- Judicial Branch: Interprets laws and can invalidate actions by both the executive and legislative branches if they are deemed unconstitutional.
Benefits of the System
- Prevents Power Abuse: Ensures no single branch can dominate or act without oversight.
- Encourages Collaboration: Forces cooperation between branches to enact or challenge laws and decisions.
- Protects Rights: Helps safeguard individual rights by preventing governmental overreach.
This system of checks and balances is fundamental to maintaining a democratic framework, ensuring that all branches function within their designated powers while maintaining fairness and justice. It is a key element in preserving the rule of law and ensuring that no entity can act unchecked.
Citizens’ Rights Under the Constitution
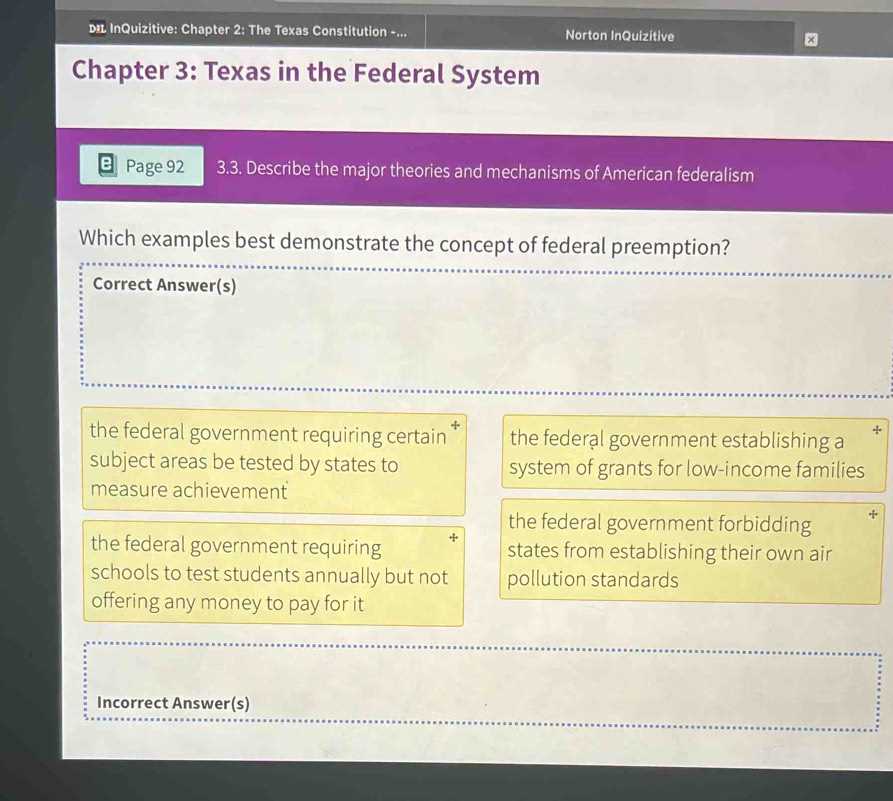
This section examines the fundamental liberties and protections afforded to individuals, ensuring that citizens are free to express themselves, participate in government, and live without fear of unwarranted government intrusion. These rights are central to maintaining a fair and just society, promoting equality, and safeguarding personal freedoms.
Over time, various laws and amendments have strengthened these protections, making sure that the rights of all citizens, regardless of background, are upheld. These rights are designed to protect people from abuses of power, providing a framework for equal treatment and freedom of expression.
Key Rights and Freedoms
| Right | Description |
|---|---|
| Freedom of Speech | Ensures individuals can express their opinions without government interference or censorship. |
| Right to a Fair Trial | Guarantees the right to a public trial, legal counsel, and an impartial jury. |
| Freedom of Religion | Protects the right to practice any religion or none at all, without government control. |
| Right to Privacy | Protects citizens from unreasonable searches and seizures, ensuring personal privacy. |
These essential rights form the bedrock of a democratic society, ensuring that individuals have the opportunity to participate fully in civic life and to be protected from unfair treatment or discrimination. It is through such protections that personal freedoms can thrive in a modern society.
Structure of the Federal Government
The framework of governance is divided into multiple branches, each with its own set of powers and responsibilities. This design ensures that no single entity becomes too dominant, and that checks and balances are in place to prevent abuses of power. The system is structured to allow for both efficiency in governance and protection of individual liberties.
Each branch plays a distinct role in the legislative, executive, and judicial functions, contributing to the broader function of maintaining a balance between authority and accountability. Understanding how each branch operates is crucial to recognizing how decisions are made and how power is distributed.
Key Branches and Their Roles
- Legislative Branch: Responsible for creating laws, this body is made up of elected representatives who deliberate and pass legislation based on the needs and desires of the population.
- Executive Branch: Tasked with implementing and enforcing laws, this branch is led by an elected head of government who has the authority to make decisions on domestic and foreign policy.
- Judicial Branch: Interprets laws and ensures they are applied fairly, resolving disputes and determining the constitutionality of laws through its court system.
Interdependence and Collaboration
While each branch is independent, they are also interdependent, ensuring a balance of power. This interrelationship helps prevent any branch from overstepping its authority and guarantees that no decision is made unilaterally. The collaborative process is designed to foster fairness and protect the rights of citizens.
This structure of government aims to create a stable system where checks and balances prevent any one branch from overpowering the others, ensuring that the needs and rights of individuals are always considered in decision-making processes.
Interpreting the Necessary and Proper Clause
This provision grants authority for actions that are not explicitly outlined but are essential for carrying out powers that are specified. It is often seen as a flexible tool, allowing lawmakers to adapt and address new situations that were not foreseen at the time of its creation. The broad scope of this clause has led to various interpretations over time, with debates on its limits and applications.
Over the years, this clause has been crucial in expanding the powers of the governing body, enabling it to act beyond the literal text and meet the evolving needs of society. However, this flexibility also brings challenges in defining what is deemed “necessary” and “proper,” raising questions about the balance of power between state and national authorities.
Scope and Limitations
- Broad Interpretation: Some argue that this clause provides extensive authority, allowing the governing body to take any action deemed necessary to achieve its goals.
- Narrow Interpretation: Others believe that the clause should only be used to enact laws directly related to the enumerated powers and not as a means to justify wide-ranging actions.
Key Court Cases and Rulings
Over time, judicial decisions have shaped the understanding of this clause. Key rulings have established precedents that continue to influence its interpretation today, determining how far-reaching its applications can be. These decisions help clarify when the clause can be used and when its powers might be deemed overextended.
Understanding this provision is essential for grasping the broader legal and political landscape, as it continues to play a central role in shaping governmental authority and the limits of its power.
The Significance of Constitutional Interpretation
Interpretation plays a critical role in understanding and applying foundational legal principles. It serves as the bridge between historical texts and modern-day governance, ensuring that these principles remain relevant in an ever-changing world. This process determines how laws are understood, enforced, and adapted to current societal needs, creating an ongoing dialogue between past intentions and contemporary challenges.
Different approaches to interpretation can significantly influence the power structure, citizens’ rights, and the overall legal framework. Whether viewed through a strict or flexible lens, each interpretation method carries its own implications for the scope of authority and governance.
Types of Interpretative Approaches
- Originalism: Emphasizes the understanding and intent of those who drafted the text, aiming to apply it as they would have understood it in their time.
- Living Constitution: Argues for a more dynamic interpretation, adapting the text’s meaning to fit evolving societal values and conditions.
Impact on Legal Precedents
How the text is interpreted can set crucial legal precedents. These decisions help shape future rulings and can influence public policy for generations. Interpretive methods guide courts in addressing complex issues, from individual rights to governmental powers, and define the limits of each.
The significance of interpretation is not just academic; it impacts day-to-day governance and citizens’ interactions with the legal system, highlighting its pivotal role in upholding justice and fairness across the nation.
How to Prepare for Government Evaluations
Preparation for legal and governmental assessments requires a structured approach to mastering key principles, historical documents, and relevant legal doctrines. A comprehensive understanding of foundational principles, along with their application in modern contexts, is essential for performing well on these evaluations. Focus should be placed on grasping both the theoretical concepts and practical implications that shape governance and law.
To excel in these evaluations, it’s important to review historical documents, study landmark rulings, and understand how different branches of power interact. Creating detailed notes, revising case studies, and taking practice assessments can provide an edge, helping reinforce important ideas and terms that are likely to appear.
Study Tips for Success
- Break Down Key Concepts: Focus on core topics such as individual rights, governmental powers, and the relationship between different branches.
- Review Historical Documents: Go over foundational documents and understand the context in which they were written and their impact over time.
- Practice with Sample Questions: Take practice quizzes or mock assessments to get familiar with the format and identify areas for improvement.
Utilizing Resources Effectively
Using study guides, online resources, and discussion forums can also help deepen your understanding. Engage with others who are preparing for similar assessments to exchange knowledge, clarify doubts, and gain insights into different interpretative approaches. Consistent practice and active learning are key to mastering the subject matter.
Common Mistakes to Avoid on the Exam
During assessments focused on governance and legal principles, many students make common errors that can negatively affect their performance. These mistakes often stem from misinterpretation of key concepts, overlooking details in questions, or failing to effectively apply knowledge in practical scenarios. Being aware of these pitfalls can help you approach the evaluation with confidence and avoid preventable mistakes.
Understanding both the theoretical and practical aspects of governance is essential. However, many candidates focus too heavily on memorizing facts rather than developing a deeper understanding of the principles behind them. This can lead to answers that are technically correct but lack depth or clarity. To succeed, aim for a balance between memorization and comprehension.
Key Mistakes to Avoid
| Common Mistake | How to Avoid It |
|---|---|
| Overlooking Key Terms | Pay close attention to terminology, definitions, and specific phrasing used in questions. |
| Failing to Read Instructions Carefully | Always read questions thoroughly to understand exactly what is being asked before answering. |
| Relying Solely on Memory | Understand the reasoning behind concepts and be able to apply them in different contexts, not just memorize facts. |
| Ignoring Practice Questions | Regularly practice with sample questions and review past assessments to familiarize yourself with the format. |
By actively avoiding these common pitfalls, you’ll be better prepared to showcase your knowledge and reasoning skills in the evaluation, leading to more accurate and comprehensive responses.