For drone operators, maintaining proficiency and staying updated with regulations is essential for safe and legal flight operations. Ensuring your knowledge remains current helps prevent violations and enhances safety during missions. Regularly reviewing key topics is necessary to keep up with the evolving rules and best practices in the industry.
Re-certification or skill refreshment for commercial pilots involves revisiting critical areas such as flight safety, weather conditions, operational limits, and airspace management. Understanding these topics not only ensures compliance with governing bodies but also fosters better decision-making during actual drone flights. This is an opportunity to refine expertise and ensure that all operational procedures are followed accurately.
Whether you’re a new operator or an experienced professional, reinforcing your knowledge base is crucial for success. By exploring common areas tested and frequently asked questions, pilots can approach re-certification with confidence, making the process smooth and effective.
Drone Operator Certification Knowledge Review
Maintaining certification as a drone operator requires ongoing education and a clear understanding of essential principles. The requalification process involves testing your knowledge on a variety of topics related to flight safety, regulations, and operational procedures. It is important for pilots to stay well-informed and up-to-date with current laws and best practices to ensure safe and legal operations.
The process is designed to assess proficiency in critical areas such as airspace rules, weather interpretation, emergency procedures, and equipment maintenance. Understanding these concepts not only ensures compliance with aviation authorities but also promotes safer flights and better decision-making on the job. Regular testing and self-assessment are essential for reinforcing the knowledge required for successful certification renewal.
For those preparing to renew their credentials, it is helpful to review common topics and areas frequently covered in the process. By focusing on frequently tested material, operators can approach the certification renewal with greater confidence and readiness, ensuring they are fully prepared for the challenges ahead.
Overview of Certification Requirements
To maintain legal status as a commercial drone operator, pilots must demonstrate their knowledge of key operational guidelines and safety protocols. This includes understanding the rules set forth by aviation authorities to ensure safe integration of unmanned aircraft systems (UAS) into national airspace. Regular certification refreshers are mandatory for keeping current with evolving regulations and best practices in the field.
Core Knowledge Areas

The certification renewal process evaluates a range of topics essential for safe flight operations. These include airspace management, operational limits, weather conditions, and emergency procedures. Operators must also demonstrate their ability to perform thorough pre-flight checks and ensure their equipment meets required standards for flight safety.
Understanding Compliance and Regulations
To stay compliant, drone operators must regularly review updated rules concerning flight restrictions, authorization processes, and safety measures. Certification requirements are designed to assess both practical and theoretical knowledge, ensuring that operators are prepared for a wide variety of real-world scenarios.
Key Topics Covered in UAS Certification

The re-certification process for drone operators involves evaluating knowledge across several essential areas that ensure safe and legal operations. These topics encompass everything from technical skills to understanding the environment in which drones operate. Mastery of these areas is critical for both passing the certification and conducting safe flights under real-world conditions.
Essential Areas of Focus
The certification process tests a variety of topics relevant to drone operations, from understanding weather conditions to airspace classification and emergency procedures. Below is a summary of the key areas typically covered:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Airspace Classification | Understanding different types of airspace and their regulations is crucial for ensuring compliance during flight operations. |
| Flight Safety | Safety procedures and risk management are critical to avoiding accidents and ensuring smooth operations. |
| Weather Interpretation | Accurate weather assessments help determine safe flying conditions and mitigate weather-related risks. |
| Emergency Procedures | Knowing how to respond to in-flight emergencies is essential for maintaining control and safety. |
| Equipment Maintenance | Ensuring that drones are well-maintained helps prevent mechanical failures during flight. |
Regulatory Knowledge
In addition to practical knowledge, operators must understand the regulatory landscape governing drone use. This includes compliance with national and local rules, airspace restrictions, and any updates to aviation laws that may impact commercial drone use.
Understanding Remote Pilot Knowledge Areas
For any drone operator seeking certification, mastering the core knowledge areas is essential to ensuring both safety and compliance. These areas encompass a range of subjects that reflect the operational, technical, and regulatory skills required for responsible flight. A thorough understanding of these concepts is vital to maintaining certification and performing safe and effective missions.
The key areas of knowledge for remote pilots cover everything from aircraft systems and flight operations to environmental factors and legal restrictions. Each of these topics contributes to a pilot’s ability to navigate complex situations, make informed decisions, and mitigate risks. Mastering these areas helps ensure that operators are well-prepared for every aspect of their flying responsibilities.
Core areas include understanding airspace rules, interpreting weather conditions, responding to emergencies, and performing routine equipment maintenance. Remote pilots must also be familiar with national and local aviation regulations that govern unmanned aircraft operations, as well as the specific requirements for various types of missions.
Flight Operations and Safety Protocols
Safe and effective drone operations require strict adherence to safety procedures and operational guidelines. Every flight, regardless of its purpose, involves potential risks that can be mitigated through thorough planning and clear protocols. Having a well-established approach to safety ensures that both the operator and the general public remain protected during flight operations.
Flight operations cover everything from pre-flight checks to emergency response strategies. Prior to each mission, operators must verify that the aircraft is in good working condition and that all safety features are functional. Additionally, understanding flight limitations and how to adjust to changing environmental conditions is critical to avoiding accidents and ensuring a successful flight.
Safety protocols must also encompass emergency preparedness, including how to handle system failures, navigation issues, or adverse weather conditions. Operators should be trained to react calmly and effectively in these situations, minimizing the risk to the aircraft and surrounding area. By following these protocols, remote pilots can maintain operational safety and avoid costly or dangerous errors during flights.
Weather and Environmental Considerations
Understanding environmental factors and weather conditions is essential for successful and safe drone operations. Changes in weather can significantly affect flight performance, and pilots must be able to assess conditions before and during a mission. By considering weather forecasts, seasonal patterns, and local environmental variables, remote pilots can make informed decisions that reduce the risk of accidents.
Key weather conditions to monitor include:
- Wind Speed and Gusts: High winds can destabilize the drone, making control difficult. Pilots must ensure conditions are within safe operational limits.
- Visibility: Poor visibility due to fog, rain, or other atmospheric conditions can impair navigation and increase the risk of accidents.
- Temperature: Extremely hot or cold temperatures can affect battery performance, reducing flight time or causing malfunction.
- Precipitation: Rain, snow, or ice can damage the drone’s sensors or disrupt flight control, so flights should be avoided in these conditions.
In addition to weather, environmental factors such as air quality, wildlife activity, and terrain should also be considered. These factors can impact both the safety of the flight and the operational effectiveness of the drone. For example, high pollution levels can affect visibility, while wildlife may pose collision hazards in certain areas.
Before each mission, pilots should check weather reports, assess environmental conditions, and adjust flight plans accordingly to ensure the safety of the operation.
Drone Maintenance and Pre-Flight Inspections
Proper maintenance and thorough pre-flight inspections are vital to ensuring the safety and reliability of drone operations. Before every mission, operators must conduct a comprehensive check of their equipment to verify that all components are functioning as expected. Regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent technical failures and reduce the likelihood of in-flight emergencies.
Key aspects of drone maintenance include:
- Battery Health: Ensure that batteries are fully charged and in good condition. Damaged or old batteries should be replaced to avoid performance issues during flight.
- Propellers and Motors: Inspect propellers for any cracks, chips, or signs of wear. Ensure motors are clean and free from debris that could hinder their function.
- Firmware and Software Updates: Check that the drone’s firmware and control software are up-to-date. Software updates often include performance improvements and safety features.
- Camera and Sensors: Verify that cameras, sensors, and GPS units are operating correctly. Clean lenses and check the calibration of sensors to ensure accurate data collection.
Pre-flight inspections should focus on confirming that all systems are ready for safe operation. This checklist typically includes:
- Verify that all equipment is properly assembled and secure, including props and landing gear.
- Check that the flight control system is responsive and the remote controller is paired with the drone.
- Ensure that GPS signals are strong, and home points are correctly set to avoid navigation errors.
- Test flight controls to make sure there are no issues with movement or stability before takeoff.
By performing these regular maintenance tasks and pre-flight checks, operators can minimize the risk of technical failures, enhance flight performance, and ensure the safety of both the drone and its surroundings.
Regulations for Commercial Drone Use
The use of drones for commercial purposes is governed by a set of rules and regulations designed to ensure safety, privacy, and accountability. These regulations apply to operators conducting business activities such as aerial photography, surveying, delivery services, and more. Adhering to these rules is crucial for maintaining legal compliance and ensuring the safety of both the drone operator and the general public.
Key regulatory requirements include:
- Operator Certification: Commercial drone operators must obtain certification, proving their knowledge of operational safety, airspace management, and aviation regulations.
- Flight Restrictions: Drones must be flown within specific altitudes, distances, and designated airspace zones. Certain areas, such as near airports or in restricted zones, require special permissions or waivers.
- Weight and Size Limits: Regulations set limitations on the maximum weight and size of drones used for commercial purposes. These restrictions are designed to ensure safe operations within controlled airspace.
- Insurance and Liability: Operators may be required to carry insurance coverage that protects against potential accidents or damage during operations. This ensures that any liabilities are covered.
- Operational Hours: Commercial drone flights are often restricted to daylight hours, with additional rules in place for flying during night time or in adverse weather conditions.
In addition to these requirements, operators must stay informed about ongoing regulatory updates and changes. Compliance with aviation authorities’ standards is essential for operating legally and avoiding penalties or suspension of privileges.
By adhering to these rules, drone operators can safely conduct their commercial activities while minimizing risks to people, property, and air traffic.
Understanding Airspace Classification Rules
Understanding airspace classification is essential for safely operating unmanned aircraft. Different types of airspace are regulated differently, and pilots must be familiar with these classifications to ensure that they fly within the allowed zones and follow the correct procedures. By knowing the rules governing each type of airspace, drone operators can avoid collisions with other aircraft and adhere to air traffic control guidelines.
The airspace surrounding the earth is divided into several classes, each with its own set of rules regarding altitude, flight restrictions, and operational requirements. These classifications help manage traffic, ensuring safe distances between aircraft and reducing the risk of accidents. Pilots must always check their flight routes and ensure they are compliant with the airspace restrictions in place for the area in which they intend to fly.
Types of Airspace
The primary classes of airspace include:
| Airspace Class | Description | Operational Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| A | Controlled airspace at high altitudes, typically above 24,000 feet. | Requires a flight plan and clearance from air traffic control (ATC). |
| B | Airspace surrounding major airports with the highest level of traffic control. | ATC clearance is required for entry, and strict operating procedures are enforced. |
| C | Controlled airspace around smaller airports with less dense traffic. | ATC clearance is generally required for entering and operating within this airspace. |
| D | Airspace surrounding airports with active control towers. | Communication with ATC is required for entry and flight within this area. |
| E | Controlled airspace that is not associated with any specific airport. | Generally requires permission from ATC, depending on altitude. |
| G | Uncontrolled airspace, typically found in rural or remote areas. | No ATC clearance is required, but pilots must follow general aviation rules. |
Familiarity with these airspace classes is crucial for planning and executing safe drone flights. Operators should always verify the airspace classification of their planned flight area, ensuring they comply with regulations and maintain communication with air traffic controllers when necessary.
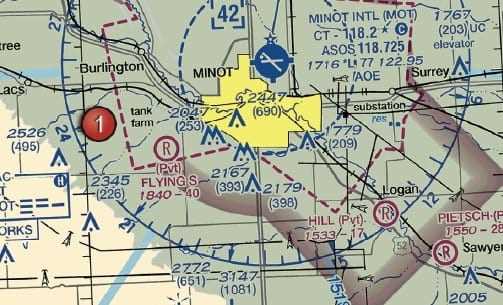
How to Interpret UAS Flight Charts
Interpreting flight charts is a crucial skill for any drone operator, as these charts provide detailed information about airspace, obstacles, and other essential factors that impact flight safety. Proper understanding of flight charts allows operators to plan their routes effectively and avoid potential hazards. These charts typically display key data on airspace classifications, navigation aids, terrain features, and restricted zones, all of which are important for safe flight operations.
Flight charts are structured in a way that makes it easier for pilots to understand the layout of the area they intend to fly in. By interpreting these charts correctly, operators can ensure that their flight path aligns with safety protocols and legal requirements. Understanding symbols, lines, and notations on a chart is vital to navigating through controlled and uncontrolled airspace, avoiding obstacles, and complying with regulatory boundaries.
Key Features of UAS Flight Charts
Flight charts contain several key elements that operators need to familiarize themselves with. Below is a table of common symbols and their meanings:
| Symbol | Meaning | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Airspace Boundaries | Indicates the limits of controlled and restricted airspace | Essential for determining where drone flight is allowed and where special permissions are needed. |
| Altitude Limits | Shows the maximum and minimum altitude for specific airspace regions | Helps operators maintain safe flight levels and avoid higher traffic zones. |
| Navigation Aids | Marks locations of VORs, waypoints, or other navigation aids | Used for route planning and ensuring proper navigation during long-distance flights. |
| Prohibited Areas | Indicates areas where flights are strictly prohibited | Prevents operators from entering restricted or dangerous zones, such as military installations or government buildings. |
| Temporary Flight Restrictions (TFR) | Temporary restrictions due to events or emergencies | Critical for avoiding flight in zones with temporary restrictions, such as during disasters or large public events. |
When preparing for a flight, always consult relevant flight charts to identify all airspace classifications and potential hazards. By paying attention to these details, operators can avoid accidents and ensure a smooth and legal flight experience. Understanding flight charts is not just about compliance; it is also about keeping both the drone and the surrounding environment safe.
Operational Limits for Drone Pilots
Drone pilots must operate within specific guidelines to ensure both safety and compliance with legal standards. These operational limits help prevent accidents and protect both the pilot and the public from harm. These limitations cover a wide range of factors, from altitude restrictions to weather conditions, and must be followed at all times. Understanding and adhering to these boundaries is essential for responsible drone operation.
While regulations vary depending on the type of operation and location, common restrictions typically involve flight altitude, proximity to other aircraft, and operating hours. Pilots must also be aware of airspace classifications, temporary flight restrictions, and environmental conditions that could impact flight safety. These limits are designed to minimize the risk of incidents while maintaining smooth integration of unmanned aircraft into the broader aviation system.
Altitude and Distance Restrictions
One of the most critical operational limits for drone pilots is the altitude restriction. In most cases, drones are not permitted to fly above a certain altitude to avoid conflicts with manned aircraft. Additionally, pilots must maintain a specified distance from certain areas, such as airports, controlled airspace, and populated zones. Below are some common altitude and distance restrictions:
- Maximum Altitude: Typically, drones are limited to 400 feet above the ground to stay clear of manned aircraft.
- Distance from Airports: Operators must maintain a safe distance from airports and heliports to prevent interference with aircraft operations.
- Restricted Zones: Certain areas, such as military bases, national parks, or disaster zones, are off-limits for drone operations.
Weather Conditions and Environmental Factors
Weather conditions play a significant role in safe drone operations. Pilots must evaluate environmental factors before each flight to ensure that conditions are suitable. Adverse weather conditions, such as high winds, thunderstorms, or reduced visibility, can pose serious risks to drone safety. Pilots should consider the following environmental limits:
- Wind Speed: Excessive wind can cause loss of control and make flying dangerous, especially for smaller drones.
- Visibility: Flights are typically prohibited in conditions where visibility is below a certain threshold, such as heavy fog or rain.
- Temperature Extremes: Extremely high or low temperatures can affect drone performance and battery life.
Adhering to these operational limits ensures that drone flights are conducted safely and in compliance with aviation regulations. Before every flight, pilots should thoroughly check weather conditions, airspace classifications, and other relevant factors to confirm that they are operating within the prescribed boundaries.
Emergency Procedures for UAS Operations
Unmanned aircraft systems (UAS) operators must be prepared for emergency situations that could arise during flight. Having a clear understanding of emergency procedures is essential to ensure the safety of the flight, the equipment, and those in the surrounding area. Operators should be familiar with a series of steps to take when things go wrong, whether it’s a sudden loss of power, a malfunction, or an unexpected environmental hazard.
Effective emergency procedures not only minimize the risk of accidents but also ensure that operators can respond swiftly and efficiently. Preparation for such events includes knowing the proper course of action, having backup systems in place, and being aware of how to land the vehicle safely in case of failure. Below are the key aspects that every drone pilot should consider when preparing for emergencies.
Common Emergency Scenarios and Responses
Understanding typical emergency situations and how to handle them can prevent confusion during critical moments. Some common emergencies include signal loss, battery depletion, and equipment malfunctions. Each of these scenarios requires a different approach to ensure safe operation and minimize damage.
- Signal Loss: If communication with the drone is lost, the first step is to engage the fail-safe function. Most systems are designed to return the drone to its home point automatically in case of signal loss.
- Battery Failure: When the battery reaches a critical level, operators must safely bring the drone down as soon as possible. It’s important to monitor battery status throughout the flight to avoid unexpected power loss.
- Mechanical Malfunctions: If there is a malfunction, such as a motor failure, pilots should immediately bring the drone down in a controlled descent to avoid losing control. Prior preparation can involve setting up an emergency landing area or an automated landing function.
Preventative Measures and Training
While emergency procedures are vital, preventative measures are just as important in avoiding situations that might require an emergency response. Proper maintenance and pre-flight checks can reduce the likelihood of failures during a flight. In addition, pilots should undergo regular training to practice handling emergencies and stay up to date with new procedures and technologies.
- Pre-flight Inspection: Thoroughly inspect the drone before each flight to ensure that all components are functioning properly, including the battery, motors, and communication systems.
- Regular Maintenance: Perform routine maintenance and calibration on the drone to prevent unexpected malfunctions.
- Simulated Emergency Training: Conduct training exercises to simulate emergency situations, allowing the operator to practice the response procedures under controlled conditions.
By being prepared for emergencies, drone operators can significantly reduce the risks associated with flying unmanned aircraft. It’s important to remember that safety should always be the primary concern during operations, and knowing how to respond quickly and correctly to unforeseen circumstances is a critical skill for any operator.
Review of Recent FAA Rule Changes
In the ever-evolving landscape of unmanned aircraft systems (UAS), the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) plays a crucial role in regulating and ensuring the safety of drone operations. With rapid technological advancements and growing usage, the FAA periodically updates its regulations to address new challenges, improve safety measures, and streamline operations. Understanding these changes is essential for operators to stay compliant and continue flying safely within the legal framework.
This section will explore some of the recent rule modifications implemented by the FAA, focusing on the key updates that impact operators and flight practices. These changes often reflect the need to balance innovation with safety, and their significance extends to both recreational and commercial users. The goal is to keep drone operations safe and efficient, while also enabling the continued growth of the industry.
Notable Changes in Certification and Operation
One of the most notable updates in FAA regulations pertains to the certification and operational standards for unmanned aircraft. The FAA has made significant strides in simplifying and clarifying the requirements for both pilots and manufacturers, ensuring that compliance is more accessible for all stakeholders.
- Remote Pilot Certification: The FAA recently streamlined the process for obtaining remote pilot certification, making it easier for individuals to legally operate drones for commercial purposes.
- Operational Limits: Changes in operational restrictions, such as altitude and airspace access, have been adjusted to allow for greater flexibility while maintaining safety standards. Pilots must stay updated on airspace restrictions and altitude limits for their specific operations.
- Night Flight Rules: There has been a change in the restrictions surrounding night operations. Previously, flying at night required special waivers, but now, under certain conditions, night flights are permitted without additional certification, provided specific safety equipment is used.
Updated Requirements for Remote Identification and Tracking
The FAA has also introduced new rules related to remote identification (Remote ID) and tracking systems. These updates are designed to improve airspace awareness and enable better integration of unmanned systems into the national airspace. The implementation of Remote ID is one of the most significant regulatory shifts aimed at enhancing safety and accountability.
- Remote ID Compliance: Drones must now be equipped with Remote ID technology to transmit their location and identification information. This allows authorities to track and identify drones in real-time, improving situational awareness for both air traffic controllers and law enforcement.
- Tracking Requirements: The new tracking requirements ensure that drones can be easily located in the event of an emergency or accident. These systems are crucial for search and rescue operations and for ensuring the safe management of unmanned flights in shared airspace.
These recent updates reflect the FAA’s commitment to ensuring that unmanned aircraft systems can be safely integrated into the national airspace system. It is important for operators to stay informed of the latest changes to avoid non-compliance and to ensure they are operating their drones safely and legally.
Study Resources for Recurrent Exam
Preparing for the renewal assessment in the unmanned aircraft system (UAS) field requires a solid understanding of regulations, safety protocols, and operational practices. As regulations evolve, it’s important to have access to reliable study materials that provide the most current and relevant information. This section highlights a range of valuable resources to assist in preparing for the required knowledge assessment, ensuring that candidates are well-equipped for success.
Whether you’re a first-time renewal or a seasoned operator, utilizing the right study materials can make all the difference. From official FAA handbooks to online courses and practice tests, there are various tools available that cater to different learning styles. The following resources can guide you through the necessary topics and enhance your ability to pass the required assessment with confidence.
Official FAA Study Materials
The Federal Aviation Administration offers several official resources to help individuals prepare for the assessment. These materials are specifically designed to ensure that pilots understand the rules and guidelines necessary for safe and legal flight operations.
- FAA Remote Pilot Knowledge Test Guide: This guide outlines the topics covered in the knowledge assessment and provides detailed explanations on each subject. It is an essential resource for anyone preparing for the test.
- FAA Regulations and Advisory Circulars: Familiarizing yourself with the latest regulations and advisory circulars is crucial. These documents are available for free on the FAA website and offer in-depth information on airspace rules, safety protocols, and operational limits.
Online Learning Platforms
Many online platforms offer specialized courses for individuals preparing for the assessment. These courses are often structured to include video lessons, interactive quizzes, and comprehensive study guides.
- Remote Pilot Courses: Websites such as Drone Pilot Ground School and UAV Coach provide extensive online courses tailored to remote pilots. These courses cover everything from airspace management to operational safety and include practice tests to help solidify knowledge.
- Practice Tests: Taking practice exams is one of the most effective ways to gauge your understanding of the material. Platforms like Prepware and other FAA test prep sites offer practice questions designed to simulate the real assessment.
Books and Study Guides
In addition to online resources, there are several books and study guides that provide comprehensive overviews of the key topics. These materials are often available in both physical and digital formats, making them accessible for on-the-go study.
- Remote Pilot Test Prep Book: Popular books such as “Remote Pilot Test Prep” by the Aviation Supplies & Academics, Inc., are invaluable resources. These guides offer structured learning, detailed explanations, and practice questions.
- Commercial Drone Pilot Handbook: Another helpful resource is the “Commercial Drone Pilot Handbook” by the Drone Pilot Ground School, which provides in-depth coverage of topics needed for the renewal assessment.
By utilizing a combination of these official resources, online courses, and books, you can significantly increase your chances of successfully passing the knowledge renewal assessment. Remember, regular practice and staying up-to-date with the latest changes in regulations are key to ensuring long-term success in the field.
Common Mistakes in UAS Exams
When preparing for the unmanned aircraft system (UAS) knowledge assessment, many candidates make common errors that can significantly affect their performance. These mistakes often stem from misunderstandings or a lack of focus on key areas of the test. By identifying these common pitfalls, you can improve your chances of success and avoid costly errors on the assessment.
In this section, we will examine some of the most frequently made mistakes and offer tips on how to address them. By recognizing these areas of weakness, you can ensure a more thorough understanding of the material and approach the test with greater confidence.
Overlooking Key Regulations
One of the most common mistakes is neglecting to fully understand the regulations governing unmanned aircraft operations. It is essential to study the rules carefully, as they form the backbone of the test. Many candidates fail to review the most up-to-date regulatory changes, which can lead to misunderstandings or incorrect answers.
- Ignoring recent updates: Ensure you are familiar with the latest changes in airspace rules, operational limits, and flight restrictions. Regulations can evolve, so it’s important to stay current.
- Misunderstanding airspace classification: Many candidates struggle with the distinctions between different types of airspace. A solid understanding of this is crucial for passing the assessment.
Failure to Master Safety Protocols
Another common mistake is underestimating the importance of safety protocols. Safety is a top priority in unmanned aircraft operations, and the knowledge assessment places a strong emphasis on understanding and applying safety procedures in various scenarios.
- Skipping pre-flight checks: Many candidates fail to emphasize the importance of conducting thorough pre-flight inspections. This step is critical to ensuring the safe operation of the aircraft.
- Not considering weather conditions: Weather and environmental factors play a significant role in flight safety. Candidates often overlook the importance of evaluating weather conditions before taking flight.
Misinterpreting Flight Charts and Maps
Flight charts and maps are integral tools for unmanned aircraft pilots, but many candidates struggle with interpreting them correctly. Understanding airspace structure, as well as navigation and altitude restrictions, is essential for safe flight planning and successful completion of the test.
- Not understanding chart symbols: Candidates often misinterpret the symbols used on charts. Familiarize yourself with the key symbols and their meanings to avoid errors.
- Failure to plan a route: Flight planning involves more than just looking at a map. Ensure you understand how to plan a s
Tips for Preparing for the Test
Successfully completing the unmanned aircraft knowledge assessment requires more than just basic knowledge of flight operations. A well-structured study plan, attention to detail, and practical understanding of key concepts are essential for ensuring a positive outcome. In this section, we will outline several effective strategies that will help you prepare for the assessment and perform at your best on the day of the test.
1. Review Official Study Materials
Familiarizing yourself with official study resources is crucial to understanding the scope of the test. These materials often include the most accurate and up-to-date information on regulations, safety procedures, and airspace classifications. Focus on the following:
- Regulatory updates: Keep track of the latest regulatory changes as they may directly impact the questions on the test.
- Flight procedures: Study both normal and emergency procedures thoroughly to ensure a complete understanding of operational protocols.
- Airspace charts and maps: Ensure that you can confidently read and interpret flight charts, including understanding airspace limits and restrictions.
2. Take Practice Tests
One of the most effective ways to prepare is by taking practice tests. These mock assessments give you a sense of the test format, the types of questions to expect, and areas where you may need additional review. By simulating the test environment, you can build confidence and improve your time management during the real test.
- Identify weak areas: Use practice tests to pinpoint topics you are struggling with and focus your study efforts there.
- Track progress: Take multiple practice tests over time to gauge your improvement and track your readiness.
3. Focus on Key Knowledge Areas
Understanding the most critical knowledge areas is vital for passing the assessment. While every test is unique, certain topics are emphasized more frequently and require greater attention. These include:
- Safety and emergency procedures: Knowing the correct actions in case of a malfunction or emergency is a key aspect of the assessment.
- Weather and environmental factors: Learn to analyze weather conditions and how they affect flight operations.
- Airspace classifications and restrictions: A clear understanding of different types of airspace and their associated rules is essential for safe and compliant flying.
4. Study with a Group or Instructor
Studying with others or under the guidance of an instructor can provide additional insights and help clarify any misunderstandings. Group study sessions allow you to ask questions, share knowledge, and learn from others’ experiences. An instructor can offer personalized feedback and guidance, ensuring you are fully prepared for the test.
- Join study groups: Collaborate with fellow candidates to exchange tips, review material, and prepare together.
- Seek professional help: If you’re struggling with specific topics, consider enrolling in a formal review course or working with a mentor to fill knowledge gaps.
By following these tips and maintaining a focused, disciplined approach to your studies, you can increase your chances of success and approach the knowledge assessment with confidence. Preparation is key, and with the right mindset and resources, you can achieve your goal of becoming a skilled and knowledgeable unmanned aircraft operator.
After the Test: Next Steps for Pilots
Completing the knowledge assessment is an important milestone, but the journey doesn’t end there. After successfully passing the test, there are several important actions and considerations that every pilot should keep in mind to maintain their certification and stay compliant with regulations. Whether you’re a new or experienced operator, understanding the next steps will ensure that you remain informed, prepared, and ready to fly safely.
1. Review and Understand Your Results
After completing the assessment, it’s essential to review your results carefully. Whether you pass or need additional study, understanding which areas you performed well in and which topics need more attention can help refine your flying skills and knowledge base.
- Analyze your performance: Focus on any areas where you may have struggled to ensure you fully understand the material before you begin flying professionally.
- Review incorrect answers: Reflect on any questions you answered incorrectly, and research the correct information to avoid similar mistakes in the future.
2. Stay Current with Ongoing Requirements
Maintaining your certification requires staying current with any applicable knowledge or skill requirements. The requirements for renewal or continued validity are important to understand, as they help ensure that you remain compliant with the latest aviation standards.
- Monitor expiration dates: Be aware of when your certification or endorsement expires and begin the renewal process well in advance.
- Participate in ongoing training: Continue to engage in professional development and training programs to ensure you stay updated on safety standards and industry changes.
3. Begin Flying Professionally
Once you’ve received your certification, you are legally permitted to begin operating unmanned aircraft for commercial purposes. However, this step involves more than just obtaining the certification–it also means embracing responsibility for safety and professionalism during every flight.
- Plan your operations: Create flight plans that adhere to legal requirements, safety protocols, and best practices.
- Document every flight: Keep a thorough log of your operations, including flight times, conditions, and any maintenance or issues with the aircraft.
4. Stay Informed on Regulatory Updates
The aviation industry is constantly evolving, and staying up-to-date with the latest regulations is crucial. Regulatory bodies often release new rules or updates that affect how unmanned aircraft are operated. By staying informed, you ensure that your practices remain legal and safe.
- Subscribe to notifications: Sign up for newsletters or official updates from aviation authorities to receive the latest information.
- Participate in webinars and workshops: Take advantage of industry events to stay engaged with regulatory changes and operational best practices.
5. Network with Other Pilots
Building connections with other professional pilots is a valuable resource for sharing experiences, knowledge, and advice. Joining professional associations or participating in online communities can help you stay connected with others in the field and learn about new opportunities.
- Join pilot groups: Connect with others in your area or within specific flight sectors to exchange tips and industry news.
- Attend industry events: Networking at trade shows, conferences, and workshops will allow you to grow your knowledge and professional circle.
By focusing on these important next steps, you can transition from successfully passing the knowledge test to becoming a competent, safe, and responsible operator in the growing field of unmanned flight operations.