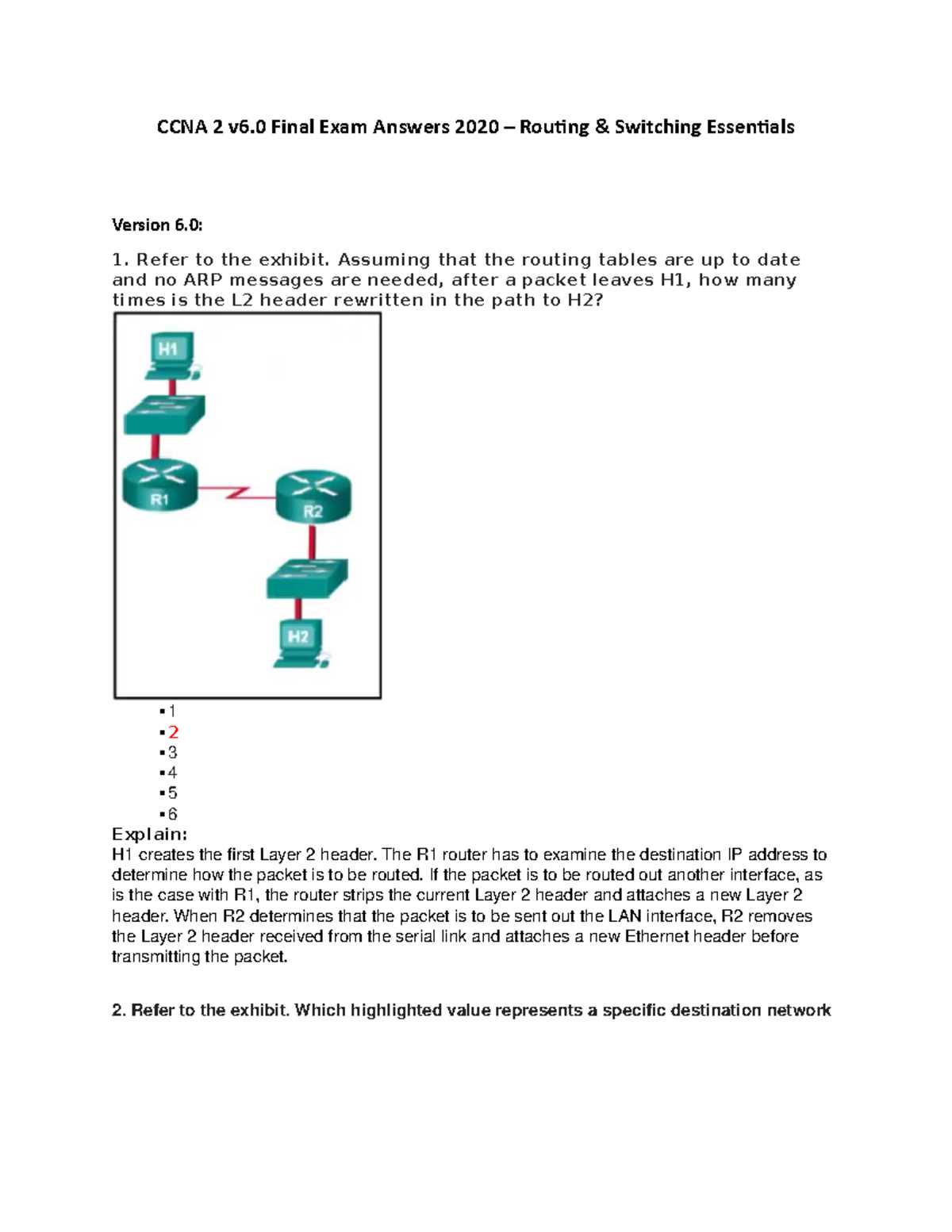
Networking is the backbone of modern communication, connecting devices, systems, and services across the globe. Understanding how data travels through various devices and networks is essential for anyone aiming to work with network infrastructure. This section delves into crucial topics that form the foundation of a solid networking knowledge base, helping to prepare for the challenges that lie ahead in the field.
Focusing on key concepts related to device communication, the process of managing network traffic, and maintaining robust systems, learners will explore both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. The ability to troubleshoot and configure network systems is vital, and this segment offers a comprehensive overview to build the required expertise. Through engaging exercises and study materials, individuals can enhance their understanding and develop the confidence needed to excel in networking tasks.
By mastering these essential building blocks, individuals can position themselves for success in the evolving world of network technology. With a deep understanding of how networks function and the protocols that govern them, learners will be better equipped to tackle complex network challenges and stay ahead in the competitive landscape of IT professionals.
Routing and Switching Essentials RSE Exam Overview
In the field of network infrastructure, mastering key concepts related to how devices interact within a system is crucial. The challenges presented in this section provide a pathway for learners to deepen their understanding of essential networking principles. From configuring hardware to troubleshooting complex systems, the material covers various practical aspects needed for a successful career in IT.
This segment introduces various critical concepts that define the modern network environment. Topics span from basic system design to more advanced techniques aimed at optimizing connectivity and managing data flow. By understanding the underlying technologies, individuals will be well-prepared for tackling real-world scenarios.
For those looking to measure their knowledge, the assessment focuses on ensuring a solid grasp of the fundamental skills required in network configuration and maintenance. Key areas covered include device management, communication protocols, and the ability to implement solutions effectively in a dynamic environment. Success in this section is not just about memorizing facts, but about developing a practical, hands-on understanding of how networking technologies function in diverse settings.
Understanding RSE Chapter 2 Key Concepts
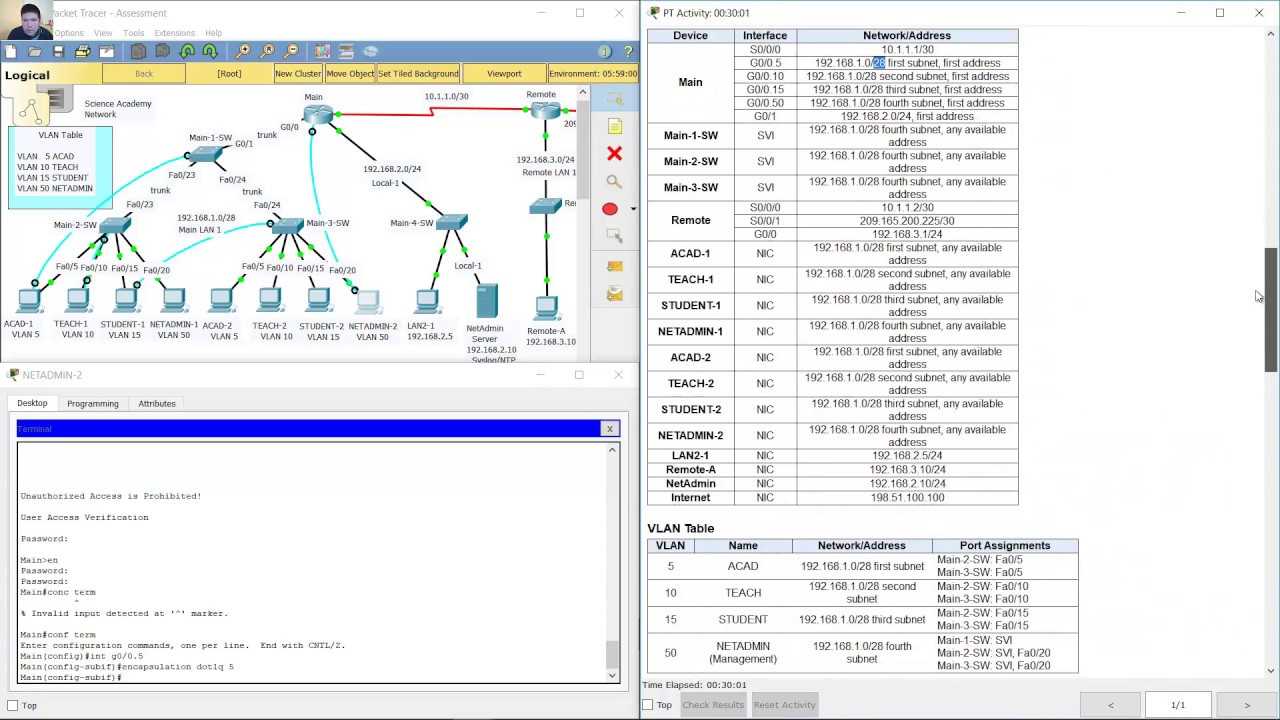
Grasping the core principles of network functionality is essential for anyone working with modern communication systems. In this section, learners are introduced to the critical building blocks that enable devices to connect and communicate within a network. Mastery of these foundational ideas is crucial for ensuring both efficiency and security in network operations.
Key areas explored in this section include:
- Network Devices: Understanding the role of routers, switches, and other network devices in managing data flow.
- IP Addressing: The importance of correctly assigning unique addresses to devices for seamless communication.
- Subnetting: Breaking down network space into smaller, manageable segments to optimize traffic and enhance performance.
- Protocols: Protocols that govern the rules for data transmission and ensure reliable communication between devices.
- Configuration Techniques: Learning how to set up, modify, and troubleshoot network devices and connections.
Each of these concepts plays a vital role in establishing a stable and secure network. Whether managing data transfer, addressing issues, or ensuring proper device functionality, understanding these core principles forms the backbone of any successful IT professional’s skill set. By mastering these key topics, individuals will be well-prepared for real-world network management tasks.
Core Topics Covered in Chapter 2
In this section, a range of fundamental concepts essential for understanding network management are introduced. These topics form the foundation for anyone seeking to deepen their knowledge in the field. By exploring these areas, learners gain a comprehensive understanding of how networks operate, including the underlying principles that govern communication between devices and how data flows through systems.
The following table outlines the core subjects that are explored:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Network Topologies | Explores different layouts of network systems, including how devices are connected and how data is routed within these configurations. |
| Device Functions | Examines the roles and functions of essential network hardware such as routers, hubs, and switches in managing communication and traffic flow. |
| IP Addressing | Introduces methods for assigning unique identifiers to devices, ensuring proper communication and preventing address conflicts. |
| Subnetting | Focuses on dividing a network into smaller, more efficient segments, enhancing both performance and security. |
| Data Transmission Methods | Details how information is transmitted across networks, including common protocols and communication standards that ensure reliable delivery. |
These key topics serve as the foundation for any network professional looking to effectively manage, maintain, and troubleshoot systems. A deep understanding of these subjects is necessary for achieving success in the field and advancing to more complex networking challenges.
Importance of Routing Protocols in Networking
In modern communication systems, the smooth flow of data between devices relies heavily on effective management and coordination. Protocols that guide how data packets are transmitted across networks are critical in ensuring reliable, efficient, and secure communication. These protocols enable devices to determine the best paths for data to travel, adapt to changes in the network, and maintain stability even in dynamic environments.
Without proper protocols in place, networks would struggle with congestion, delays, and unreliable communication. By utilizing different methods to identify optimal routes, these protocols allow devices to adjust to changing conditions, prevent traffic bottlenecks, and ensure that data reaches its destination in a timely manner. Furthermore, they play a key role in minimizing network downtime and ensuring fault tolerance, which is essential for both performance and user experience.
Overall, understanding the significance of these communication standards is vital for anyone working with network systems. As networks become increasingly complex, the ability to configure, troubleshoot, and optimize these protocols becomes a cornerstone of effective network management and troubleshooting.
How Switching Works in Network Infrastructure
In any network system, the ability to efficiently direct data between devices is crucial for maintaining high performance and stability. The process that handles the transfer of data between different networked devices ensures that information is routed correctly and efficiently. This involves making intelligent decisions about where data should be sent, based on the unique identifiers of each device and the state of the network.
Key steps involved in this process include:
- Frame Reception: Data arrives at a device in the form of frames, which contain the necessary information to guide them to their destination.
- Address Lookup: Each device on the network has a unique identifier. The system checks these identifiers to determine the correct path for the data.
- Forwarding: After determining the destination, the system forwards the data to the correct output port or device, ensuring it follows the most efficient route.
- Table Management: Network devices maintain tables that track the available connections and help in making quick decisions about data paths.
This process helps to optimize the use of network resources, avoid congestion, and improve overall system performance. Devices that handle these functions are essential for ensuring that large-scale networks can operate smoothly without bottlenecks or unnecessary delays. Understanding how data is managed and transferred within a network is fundamental to building a reliable and scalable infrastructure.
Exam Structure and Question Types
Assessments in network-related fields typically follow a structured approach to test both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Understanding the format of these tests is crucial for effective preparation. The variety of question types ensures that candidates are evaluated across a range of competencies, from fundamental concepts to hands-on troubleshooting and configuration tasks.
The structure of the assessment includes:
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): These questions test your theoretical understanding of key concepts, where you choose the correct answer from several options.
- Drag-and-Drop: These questions assess your ability to match concepts or arrange items in the correct order, simulating practical problem-solving scenarios.
- Simulations: In these tasks, you’ll be asked to configure a network or troubleshoot issues within a virtual environment, testing your practical skills and decision-making abilities.
- Fill-in-the-Blank: These questions challenge your recall of specific technical terms or values, ensuring that you remember key definitions and configurations.
By familiarizing yourself with these question types, you can focus on strengthening both your theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This balanced approach is essential for tackling the test successfully and demonstrating a comprehensive understanding of the material.
Study Strategies for Chapter 2 Success
Successfully mastering the material in any network-focused section requires a structured approach to studying. A balance of theoretical knowledge and practical experience is essential to understanding key concepts and performing well in assessments. By organizing your study sessions and focusing on critical topics, you can build a strong foundation and prepare for all types of questions.
Focus Areas for Mastery
In order to excel, it’s important to dedicate time to the most impactful topics. These areas cover both foundational knowledge and practical configuration skills that are essential for success. Focus on the following key subjects:
| Topic | Study Focus |
|---|---|
| Network Devices | Study the roles of devices such as routers, switches, and hubs in network communication. |
| IP Addressing | Understand how to assign and calculate subnet masks and IP addresses for efficient routing. |
| Protocols | Learn the protocols that govern data transmission and network behavior. |
| Configuration Skills | Develop hands-on skills by configuring devices and troubleshooting network issues. |
Effective Techniques for Studying
To reinforce your understanding, incorporate the following study strategies into your routine:
- Hands-On Practice: Use virtual labs or network simulators to practice configuring and troubleshooting devices.
- Review and Repeat: Revisit notes regularly and focus on areas where you find the most difficulty.
- Practice with Sample Questions: Solve practice tests to become familiar with the question format and to track your progress.
- Collaborative Learning: Join study groups to exchange ideas, discuss complex topics, and clarify doubts with peers.
By applying these strategies, you will enhance both your theoretical comprehension and practical ability, preparing you for success in any test or practical application related to networking topics.
Common Challenges in Routing and Switching
Working with network infrastructure often presents a variety of challenges that can complicate the setup and maintenance of connections. These difficulties may arise from configuration errors, protocol mismatches, or the need for troubleshooting complex issues. Whether managing small-scale setups or large enterprise networks, understanding and overcoming these challenges is crucial for maintaining a stable and efficient network.
Configuration Mistakes

One of the most common hurdles in networking is improper device configuration. Mistakes in setting up addresses, routing tables, or security protocols can lead to connectivity issues or network instability. Common configuration problems include:
- Incorrect subnet mask assignments
- Misconfigured routing protocols that result in traffic not reaching its destination
- Improper security settings that prevent authorized users from accessing network resources
Protocol and Compatibility Issues
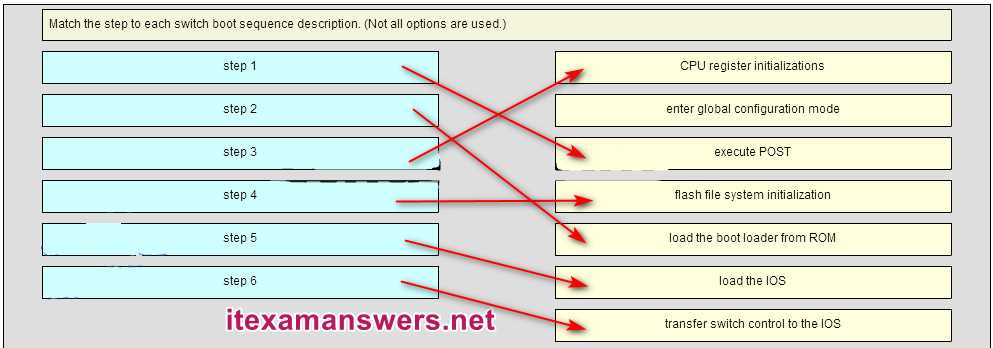
Different devices and systems often support a variety of communication protocols, which can create compatibility issues. Misunderstandings or mismatches between protocol types can hinder data exchange and network performance. Some challenges include:
- Inconsistent protocol configurations across network devices
- Inability to handle diverse communication methods due to firmware or software limitations
- Difficulty in integrating legacy systems with newer networking standards
Addressing these challenges requires a solid understanding of how each component works within the larger network structure. Through careful planning, regular updates, and vigilant monitoring, these obstacles can be minimized, leading to more reliable and efficient network performance.
Real-World Applications of Routing Techniques
In the modern digital landscape, the techniques used to direct network traffic are essential to the functionality of both small-scale systems and large global infrastructures. These methods not only ensure data reaches its intended destination but also optimize network performance and reliability. From enterprise networks to cloud services, the applications of these techniques are widespread and integral to the smooth operation of daily digital activities.
The real-world application of these methods is evident in various industries, where efficiency, speed, and reliability are paramount. Below are some key areas where these techniques are actively implemented:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Enterprise Networks | Large companies use these techniques to manage internal communication and optimize data transfer between different departments and branches. |
| Data Centers | Data centers utilize efficient traffic management methods to ensure uninterrupted data flow and reduce latency in cloud computing services. |
| Telecommunication Providers | Telecom companies rely on these techniques to route voice, video, and data traffic across the globe, maintaining quality and service continuity. |
| Internet Service Providers (ISPs) | ISPs implement these methods to direct internet traffic, handle bandwidth, and ensure that data reaches users swiftly and securely. |
| Smart Cities | Urban infrastructure depends on sophisticated traffic management to optimize communication between IoT devices, ensuring seamless city-wide operations. |
These techniques are not just theoretical concepts but have real, tangible impacts on industries that rely on effective data transfer. The evolution of these practices continues to shape how businesses and consumers interact with technology on a daily basis.
Best Resources for RSE Chapter 2 Preparation
Preparing for a networking certification or examination requires a solid understanding of key principles and hands-on experience. To ensure success, it is important to use the best available resources to enhance learning, practice skills, and gain a deeper understanding of networking concepts. Below are some of the most effective resources that can aid in preparing for this particular segment of the certification process.
Books and Study Guides
Books and study guides are invaluable tools for a structured approach to studying. Some recommended options include:
- Networking Fundamentals – A comprehensive guide to the fundamental concepts that lay the groundwork for network design and management.
- Advanced Networking Topics – A resource for deeper dives into more complex networking methods and techniques, ideal for supplementing foundational knowledge.
- Official Curriculum Guides – Published by certification providers, these guides provide the official content and syllabus, offering a clear path for preparation.
Online Learning Platforms
Interactive online courses and platforms offer practical exercises and video tutorials that can reinforce theoretical knowledge. Some great options are:
- Udemy – Features numerous courses, including beginner to advanced networking concepts, with quizzes and practice exams to test your knowledge.
- Pluralsight – Offers courses tailored to networking professionals, including real-world scenarios to apply learned material.
- CBT Nuggets – Known for high-quality video tutorials and hands-on practice, helping learners to prepare through engaging lessons and interactive content.
By combining study guides, online resources, and practice labs, learners can effectively grasp the key concepts, develop hands-on skills, and be fully prepared for success in this section of the certification process.
Top Tips for Passing the RSE Exam
Achieving success in any certification assessment requires not just knowledge but also effective preparation strategies. To increase your chances of passing, it’s important to focus on mastering key concepts, practicing essential skills, and managing your time efficiently. Here are several practical tips to help you succeed in the evaluation process.
1. Build a Strong Foundation
Focus on gaining a deep understanding of the core concepts and theories. A solid grasp of networking fundamentals, such as protocols, devices, and security measures, will allow you to approach questions with confidence and precision.
2. Hands-On Practice
Theoretical knowledge is vital, but hands-on experience is what truly prepares you for real-world scenarios. Utilize labs, simulators, or practice setups to gain experience in configuring devices, troubleshooting, and network management tasks.
3. Take Practice Assessments
Practice tests are invaluable for familiarizing yourself with the question formats and exam structure. Regularly taking mock tests will help you gauge your understanding, refine your skills, and build confidence as you approach the actual assessment.
4. Focus on Weak Areas
Identify the areas where you feel less confident and dedicate extra time to review those topics. Use diverse resources such as videos, guides, or peer discussions to ensure you’re covering every necessary detail.
5. Review Official Study Materials
Ensure that you are studying from the official curriculum or syllabus to stay aligned with the material that will be tested. These resources are often designed to target the most relevant knowledge for the test.
6. Maintain Calm and Stay Positive
On the test day, a calm and confident mindset is essential. Get plenty of rest the night before, have a nutritious meal, and approach the assessment with a clear mind. Confidence will help you to think critically and apply your knowledge effectively under pressure.
By following these strategies, you will increase your preparedness, boost your confidence, and maximize your chances of success in the certification process.
Hands-On Practice for Routing and Switching
Practical experience plays a crucial role in mastering networking techniques. While theoretical knowledge lays the foundation, hands-on exercises offer the opportunity to apply concepts in real-world scenarios. Engaging with devices, configuring networks, and troubleshooting issues will help solidify your understanding and prepare you for actual tasks. Whether in a lab environment or using simulators, practicing the skills you learn is vital for success.
Building Your Own Network Lab
One of the best ways to gain hands-on experience is to create your own network lab. This can be done with physical devices or through software simulators like Packet Tracer or GNS3. By setting up routers, switches, and firewalls, you can practice configuring network settings, testing communication between devices, and simulating network failures. This type of practice enables you to gain insight into how networks function and how different devices interact with one another.
Simulating Real-World Scenarios
In addition to basic configurations, it’s important to simulate real-world situations. These could include diagnosing network issues, testing security protocols, or ensuring redundancy in the network infrastructure. Troubleshooting exercises help develop critical problem-solving skills and prepare you for unforeseen challenges in a professional environment. Simulating different failure scenarios will teach you how to react quickly and restore network services efficiently.
Hands-on practice not only builds confidence but also enhances your ability to work under pressure. By frequently engaging in practical exercises, you will reinforce your understanding and develop the skills necessary to manage and maintain network systems successfully.
Understanding IP Addressing and Subnetting
IP addressing is a foundational concept in networking, enabling devices to identify and communicate within a network. Properly configuring addresses ensures that data packets can be routed efficiently between devices across the globe. Alongside this, subnetting is a method used to divide a larger network into smaller, manageable sections. It enhances performance, security, and organization within a network by defining which devices are part of which subnet. Understanding these concepts is crucial for network professionals, as they directly impact the structure and scalability of any network.
Basics of IP Addressing
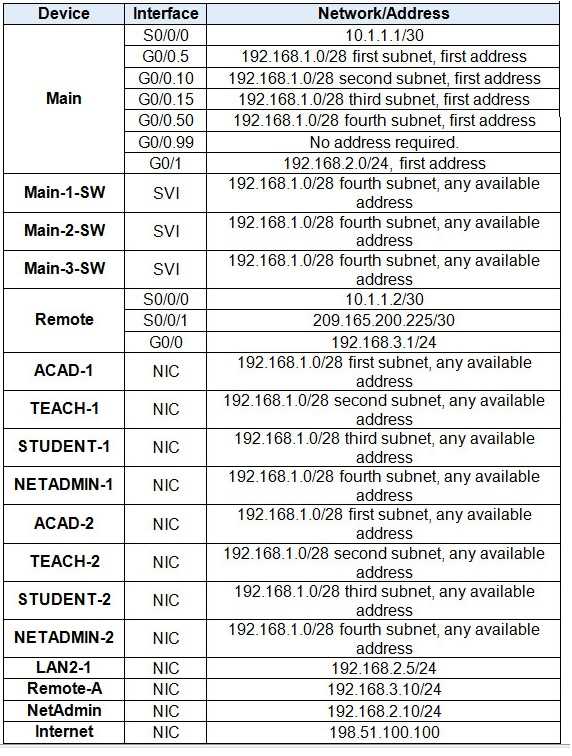
An IP address is a unique identifier for each device on a network, akin to a postal address in the physical world. It consists of four sets of numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255, separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.1.1). These numbers are categorized into two main types: IPv4, which is still the most commonly used format, and IPv6, designed to address the limitations of IPv4 due to the growing number of connected devices.
Subnetting Explained
Subnetting is the practice of splitting a larger network into smaller, more efficient sub-networks. By doing so, it limits the broadcast traffic in each subnet and improves network performance. The key to subnetting is the subnet mask, which works alongside the IP address to determine which portion of the address represents the network and which part identifies the individual device within that network. Subnetting is essential for managing IP address space efficiently, especially in larger networks.
Once you understand the basic principles of IP addressing and subnetting, you can apply these concepts to effectively configure and manage networks, ensuring that they are both functional and scalable. Mastering these skills allows you to design, implement, and troubleshoot network architectures with greater ease and precision.
Difference Between Routing and Switching
While both concepts are integral to network communication, they serve distinct roles in how data is transmitted across devices. One focuses on directing traffic between different networks, while the other deals with facilitating the movement of data within a single network. These processes ensure that information reaches its destination efficiently, but they operate at different levels and utilize different mechanisms to achieve this goal.
Functionality: The primary distinction between these two processes lies in their functionality. The first process involves determining the most efficient path for data to travel between different networks. It assesses factors like network topology, distance, and reliability. The second process, on the other hand, is responsible for forwarding data between devices within the same local network. It uses simpler, hardware-based methods to move information based on addresses.
Device Types: The devices used for these tasks also vary. The first process typically requires more advanced devices, such as routers, which analyze and determine the best paths for traffic. The second process relies on simpler devices, like switches, which manage traffic based on MAC addresses to ensure devices within the same network communicate effectively.
Protocol Differences: These processes also rely on different sets of protocols. The first process uses complex algorithms and protocols designed for long-distance communication, while the second process uses simpler, more direct methods optimized for quick, local data transfer.
In summary, while both operations are crucial for smooth data flow, their tasks, tools, and protocols are tailored to different parts of the communication process, with each focusing on a specific segment of network traffic management.
Exam Focus: Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Operations
Understanding the key differences between operations at Layer 2 and Layer 3 is crucial for anyone preparing for networking assessments. These two layers play fundamental roles in network communication, but their methods and scopes vary significantly. Layer 2 focuses on local network traffic management, while Layer 3 extends its reach to inter-network communication. Knowing how each layer functions and when each is applicable is essential for network professionals and those preparing for certification tests.
Layer 2 Operations: Local Traffic Handling
At Layer 2, devices are responsible for managing communication within a single local network. The operations at this layer are primarily concerned with the efficient transmission of data between devices that share the same physical network. This layer uses hardware addresses (MAC addresses) to forward frames and ensures that data reaches the correct destination within the local area network (LAN). Common devices operating at this layer include network switches and bridges.
Layer 3 Operations: Routing Between Networks
Layer 3 extends beyond local networks and is responsible for routing traffic between different networks. This layer uses logical addresses (IP addresses) to determine the best path for data to travel across multiple interconnected networks. Devices such as routers operate at this layer, making decisions about where to send data based on network topology and other factors. Layer 3 also introduces features such as fragmentation and addressing, which help manage the transmission of data over larger, more complex network infrastructures.
Both layers are vital for data communication, with Layer 2 managing the local delivery of information and Layer 3 enabling communication across different network segments. Understanding when each layer is responsible for data handling will help clarify the functionality of modern network designs and support exam success.
Key Terms to Know for RSE Chapter 2
Mastering the fundamental concepts and terminology is essential for understanding network operations. In this section, we’ll explore the key terms that are critical for success in the second section of the certification course. These terms form the foundation for further learning and troubleshooting in a professional network environment. Familiarizing yourself with these terms will not only help with theoretical understanding but also provide the practical knowledge required to configure, manage, and optimize network systems.
Important Concepts
- IP Addressing: A system of assigning numerical labels to devices on a network, allowing for unique identification and communication.
- Subnetting: The practice of dividing a larger network into smaller, manageable subnetworks to optimize performance and security.
- MAC Address: A hardware address assigned to a network interface for communication within the network segment.
- LAN: A local area network that connects devices within a limited geographic area, like an office or home.
- WAN: A wide area network that spans a large geographic area, connecting multiple LANs over long distances.
Networking Devices
- Router: A device responsible for forwarding data packets between networks based on logical IP addresses.
- Switch: A device that connects devices within a single network and forwards data based on MAC addresses.
- Gateway: A device that connects different types of networks, such as a local network and the internet.
- Access Point: A device that allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi.
Knowing these terms will help clarify the key principles of network design and functionality. Understanding these concepts is crucial for both the theoretical aspects of network operation and practical network management tasks.
Reviewing Key Routing Protocols for the Exam
In order to achieve success in network configuration and management, understanding the fundamental protocols that govern data transmission between devices is essential. Each protocol serves a distinct purpose and offers unique advantages in different network environments. In this section, we will review the most important protocols that are likely to appear on your certification assessments. Mastery of these protocols will not only enhance your understanding but also equip you with the skills needed to troubleshoot and optimize network performance.
Key Protocols to Understand
- RIP (Routing Information Protocol): A distance-vector protocol that uses hop count as its metric. It is simple and suitable for small to medium-sized networks but has limitations in larger, more complex environments.
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First): A link-state protocol that provides more scalability and faster convergence than RIP. It uses a more complex metric based on the cost of paths and is widely used in enterprise networks.
- EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol): A hybrid protocol that combines aspects of both distance-vector and link-state protocols. It is known for fast convergence and efficiency in large-scale networks.
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): A path-vector protocol used to exchange routing information between autonomous systems on the internet. It is the backbone of inter-domain routing and is crucial for understanding how large networks and the internet function.
Considerations for Choosing the Right Protocol
- Scalability: Some protocols are better suited for small networks, while others, like OSPF and BGP, are designed to scale in large, complex environments.
- Convergence Time: Faster convergence times are important in high-performance networks. Protocols like EIGRP and OSPF provide quicker adaptation to network changes.
- Configuration Complexity: Simpler protocols like RIP are easier to configure but lack advanced features. More sophisticated protocols offer flexibility but require more configuration effort.
Understanding these protocols and their respective strengths and limitations will help you determine the most appropriate choices for different scenarios, ensuring optimal network operation and management.
Common Mistakes to Avoid on the Exam
When preparing for a certification assessment, there are several pitfalls that candidates frequently encounter. These mistakes can undermine performance, even for those who have studied the material thoroughly. Understanding these common errors ahead of time can help you approach the test with greater confidence and avoid unnecessary setbacks. Below are some of the most frequent mistakes made during the evaluation process, along with tips on how to prevent them.
1. Misunderstanding Key Concepts
Many candidates focus too much on memorizing details without fully understanding the underlying concepts. This approach can lead to confusion during the assessment, especially when questions require critical thinking or problem-solving skills. Instead of memorizing facts, make sure you comprehend the reasoning behind key principles.
- Tip: Ensure you grasp the purpose and function of each technology or process. Understand how protocols interact and their role in different network environments.
2. Overlooking Practical Application
While theoretical knowledge is crucial, practical application is just as important. Many individuals fail to practice configuring real-world scenarios or troubleshooting problems. This leaves them unprepared for scenario-based questions that test how you would solve network issues in a real-world setting.
- Tip: Engage in hands-on labs and simulations. Set up virtual environments where you can experiment with configurations and troubleshoot issues.
3. Skipping Time Management
Time management is critical when taking any assessment. A common mistake is spending too much time on one question, which can result in not completing the entire test. It’s easy to get stuck on a challenging question, but it’s important to keep moving and come back to tough items later if necessary.
- Tip: Practice pacing yourself with timed quizzes. Aim to answer each question quickly but thoughtfully, and leave difficult ones for review at the end.
4. Ignoring Instructions and Exam Format

Failing to carefully read the instructions or understand the format of the test can lead to avoidable mistakes. Many candidates assume the structure is similar to other tests, missing key details that could affect how they approach each question type.
- Tip: Read the instructions thoroughly before beginning. Pay attention to any specific requirements, such as how many options