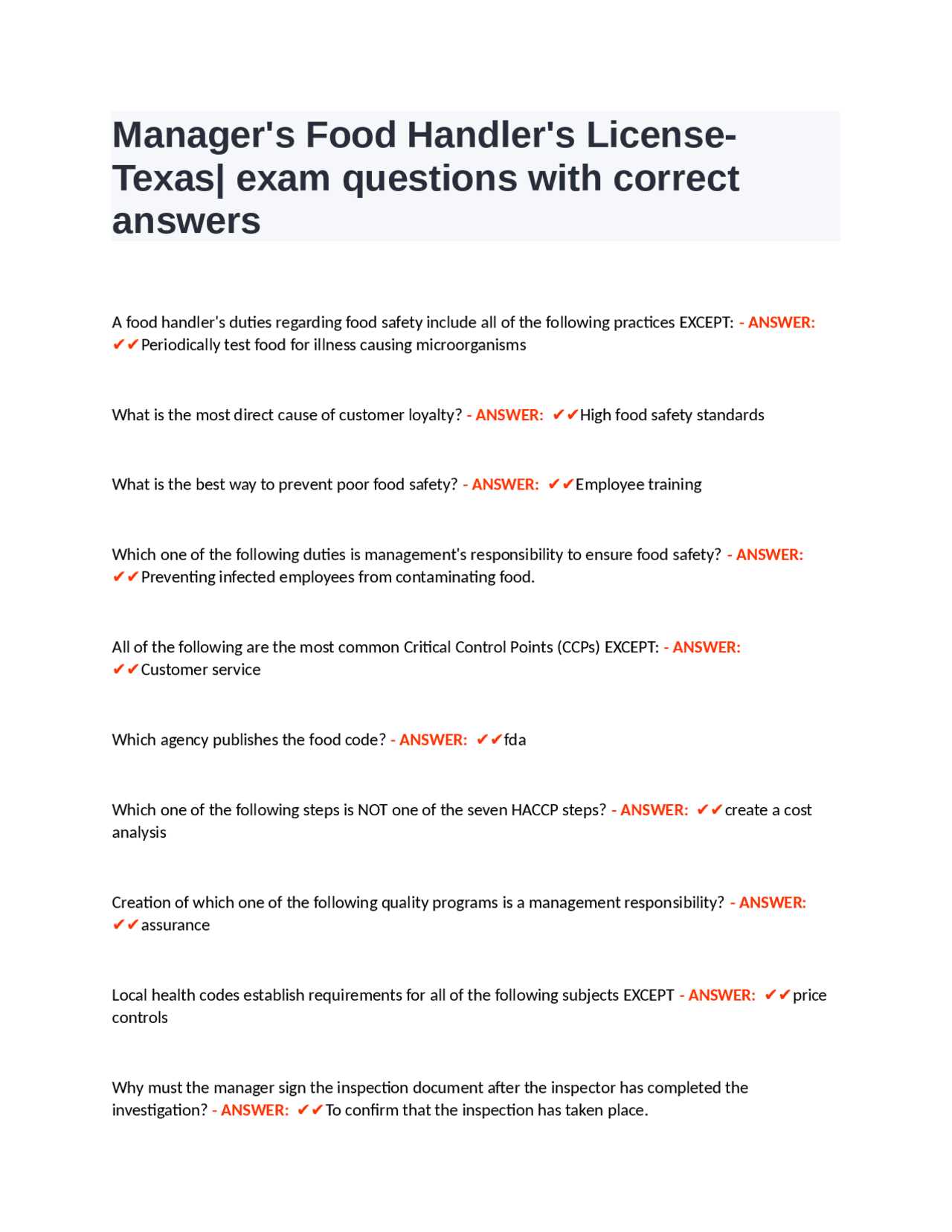
Ensuring the safety of meals in any kitchen or food-related business is a fundamental responsibility. Proper techniques and protocols are necessary to maintain hygiene, prevent contamination, and protect consumers. This section highlights the critical practices that every individual involved in food preparation and service should understand thoroughly.
From basic hygiene practices to temperature control and safe storage, mastering these essential skills is crucial. Adopting the right habits not only prevents health risks but also builds trust with customers and upholds industry standards. Whether working in a restaurant, café, or catering service, these core principles are vital for a safe and efficient environment.
As you explore these concepts, you’ll find valuable insights that help in real-world situations. By applying this knowledge, individuals can contribute to maintaining high safety standards and ensuring the wellbeing of those who rely on the food they prepare and serve.
Food Safety Basics for Beginners
For those just starting in the culinary industry, understanding the fundamental practices that ensure safe meal preparation is crucial. It’s essential to develop a clear understanding of personal hygiene, sanitation, and the prevention of contamination. These basic practices form the foundation for a successful career in any food-related field.
Newcomers to the industry must familiarize themselves with the necessary procedures to protect both themselves and their customers. Simple habits, such as proper handwashing, wearing appropriate attire, and maintaining a clean work environment, can significantly reduce health risks. Developing awareness of common safety protocols ensures a more efficient and safer workplace.
For beginners, the focus should be on learning the core principles and applying them consistently. This not only helps in daily tasks but also establishes a strong safety mindset that will support long-term success in any food establishment.
Key Concepts of Safe Meal Preparation

Maintaining a safe environment during meal preparation is essential to prevent contamination and ensure the wellbeing of consumers. There are several core principles that everyone involved in food production must understand and apply regularly. These principles not only help reduce health risks but also establish a professional standard within any kitchen.
Hygiene is one of the most critical aspects. This includes practices such as washing hands frequently, keeping nails trimmed, and wearing clean uniforms to minimize the spread of harmful bacteria. In addition, proper cleaning and sanitizing of surfaces, utensils, and equipment is essential to eliminate any pathogens that could potentially cause harm.
Another important concept is temperature control. Storing ingredients and cooked items at the correct temperature prevents the growth of bacteria. Proper cooling and reheating methods should always be followed to avoid any contamination risks. Additionally, avoiding cross-contamination by separating raw and cooked items is a vital practice for keeping meals safe for consumption.
Common Mistakes in Food Safety
Even experienced individuals in the culinary field can make errors that compromise safety standards. Some of these mistakes can lead to serious health risks, making it essential to be aware of common oversights. Identifying these missteps and correcting them is key to maintaining a safe environment for both workers and consumers.
1. Inadequate Hand Hygiene
One of the most frequent mistakes involves not washing hands thoroughly and regularly. This simple but crucial task can prevent the spread of harmful bacteria. However, many overlook it or perform it incorrectly, which increases the chances of contamination.
- Not washing hands before and after handling raw ingredients
- Skipping hand washing after touching surfaces or trash
- Failure to scrub for the recommended duration
2. Improper Temperature Control
Another common mistake is failing to manage temperatures effectively. Improperly storing ingredients or cooked items at the wrong temperatures allows bacteria to multiply, leading to potential health hazards. This mistake is often due to lack of awareness or carelessness in following established guidelines.
- Leaving perishable items at room temperature for too long
- Not using thermometers to check cooking or storage temperatures
- Improper cooling and reheating of leftovers
Understanding Personal Hygiene in Food Handling
Maintaining personal cleanliness is a fundamental aspect of ensuring a safe and sanitary environment in any culinary setting. Proper hygiene practices not only protect individuals but also prevent the transfer of harmful microorganisms to ingredients and surfaces. Developing a strong hygiene routine is essential for anyone involved in food preparation or service.
Key hygiene practices include regular hand washing, wearing clean attire, and maintaining overall cleanliness. These habits significantly reduce the risk of contamination and ensure that meals are prepared in a safe environment. Neglecting these simple actions can lead to the spread of illnesses and jeopardize consumer health.
- Handwashing: Wash hands thoroughly before and after handling ingredients, using the restroom, or touching any surfaces that may have been contaminated.
- Clean Clothing: Always wear clean aprons and gloves. Uniforms should be free from dirt and food residue to minimize the spread of harmful bacteria.
- Hair and Nail Care: Ensure that hair is tied back and nails are trimmed. Long or unkempt hair can transfer contaminants to the food, while long nails can harbor bacteria.
- Personal Health: Workers should avoid working while sick, especially if experiencing symptoms such as coughing, sneezing, or gastrointestinal issues.
How to Prevent Cross-Contamination

Cross-contamination occurs when harmful microorganisms are transferred from one surface or item to another, potentially leading to foodborne illnesses. Preventing this is a critical step in maintaining a safe environment in any kitchen or food-related setting. By understanding and practicing key methods, you can minimize the risks associated with this issue.
One of the most effective ways to prevent cross-contamination is through proper separation of raw and ready-to-eat items. It’s essential to ensure that raw ingredients like meat, poultry, and seafood are kept separate from items that will not be cooked, such as salads and fruits. This can be done by using different utensils, cutting boards, and storage containers for each type of product.
- Use Separate Equipment: Always designate separate knives, cutting boards, and utensils for raw and cooked items.
- Proper Storage: Store raw ingredients in sealed containers on the bottom shelves of refrigerators to prevent drips or spills onto ready-to-eat foods.
- Thorough Cleaning: Clean and sanitize all surfaces and utensils after handling raw items to eliminate any lingering bacteria.
- Hand Hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly between tasks to avoid transferring pathogens from raw products to other foods.
The Role of Temperature Control
Effective temperature management is crucial in ensuring the safety and quality of meals. Keeping items at the correct temperatures prevents the growth of harmful bacteria and helps preserve the nutritional value and taste of ingredients. Understanding how to control temperatures throughout the preparation, cooking, and storage processes is essential for maintaining a safe environment.
There are specific temperature ranges for both cooking and storing ingredients that help minimize the risk of contamination. For example, perishable items should be kept chilled to slow bacterial growth, while hot dishes need to be served at high enough temperatures to kill any pathogens. By maintaining these temperature guidelines, the risk of illness can be significantly reduced.
| Temperature Range | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Below 5°C (41°F) | Keep perishable items refrigerated to prevent bacterial growth. |
| Between 60°C and 75°C (140°F – 167°F) | Hot foods should be maintained at this range to prevent the growth of pathogens. |
| Above 75°C (167°F) | Cooking temperature for most dishes to ensure safety and kill harmful bacteria. |
Best Practices for Cleaning and Sanitizing
Maintaining a clean and sanitized environment is essential for preventing contamination and ensuring safety. Regular cleaning and proper sanitization help eliminate harmful pathogens, reduce the risk of illness, and create a safe space for preparation and service. Establishing a thorough and effective cleaning routine is a key responsibility in any kitchen or food-related setting.
The process of cleaning involves removing dirt, grease, and debris, while sanitizing focuses on eliminating harmful microorganisms. Both steps are crucial and should be done in the correct order to maximize effectiveness. Additionally, using the right cleaning agents and equipment is necessary to achieve proper results.
Cleaning and Sanitizing Procedure

- Step 1: Remove visible debris and dirt from surfaces using a brush, cloth, or scraper.
- Step 2: Use a suitable detergent or cleaner to wash surfaces, followed by rinsing to remove any residue.
- Step 3: Apply a sanitizer to kill any remaining pathogens, and allow it to sit for the recommended contact time before wiping off.
Common Cleaning and Sanitizing Tools
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Brushes | Used for scrubbing surfaces and equipment to remove debris. |
| Microfiber Cloths | Effective for wiping surfaces without leaving lint or residue. |
| Sanitizing Solutions | Chemicals used to kill harmful microorganisms and ensure cleanliness. |
Storage Guidelines for Safety
Proper storage of ingredients and prepared items is essential to prevent contamination and maintain freshness. Following correct procedures for organizing, refrigerating, and storing items can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses. This involves understanding the correct temperatures, shelf placement, and handling practices to ensure everything remains safe for consumption.
One of the most important aspects of safe storage is keeping perishable items at the right temperatures. Items should be stored at different temperatures depending on whether they need refrigeration or can be kept at room temperature. Additionally, items should be organized in a way that minimizes cross-contamination and allows easy access to prevent improper handling.
Temperature Guidelines for Safe Storage
- Refrigeration: Keep perishable items like dairy, meat, and cooked dishes below 5°C (41°F) to slow bacterial growth.
- Freezing: Store frozen items at -18°C (0°F) or lower to preserve their quality and prevent spoilage.
- Room Temperature: Only store dry goods such as grains, canned foods, and certain fruits at room temperature, ensuring they are in cool, dry areas.
Best Practices for Storage Organization
- Separate Raw and Cooked Items: Always store raw ingredients separately from ready-to-eat items to avoid cross-contamination.
- Proper Labeling: Label all items with dates to ensure they are used within safe time frames.
- Use Airtight Containers: Store ingredients in tightly sealed containers to maintain freshness and prevent contamination from pests.
Recognizing Foodborne Illness Symptoms
Identifying the symptoms of illnesses caused by contaminated items is crucial for early intervention and treatment. These symptoms often vary depending on the type of bacteria, virus, or parasite involved but typically include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Recognizing these signs early can help prevent further spread and promote quicker recovery.
People who experience symptoms like stomach cramps, fever, and dehydration should seek medical attention, especially if symptoms persist or worsen. It’s important to remember that some individuals, such as the elderly, young children, and those with weakened immune systems, are more susceptible to severe effects from these illnesses.
Common Symptoms to Watch For

- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling sick and throwing up are common early signs of infection.
- Diarrhea: Frequent, loose stools can signal contamination, especially when accompanied by other symptoms.
- Stomach Cramps: Abdominal pain and discomfort are common indicators of digestive issues.
- Fever: A mild or high fever can accompany foodborne illnesses as the body tries to fight off infection.
- Dehydration: Severe dehydration can occur due to prolonged vomiting and diarrhea, leading to dryness of the mouth, decreased urination, and dizziness.
When to Seek Medical Help
- Persistent Symptoms: If symptoms last for more than a couple of days or worsen, it’s essential to seek medical attention.
- Severe Dehydration: If the individual becomes severely dehydrated, seek immediate care, especially in vulnerable populations.
- High Fever or Blood in Stool: If there is blood in the stool or the individual develops a high fever, professional medical care is necessary.
The Importance of Handwashing in Food Prep
Proper hand hygiene is one of the most essential practices in ensuring the safety and quality of meals. Hands can easily carry harmful microorganisms that, if transferred to ingredients or surfaces, can lead to contamination. Washing hands thoroughly before and during preparation helps prevent the spread of these pathogens, ensuring that meals remain safe for consumption.
In environments where raw ingredients are handled or ready-to-eat items are prepared, maintaining clean hands becomes even more critical. Not only does it reduce the risk of illness, but it also ensures that the entire process is as sanitary as possible, from start to finish. It’s a simple yet highly effective method to safeguard the well-being of everyone involved in meal preparation.
When to Wash Hands
- Before Starting Preparation: Wash hands thoroughly before beginning any cooking or handling tasks.
- After Touching Raw Ingredients: Always wash hands after handling raw items like meat, poultry, or eggs to avoid cross-contamination.
- After Using the Restroom: Personal hygiene practices, including handwashing, are essential after any restroom use to prevent the spread of bacteria.
- After Handling Waste: Hands should be washed after touching trash or waste items to eliminate any harmful microorganisms.
Proper Handwashing Technique
- Wet Hands: Begin by wetting your hands with clean, running water.
- Apply Soap: Lather soap onto hands and scrub all surfaces, including between fingers and under nails, for at least 20 seconds.
- Rinse and Dry: Rinse thoroughly with running water and dry hands using a clean towel or air dryer.
Training Requirements for Food Handlers

Ensuring that individuals involved in meal preparation and service are properly educated on hygiene, safety, and proper handling practices is crucial to maintaining public health. This education typically involves a series of courses or certifications that equip staff with the knowledge necessary to prevent contamination, ensure the safety of ingredients, and manage the preparation process effectively. Training covers a range of essential topics, from understanding the risks of foodborne illnesses to learning proper cleaning techniques.
These requirements vary depending on the role, the local regulations, and the specific setting in which food is being prepared or served. In many cases, staff members need to complete a foundational course and periodically refresh their knowledge through ongoing education or certification renewal programs. Compliance with these standards is essential not only for safety but also for the overall reputation of the establishment.
Basic Training Areas for Staff Members
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Sanitation Practices | Understanding proper hygiene, handwashing, and surface cleaning techniques to prevent contamination. |
| Temperature Control | Learning the correct temperatures for cooking, holding, and storing items to minimize risks. |
| Cross-Contamination Prevention | Identifying ways to avoid mixing raw and cooked items and using separate tools for different ingredients. |
| Health and Illness Policies | Recognizing symptoms of illnesses that could be transmitted through improper handling and understanding when to stay home. |
Certification and Ongoing Education
- Initial Certification: Typically required before beginning work in the food service or preparation industry.
- Refresher Courses: Many regions require periodic updates to ensure that employees stay current with evolving safety standards and regulations.
- Specialized Training: Some roles may require advanced courses, such as food safety management or allergen awareness, to address specific risks.
Food Safety Regulations You Must Know
Understanding the rules and standards governing safe meal preparation is essential for maintaining public health and preventing illnesses. These regulations provide guidelines for how ingredients should be handled, stored, and cooked to ensure they remain free from harmful contaminants. Whether you work in a restaurant, catering service, or other food-related fields, adhering to these standards is crucial for safeguarding consumers and ensuring the overall success of the establishment.
These rules vary by location and industry, but there are fundamental principles that apply universally. By following these regulations, employees can help prevent the spread of harmful bacteria and ensure a safe environment for everyone involved in the preparation and consumption process.
Key Regulations to Follow
- Temperature Control: Ensure that all ingredients are stored at the correct temperatures to prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms. Refrigerators should be at or below 40°F (4°C), and hot foods should be held above 140°F (60°C).
- Proper Handwashing: Employees must wash their hands frequently, particularly after handling raw ingredients or using the restroom. Proper handwashing can significantly reduce the risk of contamination.
- Cross-Contamination Prevention: Use separate equipment and surfaces for raw and cooked items to prevent harmful pathogens from spreading. This includes knives, cutting boards, and utensils.
- Sanitizing Procedures: Regularly clean and sanitize all food preparation areas, surfaces, and equipment to eliminate potential contaminants. Ensure that sanitizers are approved and used correctly.
Health and Safety Reporting
- Illness Reporting: Employees must report any signs of illness, particularly those that could be transmitted through handling ingredients, such as vomiting, diarrhea, or fever.
- Inspection Compliance: Regular health inspections ensure that businesses comply with safety regulations. Always be prepared for inspections and ensure that your team is well-versed in maintaining compliance.
- Allergen Management: Properly label all ingredients and products to ensure they are safe for consumers with allergies. It is essential to avoid cross-contact between allergens and non-allergenic ingredients.
How to Handle Allergens Properly

Managing allergens effectively is a crucial aspect of maintaining a safe environment for everyone involved in meal preparation and consumption. Since allergens can cause serious reactions in individuals, it is essential to take the necessary precautions to prevent cross-contact and ensure that ingredients containing allergens are correctly labeled and stored. Proper handling minimizes the risk of exposure and ensures the safety of those with sensitivities.
To properly handle allergens, it is important to educate staff on identifying common allergens, preventing their contamination with other ingredients, and recognizing symptoms of allergic reactions. Establishing clear protocols and maintaining a safe workspace will help ensure that food safety is prioritized for everyone involved.
Key Practices for Allergen Safety

- Segregation: Store allergenic ingredients separately from other items to avoid accidental contamination. Designate specific areas or containers for allergen-containing products.
- Labeling: Ensure that all products containing allergens are clearly labeled, both for staff and consumers. This includes marking packages, menus, and prepared items.
- Dedicated Equipment: Use separate utensils, cutting boards, and other tools for allergen-containing ingredients. Always clean and sanitize equipment after use to prevent cross-contact.
- Staff Education: Train all employees on recognizing allergens, cross-contamination risks, and proper handling procedures to ensure they are aware of the necessary precautions.
Steps to Prevent Allergen Cross-Contact
- Thorough Cleaning: Clean surfaces, utensils, and equipment thoroughly after handling allergenic ingredients. Use appropriate cleaning agents to remove traces of allergens.
- Hand Hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly after handling any allergen-containing ingredients to prevent transferring allergens to other foods or surfaces.
- Monitor Symptoms: Be aware of symptoms of allergic reactions such as swelling, difficulty breathing, or hives. Ensure that employees know what to do in case of an emergency.
Managing Food Safety During Service
Ensuring safety during service is essential to prevent contamination and ensure that all meals served are safe for consumption. This involves maintaining proper temperatures, managing potential cross-contamination risks, and consistently following hygiene protocols throughout the entire service process. Effective safety practices during meal preparation and delivery directly impact the health and well-being of customers.
To maintain safety during service, it is crucial to monitor key aspects such as temperature control, sanitation of utensils and surfaces, and the proper handling of ready-to-eat meals. Keeping food at safe temperatures and minimizing exposure to contaminants are key strategies to reduce foodborne illness risks during this phase.
Essential Practices for Safe Service
- Temperature Monitoring: Ensure that hot items are kept at a minimum of 140°F (60°C) and cold items at 41°F (5°C) or lower to prevent bacterial growth.
- Clean Utensils and Surfaces: Regularly sanitize all surfaces and utensils used for serving. This includes trays, plates, and serving spoons.
- Minimize Cross-Contamination: Prevent raw ingredients from coming into contact with ready-to-eat items by using separate serving tools and maintaining clear distinctions between food types.
Preventing Contamination Risks During Service
- Proper Storage: Store prepared meals in designated areas to avoid exposure to contaminants, and keep food covered to maintain its safety and quality.
- Employee Hygiene: Ensure that staff wash their hands frequently, especially after handling raw products or before serving meals to customers.
- Serve Immediately: Aim to serve meals promptly to reduce the amount of time food spends in the danger zone (between 40°F and 140°F), where bacteria can thrive.
Creating a Food Safety Culture
Building a culture focused on health and safety in any establishment starts with a shared commitment to best practices at every level of operation. When everyone, from management to staff, prioritizes safe procedures and hygiene standards, it leads to a safer environment for both workers and customers. A strong safety culture fosters an atmosphere where safety becomes second nature and is maintained throughout daily operations.
In order to establish this culture, it is essential to integrate key values such as continuous learning, attention to detail, and accountability. Encouraging employees to take ownership of safety protocols, while providing them with the knowledge and tools they need, can lead to better decision-making and a higher standard of care.
Key Steps to Build a Strong Safety Culture
- Lead by Example: Management must model safe practices at all times, demonstrating a commitment to health and safety that inspires staff to do the same.
- Regular Education: Provide ongoing training and refresher courses to ensure that all employees are up-to-date on the latest safety standards and procedures.
- Encourage Open Communication: Foster a transparent environment where employees feel comfortable reporting safety concerns or suggesting improvements without fear of repercussions.
Fostering Employee Engagement in Safety
- Recognize Safe Practices: Celebrate individuals or teams who consistently follow safety protocols to reinforce the importance of such behavior.
- Provide Incentives: Offering rewards or recognition for maintaining high safety standards can motivate staff to remain committed to best practices.
- Empower Staff: Involve employees in safety audits and decision-making processes to increase their sense of responsibility and ownership over safety efforts.
Essential Tips for Food Handler Exams
Preparing for exams that assess your knowledge of health and safety protocols is crucial for ensuring you can apply the best practices in your work environment. A solid understanding of key concepts and the ability to recall important information quickly are essential for passing the test. Proper preparation not only boosts confidence but also enhances your ability to make informed decisions in real-world scenarios.
To succeed, focus on grasping the most frequently tested topics. These include sanitation standards, temperature control, allergen awareness, and methods for preventing contamination. The more familiar you are with these core concepts, the more prepared you’ll be for any questions that may come up.
Study Strategies for Success
- Review Key Topics: Focus on areas that are most likely to appear in the exam, such as personal hygiene, safe storage practices, and safe cooking temperatures.
- Practice Mock Exams: Take practice tests to familiarize yourself with the format and timing. This will help you identify weak spots and improve your ability to answer under pressure.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards for essential terms and guidelines to reinforce your memory and make study sessions more interactive.
Exam Day Tips
- Read Instructions Carefully: Take time to read each question thoroughly before answering. Misunderstanding the question can lead to unnecessary mistakes.
- Stay Calm: Stay relaxed and focused during the exam. Stress can hinder your ability to recall information accurately, so take deep breaths if you feel anxious.
- Manage Your Time: Keep track of time and allocate it wisely. Ensure that you have enough time to answer every question, leaving no items incomplete.