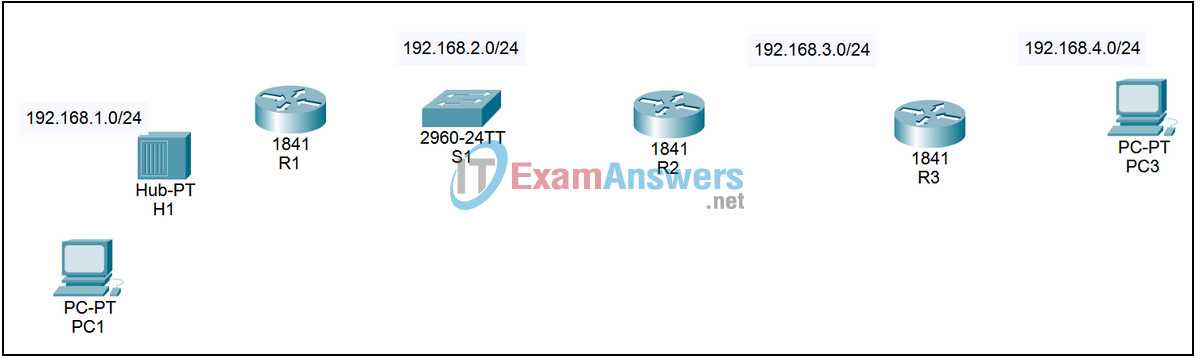
In this section, we explore how to effectively approach and solve networking challenges in simulation environments. These exercises are designed to help users enhance their skills in configuring devices, managing network protocols, and troubleshooting common issues. Mastering these tasks provides valuable hands-on experience that strengthens understanding of network operations.
By following step-by-step solutions, you can gain confidence in identifying and resolving potential problems within simulated scenarios. These tasks are not only helpful for beginners but also serve as a useful reference for more advanced learners aiming to refine their network configuration abilities. Practical application of theoretical concepts is the key to mastering the field of networking.
Whether you are preparing for certification exams or looking to expand your networking expertise, these exercises will guide you through the most crucial steps to success. Learning how to handle network devices and troubleshoot configurations will make you better equipped for real-world networking tasks.
3 Networking Simulation Solutions Overview
This section provides a comprehensive guide to solving common networking exercises within simulated environments. It focuses on key methods and strategies that help users efficiently configure and troubleshoot network setups. By mastering these techniques, individuals can improve their problem-solving skills and gain a deeper understanding of network behavior.
Key Concepts for Solving Networking Tasks
Effective solutions to simulated network problems involve a clear understanding of fundamental concepts such as IP addressing, device configuration, and network connectivity. By addressing each element methodically, users can ensure that all parts of the network function correctly. These exercises often require critical thinking to troubleshoot issues and optimize configurations for better performance.
Approaching Challenges and Troubleshooting
When faced with network simulation challenges, a logical approach to troubleshooting is essential. Identifying and isolating the root cause of a problem allows for quick resolution. Whether it’s misconfigured devices or connectivity issues, having a structured process helps reduce errors and improves efficiency in completing each task.
Understanding the Basics of Networking Simulations
Grasping the fundamentals of network simulations is essential for anyone looking to master the art of network configuration and troubleshooting. These simulations allow users to create virtual networks, configure devices, and test their setups in a controlled environment. By working with these simulations, you can gain practical experience without the need for physical hardware, making it easier to experiment and learn at your own pace.
Interface and Tools Overview
The simulation interface provides a variety of tools to design and manage networks. Users can drag and drop devices, such as routers, switches, and computers, onto the workspace. These tools also allow for configuring network settings, including IP addresses and routing protocols, making it easy to test different network scenarios. Familiarity with the interface is key to navigating through exercises efficiently.
Building and Testing Network Scenarios
Once devices are placed within the workspace, users can begin creating connections and testing network configurations. The simulation provides real-time feedback, allowing users to see how the network behaves under different conditions. This process is essential for troubleshooting issues, ensuring that the network performs as expected before implementing changes in real-world settings. Understanding these basic functions is the first step in mastering network simulations.
Key Concepts in Networking Simulation
Understanding the core principles of network simulations is crucial for mastering network management and troubleshooting. These concepts help build a strong foundation for configuring devices, optimizing network performance, and diagnosing issues in virtual environments. A clear grasp of these ideas ensures that users can efficiently design, implement, and test various network setups.
Device Configuration and Management
One of the essential concepts in networking simulations is configuring and managing network devices. Whether working with routers, switches, or end devices, users must set up proper IP addresses, subnet masks, and routing protocols. Proper configuration is necessary to ensure communication between devices, avoid conflicts, and optimize the flow of data across the network.
Connectivity and Troubleshooting Techniques
Another key aspect of network simulations is ensuring proper connectivity between devices. This involves testing cables, checking routing tables, and identifying network faults. The ability to troubleshoot effectively helps users quickly diagnose issues such as incorrect configurations, hardware failures, or connectivity problems. Hands-on experience with these techniques enhances problem-solving skills and prepares users for real-world scenarios.
How to Navigate Network Simulation Interface
Mastering the navigation of a network simulation environment is essential for efficient network design and troubleshooting. The interface provides a variety of tools and panels that enable users to interact with devices, configure network settings, and test connectivity. Familiarity with these features will allow you to work more effectively and streamline your workflow when building and testing network scenarios.
The workspace is typically divided into several sections, each with a distinct function. These include the device selection area, the configuration panel, and the simulation controls. Below is a table outlining key components of the interface and their respective functions:
| Interface Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Device Selection Panel | Used to select and place network devices such as routers, switches, and computers onto the workspace. |
| Workspace | The area where devices are placed and network connections are made. It provides a visual representation of the network layout. |
| Configuration Panel | Allows for the configuration of individual devices, such as setting IP addresses, routing protocols, and other network parameters. |
| Simulation Controls | Used to start and stop simulations, view packet flows, and monitor network performance in real-time. |
By understanding the function of each panel and tool, you will be able to navigate the interface smoothly and use the simulation environment to its full potential. Whether you’re placing devices, configuring settings, or monitoring data flow, mastering the interface is the first step in becoming proficient with network simulations.
Step-by-Step Guide to Network Simulation Task
This section provides a detailed, step-by-step guide to completing a common networking simulation task. By following these instructions, users can learn how to set up a network, configure devices, and ensure proper functionality. Each step is designed to help you build a network from scratch and resolve any issues that may arise during the simulation process.
Preparing the Network Setup
Before diving into the configuration process, it is important to properly prepare the network environment. This includes selecting devices and establishing initial connections. Follow these steps to get started:
- Select the necessary network devices such as routers, switches, and computers.
- Place them appropriately on the workspace to create a logical network layout.
- Use cables to connect the devices, ensuring proper links between them.
- Verify that all devices are correctly connected before moving to the configuration phase.
Configuring Devices and Testing Connectivity
Once the network is set up, it’s time to configure the devices and test connectivity. This phase is crucial for ensuring that all devices communicate properly with each other. Follow these steps to configure the network:
- Assign appropriate IP addresses to each device based on the network design.
- Configure routing protocols if necessary, ensuring that data can flow between different segments of the network.
- Use the simulation tool to test the connectivity between devices.
- Check for any connectivity issues, such as incorrect IP addresses or cable misconfigurations.
By carefully following these steps, you can successfully complete the network setup and troubleshooting tasks, ensuring that the simulated network operates as expected.
Common Issues in Network Simulation Exercises
When working with network simulations, it is common to encounter several issues that can prevent the network from functioning as expected. These problems typically stem from configuration errors, device mismanagement, or connectivity issues. Identifying and addressing these issues is essential to completing tasks successfully and mastering networking concepts.
Configuration and Connectivity Errors
Many issues arise from incorrect settings or improper device configurations. Here are some common configuration errors to watch for:
- Incorrect IP addressing on devices, leading to communication failures.
- Misconfigured subnet masks that prevent devices from recognizing each other.
- Improper routing protocol settings that block data flow between different network segments.
- Unassigned or incorrect gateway settings, preventing devices from accessing external networks.
Hardware and Simulation Settings Issues
In addition to configuration errors, hardware-related issues or simulation environment settings can also cause problems. These include:
- Incorrect or loose connections between devices, which can lead to disconnected networks.
- Devices placed on the workspace that do not correspond to the required network topology.
- Simulation control settings that prevent the network from being tested correctly.
- Device failure or incorrect status, which might cause delays in the simulation process.
Addressing these common problems requires careful attention to detail and systematic troubleshooting. Ensuring that each device is properly configured and that the network setup matches the intended design is crucial for successful network simulations.
Effective Troubleshooting Methods for Simulations
When working with network simulations, encountering issues is a common part of the process. Whether it’s connectivity problems or misconfigured devices, troubleshooting is key to resolving these challenges. By applying systematic methods, users can quickly identify the root cause of problems and implement effective solutions, ensuring that the simulated network functions as expected.
Systematic Problem Identification

The first step in troubleshooting any network issue is identifying the problem. Start by analyzing the symptoms and narrowing down potential causes. A logical approach helps avoid overlooking simple errors and saves time. Here are some strategies for effective identification:
- Start by checking device connections and ensure all cables are properly plugged in.
- Verify that IP addresses and subnet masks are correctly assigned to each device.
- Check the routing tables to confirm that data is being correctly forwarded between devices.
- Use basic ping tests to verify connectivity between devices.
Testing and Isolating Faults
Once you’ve identified the problem, it’s essential to test different solutions to isolate the fault. This phase involves adjusting configurations and testing connectivity to see the effect of changes. Testing tools such as simulation controls and command-line utilities can provide valuable insights into what is wrong. Common techniques include:
- Running simulation tests to observe how data flows through the network.
- Disabling and re-enabling network interfaces to reset connections.
- Reconfiguring routing protocols or adjusting device settings to troubleshoot network traffic issues.
- Using detailed logs and error messages to pinpoint misconfigurations or failures.
By methodically following these troubleshooting steps, users can efficiently resolve issues in their network simulations and ensure smooth operation.
Configuring Devices in Network Simulations
Configuring network devices in a simulation environment is a crucial step in creating a fully functional network. It involves assigning proper settings to various devices, such as routers, switches, and endpoints, so they can communicate effectively with one another. Whether you are setting up a simple local network or a complex multi-router topology, understanding the configuration process is essential for successful network operation.
Basic Configuration Procedures
The initial configuration of devices is the foundation of a functioning network. To get started, each device must be properly addressed and connected. The following steps are typically involved:
- Assigning static or dynamic IP addresses to each device to ensure proper identification on the network.
- Setting up routing information, including default gateways and DNS, to enable external communication.
- Verifying interface status and ensuring they are enabled (no shutdown command in router settings).
- Testing connectivity between devices with basic commands like ping to verify that the network is operational.
Advanced Device Configuration
Once basic configurations are in place, additional advanced settings can be implemented to optimize the network’s functionality. This step may include:
- Configuring routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF, or EIGRP to manage data flow between multiple devices.
- Setting up VLANs on switches to segment traffic and improve network security and performance.
- Applying Access Control Lists (ACLs) to filter network traffic and control access to certain network resources.
- Implementing Network Address Translation (NAT) for handling IP address management and security on the network.
By following these configuration guidelines, you can ensure that your network devices are set up correctly, enabling smooth communication and efficient data transfer between all network components.
Configuring Devices in Network Simulations
Configuring network devices in a simulation environment is a crucial step in creating a fully functional network. It involves assigning proper settings to various devices, such as routers, switches, and endpoints, so they can communicate effectively with one another. Whether you are setting up a simple local network or a complex multi-router topology, understanding the configuration process is essential for successful network operation.
Basic Configuration Procedures
The initial configuration of devices is the foundation of a functioning network. To get started, each device must be properly addressed and connected. The following steps are typically involved:
- Assigning static or dynamic IP addresses to each device to ensure proper identification on the network.
- Setting up routing information, including default gateways and DNS, to enable external communication.
- Verifying interface status and ensuring they are enabled (no shutdown command in router settings).
- Testing connectivity between devices with basic commands like ping to verify that the network is operational.
Advanced Device Configuration
Once basic configurations are in place, additional advanced settings can be implemented to optimize the network’s functionality. This step may include:
- Configuring routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF, or EIGRP to manage data flow between multiple devices.
- Setting up VLANs on switches to segment traffic and improve network security and performance.
- Applying Access Control Lists (ACLs) to filter network traffic and control access to certain network resources.
- Implementing Network Address Translation (NAT) for handling IP address management and security on the network.
By following these configuration guidelines, you can ensure that your network devices are set up correctly, enabling smooth communication and efficient data transfer between all network components.
Testing Network Connectivity in Simulations
In any network setup, ensuring that devices can communicate effectively is essential for overall functionality. Testing connectivity is a crucial step in verifying that the network infrastructure is working as expected. In a simulated environment, this can be achieved using various diagnostic tools and techniques that help identify potential issues and confirm proper network behavior. In this section, we will explore methods for testing connectivity and troubleshooting common problems.
Basic Connectivity Tests
The first step in testing network connectivity involves confirming that devices are properly connected and able to communicate across the network. Some basic tools and commands are used to perform initial checks:
- Ping: This is the most common method for testing basic connectivity. By sending a small packet to a target device, the ping command checks if the device is reachable. A successful response indicates that the network path is functional.
- Traceroute: This tool tracks the path taken by packets as they travel from source to destination. It helps identify where delays or failures occur along the route.
- Telnet/SSH: These protocols are used to test remote access to devices. They help ensure that remote login is possible and that no blocking or filtering is occurring on specific ports.
Advanced Connectivity Diagnostics

In more complex networks, issues may arise that require deeper analysis. Advanced diagnostic techniques can help isolate and resolve these problems:
- Interface Status: Verifying that all network interfaces are operational is essential. Inactive interfaces can cause interruptions in communication, and this can be checked using commands like show interface on network devices.
- Routing Table Verification: Ensuring that the routing table is correctly populated and that routes are accurately defined is vital for proper data forwarding. Incorrect or missing routes can lead to communication failures.
- Subnet Mask and IP Addressing: Mismatched subnet masks or incorrect IP configurations can cause devices to fail to communicate, even when they are physically connected. It is important to verify that each device is assigned the correct addressing scheme.
By systematically testing network connectivity using these methods, you can efficiently troubleshoot and resolve issues, ensuring that the network operates smoothly and reliably.
| Test Method | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Ping | Sends a packet to another device to check if it is reachable. | Basic connectivity check. |
| Traceroute | Tracks the route packets take to their destination. | Identifies path delays or failures. |
| Telnet/SSH | Tests remote login to devices. | Verifies remote access. |
Optimizing Your Packet Tracer Workflow
Efficient use of simulation tools can significantly improve the quality and speed of your network design and troubleshooting processes. By optimizing your workflow, you can streamline tasks, reduce errors, and enhance productivity. This section will discuss various techniques and best practices for improving your efficiency while working in a network simulation environment.
Organizing Your Network Design
One of the key aspects of an optimized workflow is organizing your design from the start. Proper organization minimizes mistakes and makes it easier to understand the network layout later on.
- Use Layers: When designing a complex network, break the design into different layers (e.g., core, distribution, access) to keep things clear and manageable.
- Label Components: Always label your devices, cables, and interfaces clearly. This helps avoid confusion, especially when dealing with multiple devices or connections.
- Group Devices: Group similar devices together in the workspace to keep related components near each other. This reduces the time spent searching for specific devices and streamlines your work.
Leveraging Built-in Tools
Many simulation platforms provide built-in tools that can greatly enhance your workflow. Take advantage of these features to reduce manual effort and increase efficiency.
- Automation: Automate repetitive tasks using pre-configured templates and scripts. This saves time, especially in large-scale simulations.
- Check Connectivity in Real-Time: Use tools like real-time network monitoring to observe packet flow and test device interactions without needing to pause or stop the simulation.
- Device Configuration Templates: Create and save configuration templates for commonly used devices. This can save a lot of time when setting up multiple similar devices.
Maximizing Efficiency in Testing and Troubleshooting
Efficient testing and troubleshooting are essential to maintaining a smooth workflow. Follow these strategies to identify and resolve issues more quickly:
- Test Early and Often: Run tests at each stage of the design process to catch problems early. This reduces the need for extensive troubleshooting later on.
- Use Logs and Reports: Keep detailed logs of configuration changes and test results. These logs can help you quickly identify where an issue occurred and simplify the troubleshooting process.
- Work with Saved States: Save your simulation states frequently. This allows you to easily revert to a previous state in case of an error, saving time and effort during troubleshooting.
By following these best practices, you can streamline your simulation workflow, minimize errors, and improve your overall productivity. With a well-organized approach, you’ll be able to focus more on solving network issues and less on managing your workspace.
Understanding Network Topology in Simulations
In network simulations, the design and structure of the network play a crucial role in ensuring that all devices and connections work efficiently. Network topology refers to the arrangement of various components, such as devices, links, and communication paths, within a network. Understanding this concept is key to building effective simulations and troubleshooting potential issues. This section will explore the importance of network topology in virtual environments and provide guidance on how to design and analyze topologies effectively.
Types of Network Topologies
Different types of network topologies serve various purposes depending on the scale, complexity, and requirements of the simulation. Below are some common topologies used in network design:
- Star Topology: In this setup, all devices are connected to a central hub or switch. It is easy to manage and troubleshoot, making it a popular choice for smaller networks.
- Bus Topology: All devices are connected to a single central cable, or bus. This is a simple and cost-effective option but can become inefficient with a large number of devices.
- Ring Topology: Each device is connected to two others, forming a continuous loop. It can provide reliable data transmission but may have challenges in case of a break in the loop.
- Mesh Topology: Devices are interconnected in a way that each device is connected to every other device. This setup provides high redundancy and fault tolerance, ideal for critical network designs.
- Hybrid Topology: A combination of two or more topologies, tailored to meet specific needs. This topology offers flexibility but requires careful management of connections.
Choosing the Right Topology for Your Simulation
Choosing the correct topology for your network simulation depends on various factors such as the number of devices, performance requirements, and fault tolerance. When designing a topology for simulation, consider the following:
- Network Size: Smaller networks can benefit from simpler topologies like star or bus, while larger, more complex networks may require the redundancy and scalability offered by mesh or hybrid topologies.
- Redundancy Needs: If the network needs to maintain operation even if one device or connection fails, opt for a topology with built-in redundancy, like mesh or hybrid.
- Performance Considerations: Consider the performance demands of your simulation. For high-throughput networks, topologies with more direct connections, like mesh, may reduce latency and congestion.
Analyzing Topology in Simulations
Once the topology is designed, it is essential to analyze how well it functions within the simulation environment. Monitoring performance and troubleshooting problems are critical to ensuring the network runs smoothly. Some strategies for analyzing network topology include:
- Simulation Testing: Run simulations to test the functionality and performance of the network. This allows you to identify bottlenecks or areas that need optimization.
- Link Status and Errors: Pay attention to the status of links between devices. Broken links, misconfigurations, or incorrect routing can often be identified through careful examination of the topology.
- Latency and Traffic Flow: Monitor the traffic flow and check for latency issues, particularly in more complex topologies. Simulations can help detect areas where data transfer may be slowed down due to inefficient routing paths.
Understanding network topology and how it affects the performance and functionality of a simulation is fundamental to effective network design and troubleshooting. With the right topology, simulations become a powerful tool for testing, optimizing, and validating real-world networks before implementation.
How to Use Packet Tracer for Practice
Practicing network configurations and troubleshooting skills in a virtual environment offers a great way to develop expertise without the need for physical devices. With the right tools, you can simulate various network setups, test different configurations, and explore troubleshooting methods without the constraints of a physical network. This section will guide you through the steps to effectively use a network simulation tool to hone your skills, allowing for hands-on practice with various network scenarios.
Starting with Basic Configurations
When you first begin using a network simulation tool, it is best to start with basic configurations. This allows you to familiarize yourself with the user interface, network components, and foundational concepts. Start by setting up simple devices such as routers, switches, and computers, and then practice configuring IP addresses, subnet masks, and routing protocols. These foundational skills will provide you with the confidence to tackle more complex network scenarios later.
Experimenting with Network Topologies
Network simulations are ideal for experimenting with different topologies. You can create and modify various types of networks such as star, bus, or mesh topologies, and test how they behave under different conditions. Through this process, you can gain a deeper understanding of how devices interact with each other, the effect of topology on performance, and the impact of network failures. Use simulations to explore how adding or removing devices affects the overall network functionality.
Testing Different Protocols and Configurations
Once you are comfortable with basic configurations, start testing more advanced protocols and features. Experiment with configuring routing protocols such as OSPF or EIGRP, implementing access control lists (ACLs), or setting up VLANs. Simulations provide the flexibility to make adjustments in real time and observe the immediate effects of those changes, making them invaluable for testing the behavior of different network protocols under various conditions.
Simulating Troubleshooting Scenarios
One of the most beneficial ways to practice is by simulating common network issues. Create deliberate misconfigurations or failures, such as incorrect IP addressing, faulty cables, or broken routing paths, and then practice identifying and resolving these problems. The ability to troubleshoot effectively in a virtual environment will help you refine your problem-solving skills and prepare you for real-world scenarios. By practicing different troubleshooting techniques in simulations, you will learn to diagnose and fix issues faster and more accurately.
Tracking Progress with Built-in Tools
Most simulation platforms come with tools that help you track your progress. Use the built-in simulation features to observe the flow of data packets, analyze network traffic, and monitor the status of devices. These tools give you a detailed view of how data moves across the network and allow you to identify issues that may not be immediately visible through configuration alone. As you continue to practice, refer to these tools to measure your improvements and refine your skills.
By leveraging network simulation tools for practice, you gain valuable experience without the need for expensive hardware or complex physical setups. Through consistent practice and experimentation, you can improve your networking skills and build a strong foundation for future certification or real-world application.
How to Use Packet Tracer for Practice
Practicing network configurations and troubleshooting skills in a virtual environment offers a great way to develop expertise without the need for physical devices. With the right tools, you can simulate various network setups, test different configurations, and explore troubleshooting methods without the constraints of a physical network. This section will guide you through the steps to effectively use a network simulation tool to hone your skills, allowing for hands-on practice with various network scenarios.
Starting with Basic Configurations
When you first begin using a network simulation tool, it is best to start with basic configurations. This allows you to familiarize yourself with the user interface, network components, and foundational concepts. Start by setting up simple devices such as routers, switches, and computers, and then practice configuring IP addresses, subnet masks, and routing protocols. These foundational skills will provide you with the confidence to tackle more complex network scenarios later.
Experimenting with Network Topologies
Network simulations are ideal for experimenting with different topologies. You can create and modify various types of networks such as star, bus, or mesh topologies, and test how they behave under different conditions. Through this process, you can gain a deeper understanding of how devices interact with each other, the effect of topology on performance, and the impact of network failures. Use simulations to explore how adding or removing devices affects the overall network functionality.
Testing Different Protocols and Configurations
Once you are comfortable with basic configurations, start testing more advanced protocols and features. Experiment with configuring routing protocols such as OSPF or EIGRP, implementing access control lists (ACLs), or setting up VLANs. Simulations provide the flexibility to make adjustments in real time and observe the immediate effects of those changes, making them invaluable for testing the behavior of different network protocols under various conditions.
Simulating Troubleshooting Scenarios
One of the most beneficial ways to practice is by simulating common network issues. Create deliberate misconfigurations or failures, such as incorrect IP addressing, faulty cables, or broken routing paths, and then practice identifying and resolving these problems. The ability to troubleshoot effectively in a virtual environment will help you refine your problem-solving skills and prepare you for real-world scenarios. By practicing different troubleshooting techniques in simulations, you will learn to diagnose and fix issues faster and more accurately.
Tracking Progress with Built-in Tools
Most simulation platforms come with tools that help you track your progress. Use the built-in simulation features to observe the flow of data packets, analyze network traffic, and monitor the status of devices. These tools give you a detailed view of how data moves across the network and allow you to identify issues that may not be immediately visible through configuration alone. As you continue to practice, refer to these tools to measure your improvements and refine your skills.
By leveraging network simulation tools for practice, you gain valuable experience without the need for expensive hardware or complex physical setups. Through consistent practice and experimentation, you can improve your networking skills and build a strong foundation for future certification or real-world application.
Reviewing Key Networking Protocols in Packet Tracer
Understanding networking protocols is essential for configuring and managing networks effectively. Simulation tools provide an opportunity to explore and experiment with these protocols in a controlled environment. In this section, we will review some of the most widely used networking protocols, focusing on how they can be applied within simulation scenarios. Gaining hands-on experience with these protocols will enhance your understanding of their functionality and how they interact within a network.
TCP/IP and Its Role in Networking
The TCP/IP protocol suite is the foundation of most modern networks. It is responsible for the end-to-end communication across devices, enabling them to exchange data reliably. In a network simulation, you can experiment with various TCP/IP configurations, including setting up IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways. By testing these configurations, you can see how devices communicate over different network segments, how packets are routed, and how the protocol ensures reliable delivery of data between systems.
Exploring Routing Protocols
Routing protocols are vital for determining the most efficient paths for data to travel across networks. Two of the most commonly used routing protocols are OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol). Within a simulation, you can configure routers to use these protocols, allowing them to dynamically exchange routing information and adjust to network changes. By reviewing how these protocols work in simulations, you can better understand the process of routing, the concept of autonomous systems, and how routers update their routing tables to reflect the network’s current topology.
Understanding VLANs and Switching
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) are used to segment a network into distinct broadcast domains, improving performance and security. In a simulation, you can configure VLANs on switches and test how they separate traffic across different logical networks. By simulating VLAN configurations, you will learn how to manage traffic flow within a network, isolate sensitive data, and troubleshoot common VLAN-related issues such as misconfigured trunking or VLAN hopping.
Implementing DHCP and DNS
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) are essential services that support network operations. DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network, ensuring smooth communication between systems. DNS resolves domain names to IP addresses, allowing users to access websites using human-readable addresses. In simulations, you can configure DHCP servers to manage IP address distribution and set up DNS to resolve names for various services, testing the interaction between these protocols to ensure network functionality.
Through practical exercises with these protocols, you can enhance your understanding of how they function in real-world scenarios. Simulating configurations, analyzing traffic flow, and troubleshooting common protocol issues will help you gain a deeper understanding of networking fundamentals and prepare you for more advanced networking tasks.
Best Practices for Packet Tracer Success
To maximize success in network simulations, it is essential to adopt effective strategies that will enhance both your learning and practical experience. Mastering the tools and workflows available in simulation software can provide you with valuable insights into network management, configuration, and troubleshooting. The following best practices will help streamline your work and ensure more efficient and accurate results.
1. Plan Your Network Design
Before starting any configuration, take the time to plan your network layout thoroughly. Mapping out how devices will connect, the use of various protocols, and the overall structure of the network is key to avoiding confusion later on. A solid plan will help you identify potential issues early and guide you through more complex setups.
2. Work with Basic Configurations First

When starting with simulations, begin with simple tasks like configuring IP addresses, basic device setup, and testing basic connectivity. This approach helps you become familiar with the simulation environment and gives you a strong foundation before tackling more complex tasks such as routing, security, and advanced protocols.
3. Continuously Test and Validate
Don’t wait until the end of your simulation to check if everything is working. Test network connectivity regularly as you configure each device and make adjustments. Using tools like “ping” and “traceroute” within the simulation environment will help you verify the functionality of your network and identify issues in real time.
4. Use Simulation Mode for Traffic Analysis
Most network simulation platforms offer a traffic analysis feature, which allows you to visualize how data moves across your network. By actively monitoring this flow, you can better understand how different protocols and configurations affect network performance. This helps pinpoint bottlenecks or misconfigurations early in the process.
5. Document Your Steps and Configuration
One of the most useful habits is to document your configuration steps. Keep track of commands, settings, and the results of your tests. Having clear documentation will not only help you troubleshoot effectively but also serve as a reference for future network simulations or real-world scenarios.
6. Make Use of Online Resources
If you run into challenges, don’t hesitate to consult online forums, guides, or expert tutorials. There is a wealth of information available to help you resolve common issues or explore advanced techniques. Engaging with the wider network community can also expose you to new methods or tools that you might not have considered.
7. Organize Your Work Environment
A well-organized simulation workspace can dramatically improve your efficiency. Keep devices labeled clearly and follow consistent naming conventions to avoid confusion. Group devices logically and keep your configurations clean and simple. An organized workspace allows for easier troubleshooting and smoother progression through tasks.
8. Collaborate and Share Ideas
Learning with others can significantly enhance your understanding of network concepts. Join study groups or online communities where you can share ideas, troubleshoot issues, and discuss different approaches to common problems. Working with others provides fresh perspectives and can improve your problem-solving skills.
By implementing these best practices, you can optimize your approach to network simulations, reduce errors, and enhance your overall understanding of networking principles. These strategies will help you succeed in your networking goals, whether preparing for exams, managing real networks, or refining your technical skills.
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Plan Your Network | Map out the network structure before configuring devices to avoid confusion. |
| Start with Basics | Begin with simple configurations and test basic connectivity before progressing. |
| Test Regularly | Check network connectivity frequently using tools like ping and traceroute. |
| Use Simulation Mode | Monitor data traffic to understand how protocols and configurations work. |
| Document Your Steps | Keep a detailed record of your configurations and troubleshooting steps. |
| Consult Online Resources | Use tutorials and forums to solve issues and learn new techniques. |
| Stay Organized | Keep your workspace clean and devices well-labeled for better workflow. |
| Collaborate with Others | Share knowledge and solve problems together to gain new insights. |