Preparing for your first test in life sciences can be challenging, but with the right approach, you can navigate the material with confidence. This guide is designed to help you review key concepts, structure your study sessions effectively, and highlight areas that require extra attention. Whether you are new to the subject or have some background knowledge, these tips will set you on the path to success.
In this section, we will focus on the most important topics likely to appear on the test, as well as practical strategies for mastering the content. By focusing on understanding core principles and practicing with sample questions, you can ensure a strong performance. The goal is to reinforce your knowledge and boost your confidence so that you approach the test with clarity and preparedness.
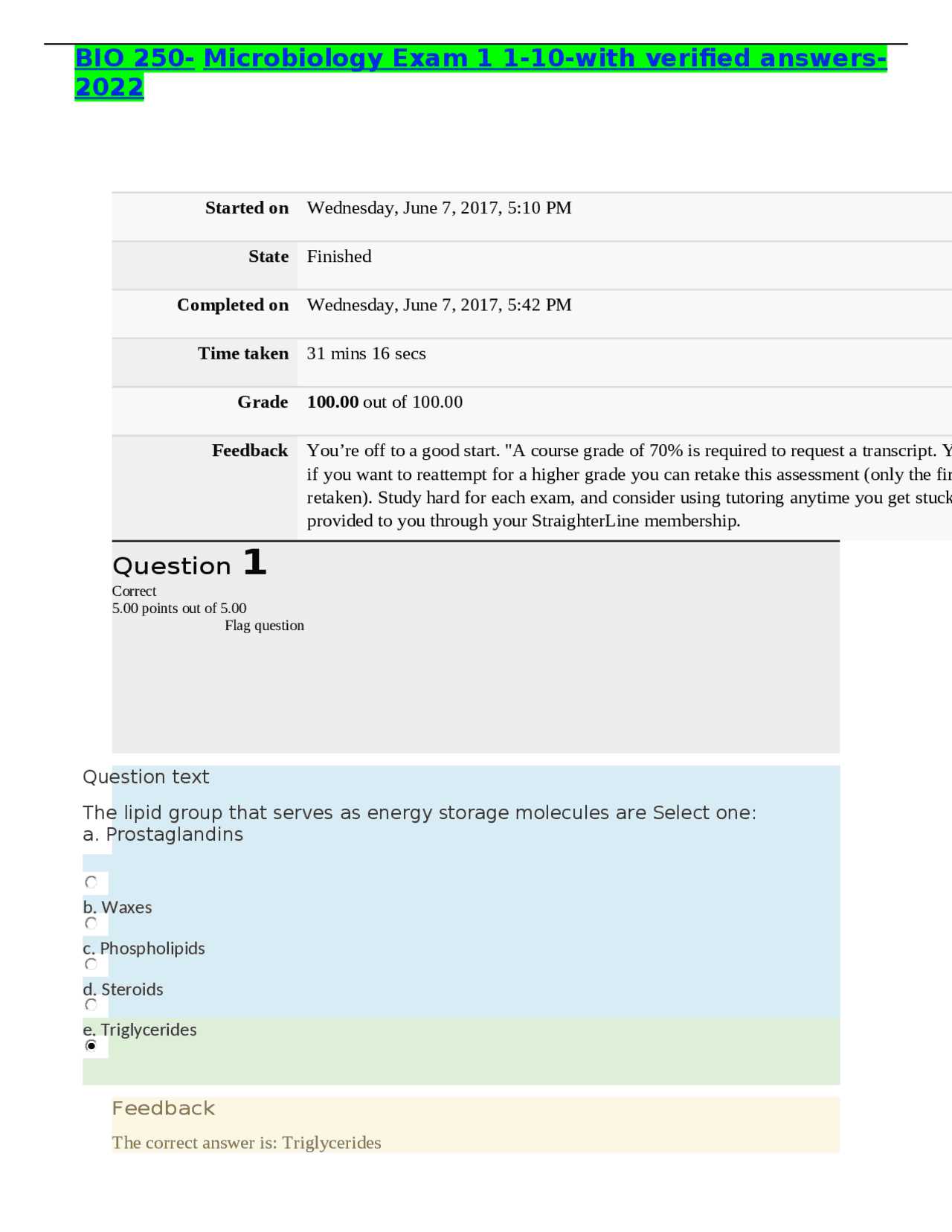
Microbiology Exam 1 Answers
For students preparing for their first major assessment in life sciences, it’s crucial to focus on the concepts and material that are most likely to be tested. This section provides a comprehensive guide to the types of questions and key topics you should be familiar with. By reviewing these, you can ensure a strong understanding of the foundational principles that will be evaluated.
Important Topics to Focus On
The test will cover a range of subjects, but some areas are more likely to be emphasized. You should prioritize understanding the classification of living organisms, their functions, and their roles in various ecosystems. Additionally, pay attention to the structure and function of cells, as these topics often feature heavily in multiple-choice or short-answer questions.
Strategies for Effective Review
To maximize your study time, use active recall techniques and practice with sample questions. Don’t just read over your notes–test yourself on key concepts regularly. Group study sessions can also be beneficial, as discussing complex topics with peers helps reinforce your understanding and highlight areas that need further clarification.
Key Topics Covered in Exam 1
In your first assessment, understanding the core subjects that will be tested is essential for focused preparation. The topics covered are foundational to the field and often form the basis for more advanced concepts. This section outlines the key areas that are critical for success, helping you prioritize your review efforts.
Essential Concepts to Master
Several areas of study are central to the test. Familiarizing yourself with the following topics will ensure a comprehensive understanding:
- Classification of living organisms and their characteristics
- Structure and function of cells and microorganisms
- Basic biochemical processes and metabolic pathways
- Principles of growth, reproduction, and evolution in microorganisms
- Interactions between organisms and their environments
Additional Focus Areas
In addition to the core topics, there are other important areas that may appear on the test. Pay attention to the following as well:
- Microscopic techniques and laboratory procedures
- Immune response and microbial defense mechanisms
- Antibiotics and their modes of action
- Human impact on microbial ecosystems
Study Tips for Success

Achieving success in the first major assessment requires more than just reviewing material–it’s about developing effective study habits and strategies. By focusing on active learning and efficient time management, you can maximize your understanding of key concepts and improve your performance.
| Study Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Active Recall | Test yourself on key concepts regularly rather than just reading your notes. This reinforces memory retention. |
| Spaced Repetition | Review material at increasing intervals to strengthen long-term memory and avoid cramming. |
| Group Study | Collaborate with peers to discuss challenging topics and gain different perspectives on difficult concepts. |
| Practice Questions | Work through practice problems or sample questions to familiarize yourself with question formats and common topics. |
| Time Management | Break study sessions into focused, timed intervals to maintain productivity and avoid burnout. |
Common Mistakes to Avoid

When preparing for a significant assessment, it’s easy to fall into certain pitfalls that can hinder your performance. Recognizing these common errors in advance can help you focus on effective study techniques and avoid wasting time on less productive methods. In this section, we will highlight frequent mistakes students make and offer advice on how to steer clear of them.
Study Habits to Improve
- Relying solely on passive reading rather than active engagement with the material.
- Underestimating the importance of consistent review and falling into last-minute cramming.
- Ignoring weak areas and not dedicating enough time to challenging topics.
- Skipping practice questions or failing to simulate the testing environment during preparation.
Test-Taking Errors to Watch For
- Not reading questions thoroughly and missing critical details in the instructions.
- Overthinking or second-guessing answers instead of trusting your initial response.
- Failing to manage time effectively during the test, leaving questions unanswered.
- Letting stress or anxiety affect your ability to concentrate during the assessment.
Essential Resources for Exam Preparation
Having the right tools and materials is essential for thorough preparation. Utilizing quality resources can make the difference between a good understanding and complete mastery of the subject. In this section, we will explore the most effective resources that will help you review the key concepts and practice for the test.
Key Materials for Effective Study
- Textbooks and Lecture Notes: Your primary sources of information; review chapters related to the topics that will be tested.
- Online Learning Platforms: Websites and apps offering interactive quizzes, flashcards, and video lessons to reinforce your understanding.
- Study Guides: Pre-made guides or outlines summarizing key concepts, often with practice questions and answers.
- Research Articles: Peer-reviewed articles for a deeper understanding of complex subjects or recent findings in the field.
Additional Helpful Tools
- Flashcards: Digital or physical cards for active recall and vocabulary practice.
- Practice Tests: Full-length tests that simulate the actual assessment to help you familiarize yourself with question formats.
- Study Groups: Collaborate with classmates to discuss difficult concepts and quiz each other on important material.
- Instructor Office Hours: Take advantage of your professor’s office hours to clarify any questions or difficult topics.
Understanding Microbial Classification
One of the foundational concepts in the study of living organisms is understanding how they are categorized and classified. Proper classification allows scientists to organize the vast diversity of life, making it easier to study their characteristics, behaviors, and interactions. This section provides an overview of the key systems used to group microorganisms and their relevance in various scientific disciplines.
Key Levels of Classification
Microorganisms are grouped based on shared characteristics, with several hierarchical levels of classification:
- Domain: The broadest category, which divides life into three main domains: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya.
- Kingdom: A subdivision within each domain, which groups organisms with similar characteristics, such as Plantae or Animalia in the Eukarya domain.
- Phylum: Groups organisms based on more specific traits, such as cell structure or mode of nutrition.
- Class, Order, Family: Further subdivisions based on more refined characteristics.
- Genus and Species: The most specific classification levels, identifying individual organisms or species within a genus.
Common Classification Systems for Microorganisms
There are several classification systems used in the study of microorganisms, each emphasizing different criteria. Some of the most widely used include:
- Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology: A comprehensive reference work for identifying bacteria and other prokaryotic organisms.
- Phenotypic Classification: Based on observable traits such as morphology, biochemical properties, and growth patterns.
- Genotypic Classification: Focuses on genetic similarities and differences, using techniques like DNA sequencing to classify organisms.
- Cladistics: A method of classification that groups organisms based on their evolutionary history and shared ancestry.
Key Terms to Memorize for Exam 1

Mastering key terminology is essential for a deep understanding of the subject matter. These terms are foundational concepts that often appear in questions and play a crucial role in building a more complex knowledge of the material. In this section, we highlight important terms that should be memorized to ensure clarity and confidence during your assessment.
Familiarizing yourself with these terms will not only improve your recall but also help you understand the relationships between different concepts. Pay attention to their definitions, functions, and relevance in various contexts to gain a well-rounded understanding of the subject.
- Cellular Respiration: The process by which cells convert glucose into energy (ATP) for metabolic activities.
- Gram Staining: A method used to differentiate bacterial species based on the structure of their cell walls.
- Prokaryote: Organisms that lack a defined nucleus, such as bacteria.
- Eukaryote: Organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other organelles, such as plants and animals.
- Pathogen: A microorganism that causes disease in its host.
- Antibiotic Resistance: The ability of microorganisms to withstand the effects of drugs designed to kill or inhibit them.
- Endospore: A dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure formed by certain bacteria as a survival mechanism under unfavorable conditions.
- Osmosis: The movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration.
- Symbiosis: A close and often long-term relationship between two different species, which may be mutualistic, commensal, or parasitic.
- Antigen: A molecule or molecular structure recognized by the immune system as foreign, often triggering an immune response.
Effective Ways to Review Material
To effectively consolidate your knowledge, it’s important to employ review methods that engage different aspects of memory retention. Simply reading over your notes isn’t enough–active recall, spaced repetition, and other targeted techniques can significantly improve how well you retain information and apply it during an assessment. This section outlines several proven strategies that will help reinforce key concepts and enhance your understanding.
Rather than rushing through content at the last minute, it’s important to use consistent and varied approaches to refresh your memory over time. By focusing on active engagement, you’ll be able to recall information more accurately and retain it for longer periods.
- Active Recall: Challenge yourself by testing your knowledge instead of passively reading through notes. Practice retrieving information from memory to strengthen your recall ability.
- Spaced Repetition: Review material at increasing intervals to ensure that information is transferred into long-term memory. Use apps or flashcards to structure your reviews.
- Practice Questions: Work through sample questions or quizzes to get a feel for the types of topics that may come up. This helps you understand how questions are phrased and what to expect.
- Summarization: After reviewing each section of content, summarize it in your own words. This helps solidify your understanding and identify areas that may need more attention.
- Teach Someone Else: Explaining the material to a peer or even to yourself is one of the best ways to reinforce what you’ve learned and identify gaps in your knowledge.
- Mind Mapping: Visualize relationships between concepts by creating diagrams or charts. This technique can help clarify complex ideas and improve recall during your review sessions.
What to Expect on the Exam
Understanding the format and structure of the assessment is crucial for effective preparation. Knowing what types of questions will be asked, the range of topics covered, and the way the material is presented can help you focus your studies and approach the test with confidence. In this section, we will go over the key elements to expect, including question formats and areas likely to be tested.
Common Question Types
Questions on the test will vary in format, testing both your knowledge and your ability to apply concepts. It’s essential to prepare for the different types of questions that may appear:
| Question Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Multiple Choice | Questions with several possible answers; you must choose the correct one based on your understanding. |
| True/False | Statements where you must determine if they are correct or incorrect. |
| Short Answer | Brief questions that require you to explain key concepts or terms concisely. |
| Matching | Pairing items, such as terms and definitions, to test your familiarity with specific knowledge. |
Key Areas Likely to Be Tested
While the specific content of the test may vary, certain topics are frequently covered. Focusing on these areas during your preparation will increase your chances of success:
- Classification and Identification: Expect questions on how different organisms are categorized and distinguished based on key features.
- Cell Structures and Functions: Know the different types of cells and their components, as well as their roles in various processes.
- Pathogenesis and Immunity: Be prepared to discuss how pathogens interact with hosts and the immune responses involved.
- Basic Laboratory Techniques: Understand common procedures used in the study and identification of microorganisms.
- Environmental and Health Impacts: Questions on the role of microorganisms in the environment and their effects on human health may appear.
Sample Questions for Your Assessment
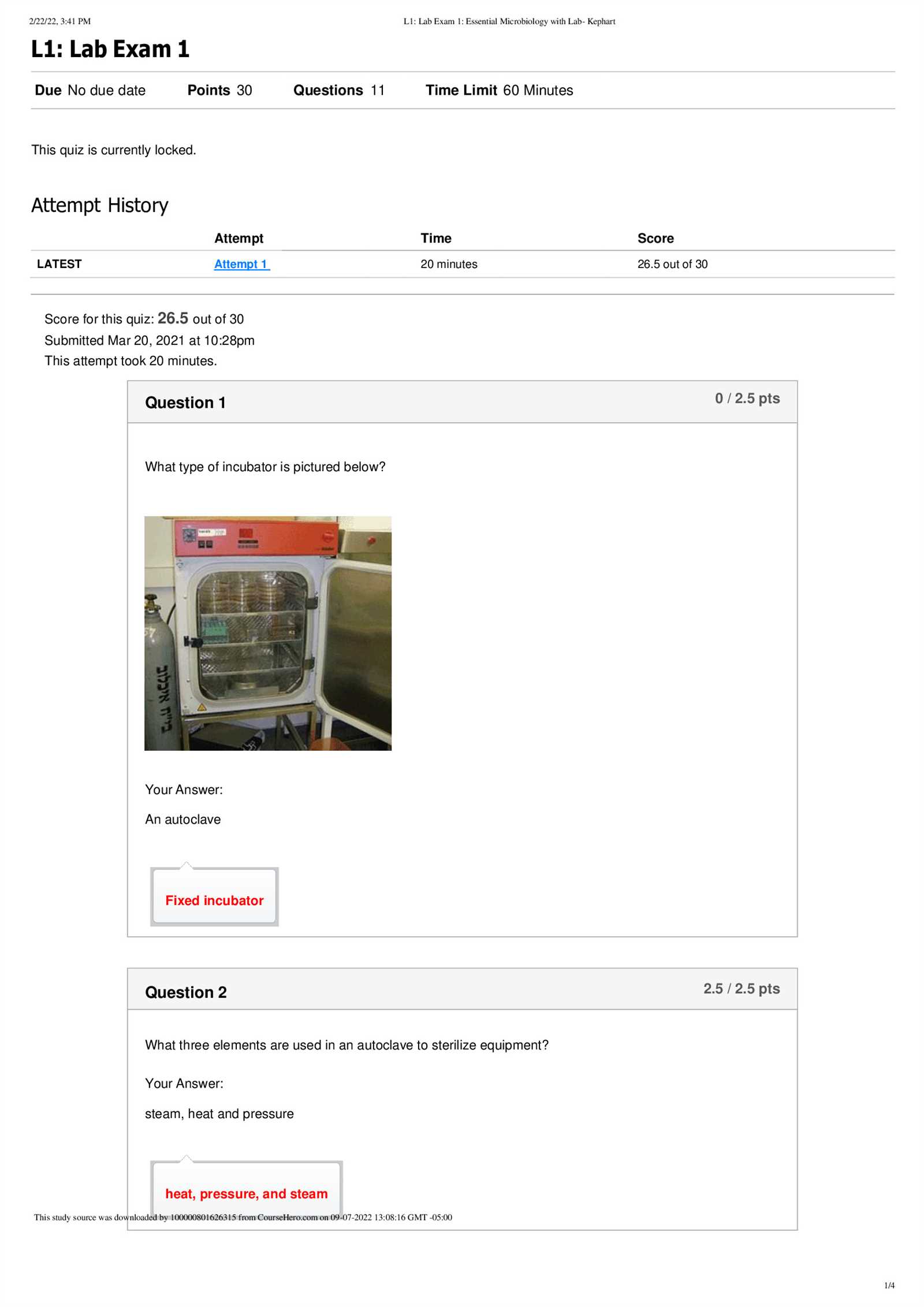
Practicing with sample questions is a highly effective way to prepare for any type of evaluation. It helps familiarize you with the format, types of questions you can expect, and allows you to test your knowledge under exam-like conditions. In this section, we provide several sample questions that mirror the style and difficulty of the actual assessment. Working through these will boost your confidence and ensure you are well-prepared.
These sample questions cover a broad range of topics and are designed to challenge your understanding. They will test your ability to recall essential concepts, apply your knowledge to new scenarios, and critically analyze information. Below are a few examples to help you get started:
Sample Multiple Choice Questions
- What is the primary function of ribosomes in cells?
- a) Energy production
- b) Protein synthesis
- c) Genetic material storage
- d) Cell division
- Which of the following is true about bacterial cell walls?
- a) They are made of cellulose
- b) They are composed of peptidoglycan
- c) They contain a lipid bilayer
- d) They are found only in animal cells
Sample Short Answer Questions
- Explain the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Describe the role of enzymes in cellular metabolism.
- What are the three primary types of symbiotic relationships between organisms? Provide examples of each.
These sample questions will help you identify key areas for further study, allowing you to focus your preparation more effectively. Practice with a variety of question types to improve your overall performance and ensure you’re fully prepared for the real test.
How to Manage Study Time

Effective time management is crucial for successful preparation. It allows you to allocate sufficient time for each subject, prioritize important topics, and avoid the stress of last-minute cramming. The key is to create a study schedule that is realistic, balanced, and allows enough flexibility to handle unexpected events. In this section, we’ll explore strategies that can help you organize your study sessions efficiently and ensure you make the most out of your time.
Creating a Study Schedule
A well-organized study plan is your first step toward effective time management. Break down your study sessions into smaller, focused blocks. Assign specific topics to each session and ensure you allocate time for review. A balanced schedule will help prevent burnout and improve retention. Try to stick to your plan, but remain flexible if you need to adjust due to other commitments.
- Set clear goals: Identify what you want to achieve by the end of each study session.
- Prioritize difficult topics: Spend more time on areas you find challenging while reviewing easier concepts regularly.
- Include breaks: Schedule short breaks between study blocks to refresh your mind and maintain focus.
- Stay consistent: Study at the same time each day to build a routine and reinforce good habits.
Maximizing Study Efficiency
Maximizing your study efficiency is about making every session count. Focus on quality over quantity, ensuring that each session contributes meaningfully to your learning. Use active learning techniques, such as summarizing material, practicing with sample questions, and teaching concepts to others. The more you actively engage with the content, the better your retention will be.
- Minimize distractions: Find a quiet, organized space where you can focus without interruptions.
- Use active recall: Test yourself frequently to reinforce memory and identify gaps in understanding.
- Review regularly: Revisit material periodically to ensure information stays fresh in your mind.
By managing your study time effectively, you’ll feel more confident and prepared when the time comes to demonstrate your knowledge. Consistency and discipline in your approach will pay off in the long run, leading to better results and less stress.
Breaking Down the Test Structure
Understanding the structure of any assessment is key to effective preparation. Knowing the types of questions, their distribution, and the format of the test will help you strategize your study sessions. This section aims to provide a detailed breakdown of the assessment’s structure so you can approach it with confidence. By recognizing the pattern of the test, you’ll be able to manage your time better and allocate effort to areas that matter most.
Question Types and Format
Assessments typically consist of various question formats, each testing different aspects of your knowledge and understanding. The most common formats include:
- Multiple Choice: These questions assess your ability to recall facts and concepts. They often require quick decision-making skills and a strong grasp of key information.
- Short Answer: These questions demand a more detailed response, allowing you to demonstrate your understanding of specific concepts and provide explanations or examples.
- Essay Questions: These questions require critical thinking and the ability to synthesize information from various topics, often requiring you to argue a point or analyze a situation.
- True or False: These test your ability to identify factual statements quickly and accurately.
Time Allocation and Strategy
Effective time management during the test is essential. Understanding how much time to spend on each section is critical to finishing the test on time without rushing. Here’s a general approach to allocating your time:
- Multiple Choice Questions: These tend to be quicker to answer, so allocate approximately 1-2 minutes per question.
- Short Answer and Essays: These require more time to craft thoughtful responses, so set aside more time per question (about 3-5 minutes for short answers and 10-15 minutes for essays).
- Review Time: Always leave a few minutes at the end to review your answers and ensure you haven’t missed anything important.
By breaking down the test structure, you can create a more focused study plan and enter the assessment with a clear strategy. Knowing what to expect allows you to be more relaxed and prepared, improving your performance overall.
Focus Areas for a High Score
To achieve a high score in any assessment, it’s important to concentrate on the areas that carry the most weight and are most likely to be tested. Understanding key concepts, mastering core topics, and practicing common question types can significantly improve your performance. In this section, we’ll highlight the critical focus areas that will help you excel and score higher, ensuring you are fully prepared for the challenge.
Core Topics to Master
Some topics are fundamental and more likely to be emphasized during the assessment. Prioritizing these areas will give you a solid foundation and increase your chances of answering questions correctly. Focus on the following key concepts:
| Topic | Importance | Study Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Concepts | High | Ensure a solid understanding of fundamental principles and definitions. |
| Processes and Mechanisms | High | Be able to explain biological processes and their real-world applications. |
| Techniques and Methods | Medium | Learn how various techniques are applied in different situations. |
| Terminology | Medium | Memorize key terms and definitions to recognize them in questions. |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even if you know the material well, it’s easy to fall into common traps during assessments. Avoid these frequent mistakes by focusing on accurate recall and logical reasoning:
- Rushing through questions: Take your time to read each question carefully and consider all options before answering.
- Overlooking small details: Pay attention to every part of the question, as small details can sometimes be the key to a correct answer.
- Skipping review: Always leave time to revisit your answers and ensure that you’ve addressed every part of each question.
By concentrating on these focus areas and avoiding common pitfalls, you will be well-equipped to perform at your best and secure a high score in the assessment.
Handling Multiple-Choice Questions
Multiple-choice questions can be challenging, but with the right strategy, you can effectively tackle them and increase your chances of selecting the correct answers. These types of questions often require more than just recall; they test your ability to understand key concepts, analyze information, and eliminate incorrect options. In this section, we’ll explore some techniques that can help you approach these questions confidently and strategically.
Key Strategies for Success
To excel at multiple-choice questions, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Read All Options Carefully: Avoid jumping to conclusions too quickly. Read through all the answer choices before selecting the one that best fits the question.
- Eliminate Clearly Wrong Answers: If you can identify answers that are obviously incorrect, cross them off immediately. This improves your chances of selecting the right option from the remaining choices.
- Look for Keywords: Pay attention to keywords or phrases in both the question and answer choices that hint at the correct response. Words like “always,” “never,” “except,” or “most” can indicate important clues.
- Use Contextual Clues: If the question seems complex, try to use related knowledge or context to deduce the correct answer. Sometimes, your background knowledge can help clarify ambiguities in the question.
- Don’t Overthink: Trust your first instinct unless you’re certain you’ve misinterpreted the question. Overthinking can lead to second-guessing and often results in errors.
Managing Time Effectively
Time management is crucial when dealing with multiple-choice questions. Here’s how to pace yourself:
- Set a Time Limit: Give yourself a set amount of time to answer each question to ensure that you don’t spend too much time on any single one.
- Skip and Return: If you’re unsure about a particular question, skip it and move on to the next one. You can always return to it once you’ve answered the others.
- Practice Regularly: The more you practice with multiple-choice questions, the faster and more accurate you’ll become at identifying the correct answers.
By applying these strategies and managing your time efficiently, you’ll be able to handle multiple-choice questions with greater ease and accuracy, maximizing your chances of success.
Best Practices for Answering Essay Questions
Essay questions assess your ability to articulate your knowledge and understanding of a subject in a clear and organized manner. These types of questions typically require more than just simple recall; they challenge you to explain, analyze, and demonstrate your depth of comprehension. In this section, we’ll discuss strategies to effectively answer essay questions, ensuring that your responses are well-structured and impactful.
Planning Your Response

Before jumping into writing, take a few moments to plan your response. This step can make a big difference in the clarity and depth of your answer.
- Understand the Question: Carefully read the essay prompt to ensure you understand what’s being asked. Look for key verbs such as “analyze,” “explain,” or “compare” to guide your response.
- Brainstorm Key Points: Jot down important concepts, terms, or arguments related to the question. Organizing your thoughts before writing helps create a more coherent and structured answer.
- Create an Outline: A brief outline can help you organize your ideas logically. Make sure each paragraph focuses on a single point that supports your overall argument.
Writing a Clear and Concise Response
When you start writing, aim for clarity and precision. Avoid unnecessary details that don’t directly support your answer. Focus on the main ideas and present them in a clear, logical order.
- Introduction: Start with a brief introduction that restates the question in your own words. This helps set the stage for your argument and shows that you understand the topic.
- Body Paragraphs: Each paragraph should cover a specific point. Start with a clear topic sentence, then provide evidence or examples that support your argument. Use transitions to connect your ideas smoothly.
- Conclusion: End with a concise summary of your main points. Reinforce the key takeaways and ensure that your answer addresses the question fully.
By following these best practices, you can approach essay questions confidently, ensuring that your responses are well-organized, focused, and compelling.
Post-Exam Review and Learning
After completing an assessment, it’s essential to take the time to reflect on your performance. This process not only helps you identify areas of strength but also allows you to pinpoint areas that need further improvement. By carefully reviewing your responses, you can turn the assessment into a valuable learning opportunity that enhances your overall understanding of the subject.
Analyzing Your Performance

Reviewing your responses and understanding where you went wrong is crucial for improvement. Take the following steps to analyze your performance effectively:
- Identify Mistakes: Go through each question you answered and check for any mistakes. Were there gaps in your knowledge, or did you misinterpret the question?
- Understand Why: Reflect on why you made those mistakes. Was it due to a lack of understanding, poor time management, or not reviewing the material thoroughly?
- Seek Feedback: If possible, ask your instructor or peers for feedback on your responses. Understanding their perspective can provide valuable insights into how you can improve in the future.
Improving for Future Success
Once you’ve reviewed your performance, it’s time to make adjustments and develop strategies for future success. Consider these tips for improving your preparation and response strategies:
- Focus on Weak Areas: Identify specific topics or concepts you struggled with and spend more time reviewing them. Use additional resources such as textbooks, videos, or online courses to strengthen your understanding.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice helps reinforce your knowledge. Use practice questions, flashcards, or study groups to test your understanding and improve retention.
- Refine Test-Taking Strategies: Learn from your mistakes in the test-taking process. Whether it’s improving time management or practicing how to break down complex questions, refining your strategies can help you perform better in future assessments.
By taking a proactive approach to post-assessment review, you can not only learn from your mistakes but also gain a deeper understanding of the material, setting yourself up for future success.