
Preparing for a comprehensive assessment on historical events requires a solid understanding of key moments, influential figures, and significant cultural developments. This section offers a structured approach to mastering essential topics, helping you build a strong foundation for success. Focusing on critical periods and their impact on modern society will allow you to recall relevant information with confidence.
Each area covered will guide you through important themes, from ancient empires to revolutionary movements. Understanding the rise and fall of powerful states, the dynamics of trade, and the evolution of political systems will enable you to form a complete picture of past events. Whether you’re reviewing early cultures or examining the outcomes of pivotal conflicts, these insights are designed to help you excel.
Key Concepts and Review for the History Assessment
Understanding the key events and developments in history is essential for succeeding in your upcoming test. This section covers the most important topics you should focus on, providing an overview of the major periods, figures, and concepts that shaped human societies. By breaking down the material into manageable categories, you’ll be able to organize your knowledge more effectively.
- Ancient Civilizations: Focus on the emergence of early societies, their innovations, and their influence on later cultures.
- Important Leaders and Figures: Review the roles of influential rulers, philosophers, and military leaders who impacted global history.
- Major Conflicts: Understand the causes and outcomes of key wars and revolutions throughout history.
- Technological Advancements: Study the innovations that transformed societies and economies.
- Political Systems: Examine the development of government structures and ideologies, from monarchies to democracies.
In addition to these broad topics, it’s important to remember specific events and their long-term effects on global dynamics. Pay attention to the connections between different historical periods, as understanding these relationships will allow you to answer more complex questions with ease.
- Economic Systems: Review the progression of trade, commerce, and economic models throughout history.
- Religious Movements: Study how different belief systems have shaped cultures and social structures over time.
- Social Structures: Understand the roles of class, race, and gender in historical contexts.
By thoroughly reviewing these key areas and understanding their broader significance, you will be better prepared to tackle any question that arises in the assessment. This section will help ensure you grasp the essential concepts, enabling you to approach the test with confidence and clarity.
Key Topics to Review for the Assessment
To perform well in your upcoming history assessment, it’s crucial to focus on the most influential topics that have shaped societies over time. These areas highlight essential developments, major conflicts, and pivotal figures whose actions have had long-lasting impacts. Reviewing these subjects will provide you with a comprehensive understanding, allowing you to answer a wide range of questions confidently.
- Ancient Cultures: Examine the rise of early societies, their innovations, and how they laid the foundation for future civilizations.
- Notable Leaders: Study the contributions of key individuals who directed political, military, and social change.
- Key Wars and Revolutions: Focus on significant conflicts and their outcomes, including how they altered the political and social landscapes of their time.
- Technological Breakthroughs: Understand how inventions and advancements shaped economies, societies, and global interactions.
- Political Evolution: Review the development of governance systems, including shifts from monarchies to republics and the emergence of democratic ideals.
Additionally, it’s important to understand the connections between these topics. Knowing how different events influenced one another will help you develop a deeper perspective on the progression of human history. By organizing your review around these key themes, you’ll be well-prepared to tackle any question during the assessment.
- Religious Movements: Explore the role of various belief systems and their impact on societies and conflicts.
- Social Structures: Review how social hierarchies, class divisions, and gender roles have evolved and influenced history.
- Economic Systems: Focus on the growth of trade, the shift from feudal economies to more globalized markets, and their lasting effects.
Important Events in World History
Throughout history, certain key moments have dramatically reshaped the course of human societies. These events often mark the turning points in political, economic, and cultural developments, influencing the way people live, govern, and interact with one another. Understanding these moments is crucial for grasping how the past has shaped the present and continues to impact our future.
- The Rise of Ancient Empires: The formation of early states such as Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Rome established models for governance, law, and culture that influenced later civilizations.
- The Spread of Major Religions: The growth of belief systems like Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism led to significant cultural exchanges and reshaped entire regions.
- The Fall of Great Empires: The collapse of powerful civilizations, such as the Roman Empire, led to the reorganization of territories and shifts in power dynamics.
- The Age of Exploration: The discovery of new lands and sea routes not only expanded global trade but also initiated cultural exchanges between distant peoples.
- The Industrial Revolution: Technological advancements in manufacturing and transportation transformed economies and societies, sparking the rise of modern industry.
These events, among others, have laid the foundation for modern institutions, economies, and cultures. Their long-lasting effects continue to shape our world today, influencing everything from global politics to cultural norms. Recognizing the significance of these moments will help you understand how societies have evolved and interacted throughout history.
- The American and French Revolutions: These revolutions challenged traditional political structures and introduced new ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity.
- The World Wars: The impact of the two World Wars not only changed political boundaries but also altered global power dynamics, setting the stage for the Cold War and the modern era.
- The Cold War: The ideological and political rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union influenced global alliances, conflicts, and diplomacy during the 20th century.
Major Civilizations and Their Contributions
Throughout history, several advanced societies have left a profound impact on human development. These societies introduced key innovations, cultural practices, and governing systems that continue to influence modern life. By studying their achievements, we can better understand how past cultures shaped our world today.
- Mesopotamia: Often referred to as the “Cradle of Civilization,” this ancient society introduced writing systems, the wheel, and early legal codes that laid the foundation for future societies.
- Ancient Egypt: Known for monumental architecture like the pyramids, the Egyptians also made significant advances in mathematics, astronomy, and medicine.
- The Indus Valley: This civilization developed one of the earliest urban planning systems, including well-organized cities with drainage and standardized weights and measures.
- Ancient China: Chinese contributions include inventions such as paper, gunpowder, and the compass, as well as influential philosophies like Confucianism and Daoism.
- Ancient Greece: Greek thinkers made lasting contributions to philosophy, democracy, and the arts, while their achievements in science and mathematics set the stage for modern understanding.
Each of these societies, through their advancements in various fields, has helped shape our modern world. Their ideas on governance, science, and culture have influenced generations and continue to be relevant today. Recognizing these contributions will deepen your understanding of the historical forces that have shaped human progress.
- The Roman Empire: Known for its law codes, architecture, and military strategies, Rome’s influence on Western civilization remains profound in modern legal and political systems.
- The Maya and Aztec: These civilizations made remarkable achievements in astronomy, mathematics, and agriculture, alongside their rich cultural and religious practices.
- The Ottoman Empire: A bridge between East and West, this empire contributed to art, architecture, and trade, fostering cultural exchanges between Europe, Africa, and Asia.
Understanding Ancient Societies and Cultures
To fully comprehend the foundations of modern societies, it’s essential to examine the early groups that shaped the course of history. These societies developed unique systems of governance, religion, and social structure, all of which laid the groundwork for future civilizations. By exploring their cultural practices, technological innovations, and interactions with other groups, we gain insight into the complexity of human development.
Social and Political Structures
Ancient groups organized themselves through various forms of governance, from tribal systems to more centralized states. Their rulers often held both political and religious authority, influencing all aspects of life. Social hierarchies were deeply ingrained, with roles defined by class, occupation, and gender. Understanding these systems helps explain how power was distributed and maintained in early societies.
Cultural Achievements and Beliefs
In addition to governance, these early communities made remarkable contributions to art, architecture, and intellectual pursuits. Religious beliefs played a central role, often guiding their understanding of the world and shaping their daily activities. The construction of monumental structures, the creation of written languages, and the development of advanced technologies demonstrate the ingenuity of these early people.
Critical Figures in History
Throughout human history, certain individuals have played pivotal roles in shaping the course of events. These figures–whether rulers, philosophers, military leaders, or innovators–have left lasting legacies that continue to influence contemporary society. Understanding their contributions helps illuminate the key turning points in political, social, and cultural development.
- Alexander the Great: His conquests stretched across much of the known world, spreading Greek culture and influencing the development of Hellenistic civilizations.
- Julius Caesar: As a military leader and statesman, Caesar’s actions paved the way for the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire.
- Confucius: A philosopher whose teachings on ethics, politics, and morality deeply influenced Eastern thought and governance for centuries.
- Cleopatra: The last active ruler of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, known for her political acumen and alliances with Roman leaders.
- Leonardo da Vinci: A polymath whose work in art, science, and engineering helped shape the Renaissance and the course of Western thought.
The influence of these individuals reaches far beyond their lifetimes. Their actions, ideas, and innovations were often catalysts for broader historical changes, whether in politics, culture, or science. By studying their lives, we gain insight into the forces that have shaped the development of civilizations across time.
- Martin Luther: A theologian whose 95 Theses sparked the Protestant Reformation, challenging the religious and political status quo of Europe.
- Napoleon Bonaparte: A military leader whose campaigns across Europe led to the rise of the French Empire and the spread of revolutionary ideals.
- Mahatma Gandhi: A leader of India’s independence movement, known for his philosophy of nonviolent resistance and his influence on global social movements.
Rise and Fall of Empires
The history of human societies is marked by the emergence and eventual decline of powerful states and empires. These entities often rose to dominance through military conquest, strategic alliances, and cultural achievements, only to fall due to internal struggles, external pressures, or shifts in economic and political systems. Understanding the patterns behind these rises and declines provides valuable insights into the factors that shape the fate of great powers.
Factors Behind the Rise
Empires typically begin with strong leadership, military prowess, and the ability to control vast territories. Key factors that contribute to their rise include:
- Military Expansion: Successful conquests and the ability to defend borders are critical for establishing dominance.
- Economic Strength: The ability to build trade networks, collect taxes, and manage resources effectively ensures long-term stability.
- Cultural Influence: The spread of cultural, religious, and technological innovations can solidify an empire’s power over a vast area.
Decline and Fall
No empire remains invincible forever. The factors that contribute to their downfall often stem from a combination of internal decay and external challenges:
- Political Instability: Corruption, ineffective leadership, and infighting among elites can weaken an empire’s ability to function smoothly.
- Economic Decline: Overexpansion, overtaxation, and failure to adapt to new economic realities can lead to financial collapse.
- External Threats: Invasions by rival powers or the inability to defend against military aggression often lead to the collapse of empires.
Understanding these cycles of growth and decay offers important lessons on how societies can maintain stability and avoid the common pitfalls that have led to the fall of some of the most powerful empires in history.
Global Trade and Its Impact
Over the course of history, the exchange of goods and services between different regions has shaped economies, cultures, and political systems. The rise of international commerce has not only facilitated the spread of products and resources but also led to significant changes in how societies interact with each other. The flow of trade has brought prosperity to some regions while exposing others to new challenges and opportunities.
The Growth of Trade Networks
The expansion of trade routes, such as the Silk Road and maritime routes during the Age of Exploration, enabled civilizations to access new materials, technologies, and cultural influences. These networks fostered economic growth, while also promoting the exchange of ideas, languages, and religious beliefs across continents. The ability to trade over long distances encouraged the development of better transportation methods, infrastructure, and financial systems.
- Silk Road: This vast trade route linked the East and West, facilitating the exchange of silk, spices, and knowledge between Asia, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Maritime Trade Routes: By sea, nations like Spain, Portugal, and later Britain and the Netherlands, established vast networks, increasing their influence globally.
- Transatlantic Trade: The movement of goods, slaves, and ideas between Africa, Europe, and the Americas transformed economies and societies.
The Social and Economic Impact
Global commerce has had profound effects on both the wealth and well-being of different societies. On the positive side, trade has contributed to economic prosperity, the spread of innovations, and the enhancement of cultural exchanges. On the negative side, it has also been a vehicle for exploitation, such as the transatlantic slave trade, and has sometimes led to the erosion of traditional industries.
- Economic Growth: Trade has provided access to raw materials, advanced technology, and luxury goods, stimulating economic development in many regions.
- Social Inequality: The unequal distribution of wealth resulting from trade has often exacerbated social divisions and created disparities between nations and classes.
- Cultural Exchange: The movement of goods has also led to the exchange of art, literature, and knowledge, influencing cultural development worldwide.
Ultimately, global trade has been a driving force in shaping the modern world. It has created opportunities for growth and innovation but also highlighted the challenges of managing resources and ensuring fair distribution. Understanding its complex history is essential to addressing the issues we face in today’s interconnected world.
Revolutionary Movements and Their Effects
Throughout history, uprisings and movements seeking radical change have reshaped societies. These revolutions, often sparked by dissatisfaction with political, social, or economic systems, have had profound impacts on governance, social structures, and cultural identities. The aftermath of these upheavals can lead to the formation of new ideologies, the redistribution of power, and the establishment of more inclusive or authoritarian regimes.
Key Factors Driving Revolutionary Change
The motivations behind revolutions are diverse, but they often stem from widespread inequality, oppression, and the desire for greater freedom or justice. Common triggers include:
- Economic Inequality: Disparities in wealth distribution can create unrest, leading to demands for a fairer system.
- Political Corruption: When governments fail to serve the interests of the people, they risk losing legitimacy, leading to calls for change.
- Social Unrest: Cultural or ethnic tensions, combined with economic hardships, can ignite movements for reform or revolution.
Impact on Societies and Governance
Revolutions can lead to immediate social changes, but their long-term effects often extend well beyond the initial conflicts. Some key consequences include:
- Redefinition of Political Power: Revolutionary movements can overthrow long-standing regimes and replace them with new forms of government, such as democracies or authoritarian states.
- Social Reorganization: These movements often challenge existing social hierarchies, leading to changes in class structure, gender roles, and societal norms.
- Cultural Transformation: New ideologies and philosophies can emerge, changing how people view their role in society and their relationships with others.
Revolutions have sparked major changes in history, creating new political landscapes and altering the course of human development. Understanding their causes and effects helps to grasp the complexities of historical progress and the challenges faced by societies in times of transformation.
Significant Wars and Their Consequences
Throughout history, large-scale conflicts have dramatically reshaped nations, economies, and the balance of power. These wars have not only been pivotal moments in military history but have also led to profound social, political, and economic changes. The outcomes of these conflicts have often determined the future direction of entire regions, affecting everything from borders to ideologies and international relations.
Major Conflicts and Their Causes
Many of the most significant wars have been driven by a combination of factors, including territorial disputes, ideological differences, and competition for resources. The following are some of the key causes of major historical conflicts:
- Territorial Expansion: The desire to expand national boundaries often led to violent confrontations, as empires and states sought to control more land.
- Ideological Struggles: Conflicts rooted in differing political, religious, or economic ideologies have sparked some of the most intense and far-reaching wars.
- Resource Competition: Competition for natural resources, trade routes, and economic dominance has often been at the heart of major wars.
Consequences of Major Conflicts
The aftermath of these wars has varied widely, but several common themes emerge, particularly in the realms of social change, political realignment, and economic impact:
- Political Realignment: Many wars have led to the collapse or transformation of governments, the rise of new political ideologies, and the reshaping of borders.
- Social Disruptions: Wars often result in mass displacement, changes in social hierarchies, and shifts in cultural identities, as populations are affected by loss, migration, and reconstruction efforts.
- Economic Impact: Conflicts tend to drain national resources, cause widespread destruction, and lead to long-term economic challenges, even as some industries benefit from wartime production.
Understanding the causes and consequences of significant wars allows us to better comprehend the forces that shape global history. These conflicts, while often tragic, have been central to the development of modern nations and continue to influence international relations today.
Religious Movements Throughout History
Religious movements have played a crucial role in shaping human history, influencing everything from politics to culture. These movements, often born out of a desire for spiritual reform, have led to the rise of new belief systems, changes in existing traditions, and the spread of ideologies across regions and continents. They reflect the ever-evolving relationship between individuals, communities, and the divine, often challenging established social orders or promoting unity among people of shared faith.
From the emergence of major faiths to the reformations and revitalizations within older traditions, religious movements have had both immediate and long-lasting impacts. These shifts have often brought about social cohesion or division, led to the establishment of new institutions, and sometimes sparked violent conflicts or periods of intense peace-building and cooperation. By understanding the development of these movements, we gain insight into their far-reaching influence on the world.
Technological Advancements in Civilizations
The development of technology has always been a key factor in the progress of human societies. Innovations in tools, infrastructure, and systems have shaped the way people live, work, and interact with their environment. From the discovery of fire to the invention of the printing press, these breakthroughs have not only solved practical challenges but also opened up new possibilities for cultural, scientific, and economic growth. Technological progress has often been the driving force behind societal transformations, enabling civilizations to expand, thrive, and influence the course of history.
Key Technological Breakthroughs
Throughout history, several pivotal advancements have drastically changed the trajectory of human development. These innovations in technology laid the foundation for further progress and continue to influence contemporary society.
| Technology | Impact | Time Period |
|---|---|---|
| Wheel | Revolutionized transportation and machinery | Mesopotamia, circa 3500 BCE |
| Writing Systems | Enabled record-keeping, communication, and cultural preservation | Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, circa 3000 BCE |
| Printing Press | Mass production of books, spread of knowledge, and rise of literacy | Europe, 1440 CE |
| Steam Engine | Facilitated industrialization and powered machines | 18th century, Europe |
| Internet | Global connectivity, information exchange, and technological networks | Late 20th century |
Influence on Society and Culture
Each technological advancement has had profound effects on social structures, economies, and cultural practices. The wheel, for example, revolutionized transport and trade, allowing for faster movement of goods and people. The printing press transformed education, making books more accessible and encouraging literacy, which in turn fostered the spread of new ideas. Similarly, the internet has created a global network of communication and knowledge, radically altering modern societies in ways that were once unimaginable. These breakthroughs, though varied in nature, have all contributed to the shaping of human progress.
Political Systems in Ancient Societies
Throughout history, the way societies organized themselves politically has greatly influenced their structure and development. Early political systems were formed to establish order, manage resources, and protect territories. These systems, whether centralized or decentralized, provided frameworks for governance and law, often dictating the relationship between rulers and their people. As societies grew in complexity, political systems evolved, laying the foundation for modern governance structures.
Types of Political Structures
The forms of governance in ancient societies varied widely, ranging from monarchies to republics, each with its own methods of rule and social hierarchy. These early systems reflected the needs of their time, often balancing the roles of kings, priests, and elected officials, and influencing the daily lives of the population.
- Monarchy: A system where a single ruler holds supreme authority, often seen in ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, where pharaohs and kings governed with divine right.
- Democracy: The rise of participatory government in places like Athens, where citizens could vote on key issues, marked an early form of direct governance.
- Republic: In ancient Rome, a system of elected representatives governed on behalf of the people, with a complex structure of checks and balances.
- Feudalism: In medieval Europe and parts of Asia, land was exchanged for loyalty and military service, with lords holding power over peasants and vassals.
Impact on Society and Culture
The political structures in ancient times had lasting effects on the social, economic, and cultural life of their people. In many cases, rulers used religion and tradition to legitimize their power, leading to a deeply intertwined relationship between governance and belief systems. For example, the divine kingship in Egypt helped maintain the status quo and was essential in uniting the nation under a single authority. Similarly, the Roman Republic laid the groundwork for modern political thought, influencing ideas about citizenship, law, and public service that still resonate today.
Social Hierarchies and Inequality

Throughout history, societies have structured themselves into different layers or classes, often based on factors such as wealth, birth, occupation, or power. These hierarchical systems determined individuals’ access to resources, rights, and privileges, often creating significant disparities between different groups. While some groups enjoyed privileges and influence, others faced limitations and oppression. The origins and impact of these social distinctions have shaped the development of many cultures and continue to influence societal dynamics today.
Origins of Social Stratification
Social hierarchies have deep roots in the earliest human societies, where divisions were often based on basic needs and functions. As societies grew in complexity, these divisions became more rigid, often reinforced by religion, tradition, or law. The ruling classes, typically small in number, maintained control over land, labor, and resources, while lower classes were often subjected to servitude or limited opportunities.
- Elite Classes: These individuals or groups held political, religious, or economic power, such as kings, priests, and wealthy landowners.
- Middle Classes: Often made up of merchants, craftsmen, and professionals, these groups had more freedom but still lacked the privileges of the elite.
- Lower Classes: Comprising peasants, slaves, and workers, these individuals often had little to no say in governance and lived under harsh conditions.
Consequences of Inequality
Social inequality has had lasting effects on societies, often resulting in limited upward mobility for lower classes and significant tensions between different groups. The concentration of power and wealth among the elite led to exploitation and social unrest in many civilizations. However, these systems also fostered the development of social movements, revolutions, and reforms aimed at challenging the status quo and demanding equal rights and opportunities.
- Revolts and Revolutions: Inequality often spurred revolutions, such as the French and Russian Revolutions, where oppressed groups rose against their rulers.
- Social Movements: Over time, many societies witnessed the rise of movements advocating for human rights, workers’ rights, and the end of slavery.
Economic Systems and Their Development

The organization of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services has been central to the growth and functioning of societies throughout history. Economic systems have evolved from basic subsistence economies to more complex systems driven by markets, trade, and state intervention. These developments have not only influenced the wealth and power of nations but also shaped social structures and cultural norms. The transition from barter to currency-based economies and the rise of capitalism and socialism reflect the ongoing quest to organize resources efficiently and equitably.
Early Economic Systems
In the earliest stages of human development, economic activities were often centered around subsistence farming, hunting, and gathering. As societies grew in complexity, the need for trade and specialized labor led to the emergence of early systems of exchange and market trade. These early economies were often localized, with limited surplus and little specialization beyond basic needs.
| Economic Activity | System Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Barter System | Goods and services exchanged directly without money, based on mutual need. |
| Feudal Economy | Land-based production system, where peasants worked the land in exchange for protection and sustenance. |
| Mercantile Economy | Trade and accumulation of wealth through commerce, often controlled by monarchies or empires. |
Modern Economic Systems
As trade expanded and industrialization took hold, new economic models began to emerge. The rise of capitalism emphasized private ownership and profit-driven market economies, while socialism and communism focused on collective ownership and the redistribution of wealth. Each system sought to address issues of inequality, wealth distribution, and the role of the state in economic affairs, leading to different outcomes and challenges for societies.
- Capitalism: Private ownership of the means of production and market-based economy driven by competition and profit.
- Socialism: Collective or state ownership of resources, with an emphasis on equality and wealth redistribution.
- Communism: A classless society where all property is communally owned, with no private enterprise.
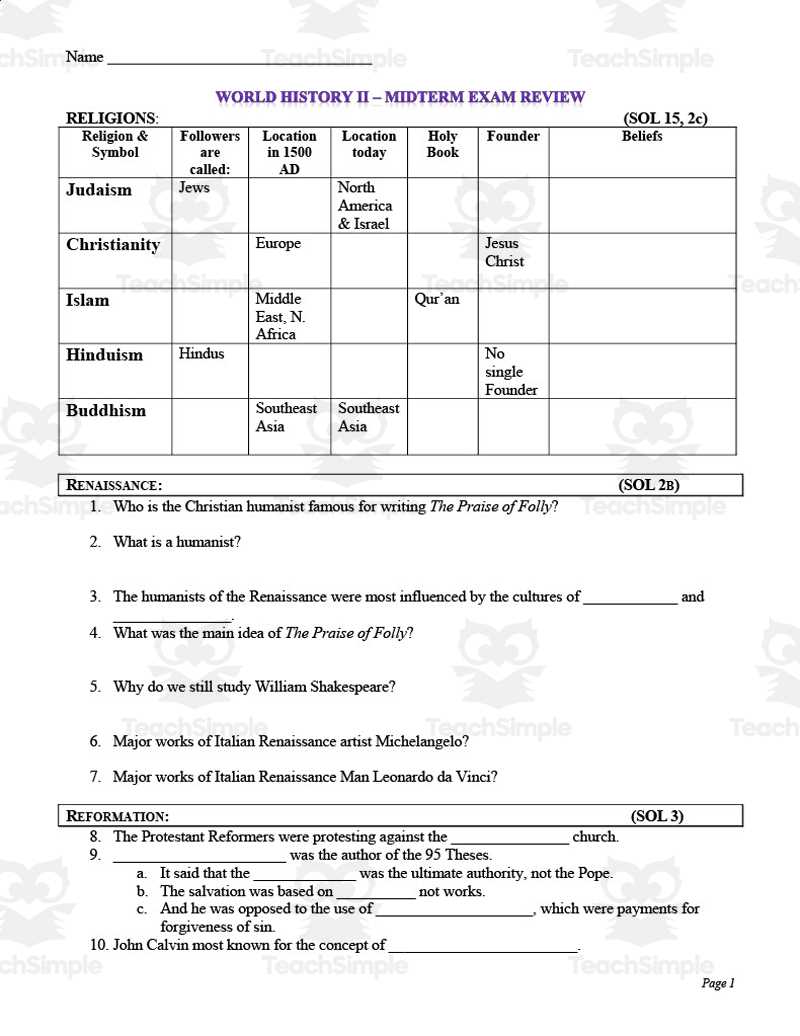
Preparing for the Final Exam Effectively

Successful preparation for any major assessment requires both strategy and dedication. It’s not just about reviewing notes; it’s about understanding key concepts, organizing your thoughts, and creating a plan that allows for focused learning. Effective preparation involves breaking down complex topics into manageable parts and ensuring that each area is thoroughly reviewed before the test. By using a variety of methods, from active recall to practice questions, you can reinforce your understanding and increase your confidence.
One of the most important elements of preparing well is time management. Setting aside specific periods for review, along with regular breaks, ensures you don’t become overwhelmed. Additionally, identifying your strengths and weaknesses can help you prioritize areas that need more attention. Practicing under timed conditions can also simulate the pressure of the actual assessment, making you more comfortable with the process.