
In the world of competitive sports, having a strong understanding of emergency care is crucial. Whether you’re a coach, player, or volunteer, being equipped with the right knowledge can make all the difference in critical situations. This section aims to guide you through the necessary steps to succeed in medical certification for athletes, with a focus on key concepts and skills that will ensure you are ready for any emergency on the field.
While the certification process may seem daunting at first, it is designed to equip you with the confidence and expertise to handle medical situations effectively. The key to passing is not just memorizing specific procedures, but understanding the reasoning behind them. A well-prepared individual can recognize the signs of injury or distress and take swift, informed action.
Mastering basic techniques such as wound management, resuscitation, and injury assessment is essential for all sports professionals. It’s also important to stay updated on the latest practices and guidelines, as emergency care evolves over time. This guide will break down the most important areas to focus on, helping you approach the certification with a clear and structured mindset.
Sports Medical Certification Preparation
In the world of athletic competition, emergency response knowledge is vital for ensuring the safety of players. Individuals seeking certification in medical care for sports must demonstrate an understanding of key procedures and protocols. This section focuses on what you need to know to prepare thoroughly, highlighting the essential areas and skills tested in the certification process.
Critical Concepts and Skills to Master
The evaluation for medical certification involves several core areas. Candidates are assessed on their ability to respond effectively to common injuries and emergencies encountered in the sporting environment. Understanding the correct approach to injury prevention, response to trauma, and maintaining safety protocols is fundamental to passing the assessment.
| Skill Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Injury Assessment | Ability to identify symptoms and severity of injuries, including fractures, sprains, and soft tissue damage. |
| CPR and Resuscitation | Knowledge of life-saving procedures in case of respiratory or cardiac failure. |
| Concussion Management | Recognizing signs of concussion and knowing how to manage athletes who may have sustained a head injury. |
| Wound Care | Proper techniques for controlling bleeding and preventing infection in open injuries. |
Preparing for the Assessment
To excel in this certification process, it’s essential to study the foundational principles thoroughly. Reviewing case studies, practicing hands-on scenarios, and familiarizing yourself with emergency protocols will help you confidently approach the assessment. Additionally, maintaining calm and clarity during stressful situations is key to demonstrating your readiness.
Understanding the Medical Certification Assessment Structure
When preparing for a medical certification test in sports, it’s essential to grasp the structure of the assessment. The evaluation is designed to test both theoretical knowledge and practical application, ensuring that candidates are fully prepared to handle real-world situations. Understanding the format of the assessment helps you focus your study efforts and approach the process with confidence.
The assessment typically consists of multiple sections, each targeting a different aspect of emergency care. Some sections are theoretical, testing your understanding of procedures, protocols, and injury management, while others are practical, requiring you to demonstrate specific skills in simulated scenarios. A strong balance of both theory and hands-on experience is crucial for success.
Theoretical Components: These parts of the assessment often include written questions and multiple-choice tests. You will be asked to explain various procedures, such as how to recognize the symptoms of common injuries or how to perform basic life support techniques. Mastery of medical terminology and understanding standard emergency protocols is key.
Practical Components: In this section, you may be required to demonstrate your ability to apply your knowledge in real-time scenarios. This could involve performing CPR, immobilizing a limb, or managing a suspected concussion. Candidates will be assessed on their ability to stay calm under pressure and execute the correct procedures quickly and efficiently.
Key Topics Covered in the Assessment
To successfully complete a sports-related medical certification, it’s essential to understand the core topics that are tested. The evaluation covers a wide range of skills and knowledge areas, each focusing on specific aspects of injury prevention, treatment, and emergency response. Familiarity with these key topics is crucial for both theoretical understanding and practical application during the assessment.
The assessment typically includes subjects such as recognizing and managing common sports injuries, performing life-saving procedures, and understanding the protocols for specific emergency situations. A well-rounded understanding of these areas ensures that candidates are prepared for the challenges they may face in real-world scenarios, both on and off the field.
Among the topics covered, you can expect to encounter:
- Injury recognition and management techniques
- CPR and basic life support procedures
- Trauma care for head, neck, and spinal injuries
- Understanding concussion protocols and treatment
- Wound care and infection prevention
- Response strategies for breathing and cardiac emergencies
- Guidelines for assessing and managing shock
Mastery of these key areas is not only necessary for passing the certification but also for ensuring that you are well-prepared to respond to medical emergencies in an effective and professional manner.
Essential Medical Skills for Sports
In the fast-paced environment of competitive sports, knowing how to respond quickly and efficiently to injuries is crucial. Having the right set of medical skills ensures that players receive prompt and appropriate care, minimizing the risk of long-term damage. This section highlights the core medical skills required to manage common injuries and emergencies effectively during athletic events.
Core Skills Every Sports Professional Should Master
Medical personnel and coaches must be equipped with the necessary skills to assess and treat a variety of injuries, from minor cuts to more serious conditions such as fractures or head trauma. The ability to recognize and respond to these situations is key to ensuring the safety and well-being of all involved. Here are the essential skills needed:
- Injury Assessment: Quickly evaluating the severity of an injury to determine if immediate treatment is necessary.
- CPR and Resuscitation: The ability to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation effectively in emergency situations.
- Concussion Recognition: Identifying the symptoms of a concussion and taking the proper steps to manage it.
- Wound Care: Proper techniques for cleaning and dressing wounds to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Fracture Management: Knowledge of how to stabilize broken bones and prevent further harm before professional medical help arrives.
Responding to Specific Sports Injuries
Each type of injury requires a tailored approach to ensure proper care. Some common scenarios in sports include:
- Soft Tissue Injuries: Sprains, strains, and muscle tears that require rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E).
- Heat-Related Illnesses: Recognizing symptoms of heat exhaustion or heat stroke and knowing how to manage body temperature.
- Head and Neck Injuries: Ensuring that the athlete is immobilized properly and assessing for signs of serious trauma.
Mastering these essential medical skills helps ensure the safety of athletes and prepares you to handle emergencies efficiently and confidently during any sport.
Top Resources for Certification Preparation
Preparing for a sports medical certification requires more than just basic knowledge; it demands the use of targeted resources to help you succeed. With the right materials and tools, you can strengthen your understanding of critical procedures, enhance your practical skills, and confidently approach the evaluation. This section outlines some of the best resources available for thorough preparation.
Recommended Books and Study Guides
Books and study guides are fundamental resources for understanding the key concepts and techniques tested during the certification process. They provide in-depth explanations, practice scenarios, and tips to help reinforce your learning. Here are some of the best options:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Sports Injury Handbook | A comprehensive guide that covers the most common injuries in sports and how to manage them effectively. |
| Emergency Care in Sport | Focuses on emergency protocols, CPR, and injury response strategies for sports professionals. |
| First Responder Field Manual | A practical manual for those needing hands-on guidance in real-life situations, covering a variety of injuries and emergencies. |
Online Courses and Practice Tests
In addition to traditional study materials, online courses offer a flexible and interactive way to prepare. These platforms provide video tutorials, quizzes, and simulated emergency scenarios that help you assess your progress and reinforce your learning. Some recommended online platforms include:
- Red Cross Online Certification: An accredited program offering both theoretical lessons and practical video demonstrations.
- CPR Certification Academy: Specialized in life-saving procedures with interactive tutorials and quizzes.
- Sports Medicine Online Learning: An online platform focusing on injury prevention, treatment, and recovery in athletic environments.
By combining these resources, you can ensure a well-rounded preparation strategy, improving your chances of success in the certification process.
How to Pass the Sports Medical Certification Test

Successfully completing a sports-related medical certification requires a combination of theoretical knowledge, practical skills, and the ability to stay calm under pressure. To pass the assessment, candidates need to demonstrate their understanding of emergency procedures, injury management, and how to effectively apply first response techniques. This section outlines key strategies and tips to help you prepare and succeed in the certification process.
Study and Understand the Core Topics
To excel in the test, it’s crucial to master the essential concepts that will be evaluated. Focus on the most common injuries in sports, emergency protocols, and basic life support procedures. Key areas to prioritize include:
- Trauma Management: Know how to assess and treat common injuries such as sprains, fractures, and dislocations.
- CPR and Resuscitation: Be comfortable with life-saving procedures and understand when and how to perform them.
- Concussion Protocol: Recognize the signs of head injuries and understand how to manage them effectively.
- Wound Care: Learn proper techniques for stopping bleeding, cleaning wounds, and preventing infection.
Practice Hands-On Skills
While theoretical knowledge is important, the ability to apply this knowledge in real-world scenarios is equally critical. Practice practical skills such as:
- Performing CPR on a mannequin or in a controlled setting.
- Immobilizing a limb to prevent further injury.
- Applying dressings and bandages for different types of injuries.
Tip: Many certification programs include hands-on assessments where you’ll be asked to demonstrate your ability to handle emergency situations. Be sure to practice under timed conditions to simulate the pressure of a real incident.
With a focused approach to studying and hands-on practice, you’ll be well-prepared to succeed in the certification process. Remember, the key to passing is not only knowing the right answers but also being able to execute the proper techniques confidently and efficiently.
Common Mistakes in the Medical Certification Assessment
Many candidates struggle during the medical certification assessment due to common mistakes that can be easily avoided with proper preparation. These errors often stem from misinterpreting questions, forgetting essential steps in emergency procedures, or not practicing enough under pressure. By identifying these pitfalls in advance, you can take proactive steps to ensure success and avoid unnecessary mistakes during the test.
Frequent Errors and How to Avoid Them
Understanding the most common mistakes can help you stay focused and confident during the assessment. Here are some key errors to watch out for:
| Mistake | How to Avoid |
|---|---|
| Skipping Critical Steps | Always follow the correct order of procedures in emergency care. Review standard protocols for each type of injury. |
| Failing to Check for Breathing | Make it a habit to check the airway and breathing first in any emergency scenario before proceeding with other actions. |
| Overlooking Wound Care | Ensure proper cleaning, dressing, and bandaging to prevent infection. Always follow sterilization procedures. |
| Not Using Proper Body Mechanics | When handling injured individuals, practice proper lifting and stabilization techniques to avoid further injury. |
Practical Scenarios and Hands-On Mistakes
In addition to theoretical mistakes, many candidates falter during hands-on evaluations. Some common errors during practical scenarios include:
- Panicking Under Pressure: Stay calm and focused even in high-pressure situations. Practice timed drills to get comfortable with the pace.
- Incorrect Technique: Misapplying techniques like CPR or immobilization can have serious consequences. Rehearse skills regularly with feedback from experienced instructors.
- Ignoring Communication: In team-based simulations, clear and concise communication is key. Always speak clearly and coordinate with your team members.
By understanding these common mistakes and practicing regularly, you will improve both your confidence and your ability to pass the certification with ease.
Practical Tips for Test Success
Achieving success in a medical certification assessment requires more than just theoretical knowledge; it demands effective strategies for both preparation and execution during the test. By focusing on essential tips and approaches, candidates can enhance their chances of success, reduce anxiety, and demonstrate competence when it matters most. This section offers actionable advice to help you navigate the process with confidence.
Effective Study Strategies
Proper preparation is the foundation for test success. To make the most of your study time, follow these strategies:
- Create a Study Plan: Organize your study sessions by topic and allow ample time for both theoretical review and practical skills practice.
- Review Past Scenarios: Use real-world case studies and simulations to familiarize yourself with the types of questions and situations that may arise.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Identify the areas where you feel least confident and dedicate extra time to mastering those topics.
- Use Flashcards: For quick recall, create flashcards for essential terms, techniques, and steps to reinforce your memory.
Maximize Performance on Test Day
On the day of the assessment, it’s important to approach the situation with a clear mind and a structured approach. Consider these tips to maximize your performance:
- Stay Calm and Focused: Nerves are natural, but staying calm will help you think more clearly and perform tasks accurately. Practice deep breathing techniques to manage stress.
- Read Instructions Carefully: Before answering questions or performing tasks, take a moment to read all instructions thoroughly. Missing key details can lead to mistakes.
- Prioritize Safety: Always begin by assessing the situation to ensure the safety of yourself, the injured person, and anyone nearby. This should be your first priority in any scenario.
- Take Your Time: Don’t rush through tasks. While time management is important, accuracy should always come first when performing critical procedures.
By adopting these practical tips and focusing on both mental and physical preparation, you will be well-equipped to succeed in the certification process.
Mastering CPR and Emergency Response
In emergency situations, knowing how to effectively perform life-saving techniques such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and respond swiftly to injuries is critical. Whether dealing with a collapsed individual or managing a breathing emergency, mastering these skills can make the difference between life and death. This section provides essential guidance on how to approach CPR and emergency response protocols with confidence and efficiency.
Understanding the Basics of CPR
CPR is a crucial skill in any medical emergency, particularly when someone’s heart has stopped or they are not breathing. The primary objective is to restore circulation and oxygen flow to vital organs, especially the brain. To perform CPR correctly, follow these steps:
- Check Responsiveness: Before starting, check if the person is unresponsive. Tap their shoulder and shout loudly to ensure they do not react.
- Call for Help: Immediately ask someone to call emergency services or do so yourself if you’re alone.
- Start Chest Compressions: Begin chest compressions by placing your hands on the center of the chest and pressing down hard and fast, about 2 inches deep and at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Rescue Breaths: If trained, provide two rescue breaths after every 30 compressions, ensuring the chest rises with each breath.
Handling Other Emergency Responses
In addition to CPR, responding to injuries or medical conditions requires knowledge of appropriate steps. Here are some key areas to focus on:
- Bleeding Control: Apply direct pressure to wounds using a clean cloth or bandage. If bleeding doesn’t stop, continue applying pressure or consider using a tourniquet for severe injuries.
- Airway Management: Clear the airway if someone is choking or experiencing difficulty breathing. Perform the Heimlich maneuver if necessary.
- Shock Treatment: Lay the individual down with their legs elevated and cover them with a blanket to maintain body temperature while awaiting medical help.
Being proficient in CPR and emergency response techniques can greatly enhance your ability to provide immediate and effective help in critical situations. Regular practice and familiarity with these life-saving skills ensure that you are prepared when every second counts.
How to Handle Head Injuries in Rugby
Head injuries are among the most serious types of trauma that can occur during physical activities. Whether it’s a concussion, a cut, or a more severe injury, quick and effective intervention is crucial to ensure the safety of the individual involved. This section outlines the steps you should take to properly manage head injuries on the field, emphasizing the importance of precaution and timely medical attention.
Identifying the Severity of Head Injuries
Not all head injuries are immediately apparent, so it’s essential to recognize the signs that indicate the severity of the injury. Some symptoms may require immediate intervention, while others may allow for monitoring until help arrives. Look out for the following:
- Loss of Consciousness: Any loss of consciousness, even for a brief moment, requires urgent medical assessment.
- Confusion or Disorientation: If the individual appears confused or unable to recall recent events, it could indicate a concussion or more serious trauma.
- Visible Cuts or Bruises: Large cuts or bruises on the head can lead to excessive bleeding, requiring immediate attention.
- Severe Headache or Nausea: Persistent headache or vomiting are clear signs that the injury may be more serious than initially thought.
Immediate Steps to Take
If you suspect a head injury, here are the steps you should follow to manage the situation effectively:
- Stop Play: Cease all activity immediately. Allow the injured player to receive attention and prevent any further harm.
- Assess the Injury: Approach the injured person calmly. Check for signs of consciousness, confusion, or other symptoms. Do not move the individual unless absolutely necessary to avoid further harm.
- Apply Pressure if Necessary: If the injury has resulted in bleeding, apply gentle pressure with a clean cloth to stop the bleeding.
- Seek Medical Help: Call for medical assistance immediately if there is any suspicion of a serious head injury, particularly if the person is unconscious, vomiting, or exhibiting unusual behavior.
- Monitor Vital Signs: While waiting for medical personnel to arrive, monitor the individual’s breathing, pulse, and level of consciousness. If the person loses consciousness again or exhibits difficulty breathing, begin CPR and continue until help arrives.
Even if the injury appears minor, it is always best to err on the side of caution. Head injuries, especially concussions, can have long-term consequences if not managed properly, so never hesitate to seek professional evaluation for any suspected head trauma.
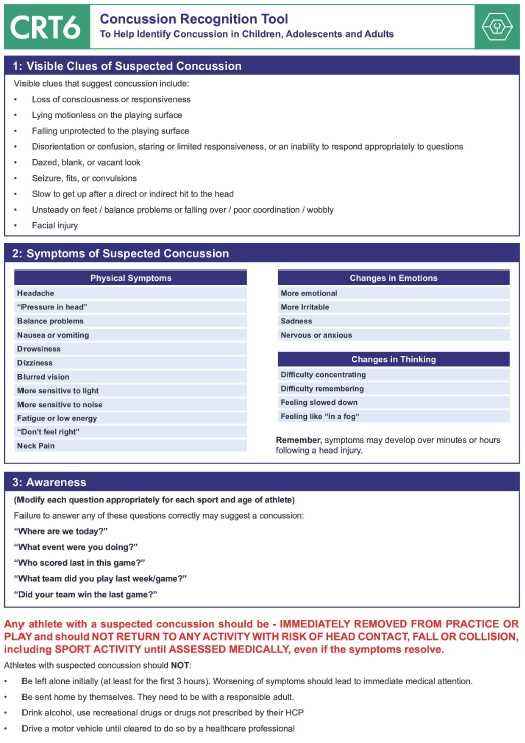
Dealing with Concussions in Players
Concussions are a common but serious injury that can occur during high-contact sports. A concussion results from a blow to the head or body, causing the brain to move inside the skull. Even if a player appears fine after the impact, it is crucial to take immediate steps to assess and manage the situation appropriately. Understanding the signs and symptoms of a concussion, as well as knowing how to react, can prevent further injury and ensure the player’s safety.
Recognizing the Signs of a Concussion
The symptoms of a concussion can vary widely, and in some cases, may not appear until hours or even days after the incident. It’s essential to be vigilant and watch for common signs that indicate a player might have sustained a concussion:
- Loss of Consciousness: While not always present, even a brief loss of consciousness after a blow to the head is a red flag.
- Confusion or Disorientation: A player may appear confused, forget the events leading up to the injury, or seem unsure of where they are.
- Headache or Dizziness: Persistent headache or feeling lightheaded can indicate a concussion.
- Nausea or Vomiting: These symptoms often accompany concussions and should be taken seriously.
- Balance Problems: Difficulty standing or walking, or uncoordinated movements, may suggest a brain injury.
Steps for Managing a Suspected Concussion
If a concussion is suspected, it is important to take immediate action. The following steps outline the best course of action:
- Remove the Player from Play: If a concussion is suspected, the player must be removed from the game or activity immediately. Do not allow them to return to play, even if they insist they feel fine.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep a close eye on the player’s condition. Check for worsening symptoms, such as increased confusion, repeated vomiting, or unusual behavior. In such cases, seek medical attention immediately.
- Seek Medical Evaluation: A healthcare professional should evaluate the player as soon as possible. Only a trained medical professional can confirm a concussion and determine when it is safe for the player to return to activity.
- Follow a Graduated Return to Play Protocol: If diagnosed with a concussion, the player should follow a careful and gradual return-to-play plan under the guidance of a medical professional. Returning to activity too soon can increase the risk of further injury.
When to Seek Emergency Care
In some cases, the symptoms of a concussion may worsen, and emergency medical attention is necessary. Call emergency services if:
- The player becomes unconscious or semi-conscious and cannot be roused.
- There are signs of a severe brain injury, such as seizures, persistent vomiting, or difficulty breathing.
- The player experiences severe or worsening headache, confusion, or memory loss.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Loss of Consciousness | Seek emergency medical attention immediately. |
| Confusion or Disorientation | Remove player from play, monitor, and consult with a medical professional. |
| Headache or Dizziness | Allow the player to rest, and seek medical advice. |
| Nausea or Vomiting | Monitor closely, consult a doctor if symptoms persist. |
Concussions are serious injuries that should never be taken lightly. Immediate action and proper management can help prevent long-term effects and ensure the safety and well-being of the player.
Legal Responsibilities of First Aiders

Individuals who provide immediate assistance to those injured or unwell during an emergency have both ethical and legal obligations. Understanding the responsibilities involved can help ensure that first responders act in accordance with the law, protecting themselves and the individuals they assist. These duties encompass various aspects of care, including consent, maintaining confidentiality, and ensuring that their actions do not cause further harm.
Duty of Care
First responders are expected to provide care that meets the standards of a reasonable and prudent person in their situation. This means offering appropriate assistance based on their training, knowledge, and the circumstances at hand. A failure to provide proper care or neglecting to take action when required can result in legal consequences such as negligence claims. Ensuring that the level of care is appropriate to the situation is a fundamental aspect of a responder’s legal responsibility.
Consent and Privacy
Before providing any form of medical help, it is essential to obtain consent from the individual, if they are conscious and capable of understanding the situation. This can be a verbal or implied consent, depending on the circumstances. However, if the individual is unconscious or unable to respond, implied consent is assumed in most jurisdictions. It is also crucial to respect the individual’s privacy, keeping any medical information confidential and only sharing details with relevant medical professionals or authorities when necessary.
What to Do in Case of Legal Issues
If a first aider faces legal challenges regarding their actions during an emergency, it is important to understand the potential defenses. In many cases, individuals acting in good faith and following appropriate protocols are protected by “Good Samaritan” laws, which shield them from liability as long as they are not grossly negligent or acting recklessly. However, it is vital for first responders to document their actions clearly, as this can help protect them in the event of legal scrutiny.
Understanding and adhering to these legal responsibilities ensures that first responders can effectively assist those in need while safeguarding themselves from potential legal issues.
Understanding Wounds and Bleeding Control

When an injury results in a break in the skin or tissues, it is crucial to assess the extent of the damage and control bleeding to prevent further complications. Effective bleeding management is essential for preventing shock and ensuring that the body can begin the healing process. Different types of wounds require different approaches, but all injuries should be treated with care and urgency to minimize risks and complications.
Types of Wounds
Understanding the different types of wounds is essential in providing the appropriate care. Here are some common categories:
- Cut or Incision: A clean, straight wound often caused by sharp objects. These may bleed heavily but can be controlled with direct pressure.
- Scrape or Abrasion: Shallow wounds that occur when the skin is rubbed or scraped. They usually cause minor bleeding but are prone to infection if not cleaned properly.
- Puncture: A deep, narrow wound caused by objects like nails or needles. These can be dangerous due to the risk of internal injury or infection.
- Laceration: Irregular, jagged wounds typically caused by blunt force trauma. Lacerations can involve deep tissue damage and may require stitches.
Methods for Controlling Bleeding
There are several methods used to manage bleeding, depending on the severity and type of injury. The following techniques are essential for controlling blood loss effectively:
- Direct Pressure: Apply firm, direct pressure on the wound using a clean cloth or bandage to stop bleeding. This is the most common and effective method for controlling most external bleeding.
- Elevation: If the injury is to a limb, raise the affected area above the level of the heart. This can help reduce blood flow to the area and slow the bleeding.
- Pressure Points: In some cases, applying pressure to specific points on the body where major arteries are located can help control more severe bleeding.
- Tourniquet: If the bleeding is severe and cannot be controlled by other means, a tourniquet may be used to stop blood flow to the limb. This should only be done when absolutely necessary and with caution to avoid tissue damage.
Signs of Severe Bleeding
It is important to recognize the signs of severe bleeding and take immediate action:
- Profuse blood loss that cannot be controlled by direct pressure
- Blood spurting from the wound, indicating arterial bleeding
- Signs of shock, such as pale skin, rapid pulse, and shallow breathing
By understanding the types of wounds and how to manage bleeding effectively, responders can reduce the risk of complications and provide immediate care to injured individuals. Ensuring proper bleeding control is a fundamental skill in emergency response.
The Importance of Quick Decision-Making
In emergency situations, the ability to make swift, accurate decisions is vital. Every moment counts when responding to an injury or health crisis, and quick thinking can make the difference between a positive outcome and a worsening situation. Whether it’s assessing the severity of an injury or deciding on the appropriate response, rapid decision-making allows for timely interventions that can save lives and minimize long-term damage.
Responding to Critical Moments
When faced with an urgent situation, it is essential to stay calm and focused. The following factors highlight the importance of quick decision-making:
- Minimizing Delay: The longer it takes to act, the more severe the consequences can be. Immediate intervention is often critical in preventing further harm.
- Preventing Complications: Rapid decisions help avoid additional injuries or complications, such as infections or internal damage, which can arise from delayed care.
- Resource Allocation: Quick decision-making helps identify and prioritize the use of available resources, such as medical tools, personnel, or emergency services.
Training for Quick Thinking
While it’s natural to feel pressured during high-stakes situations, proper training equips individuals to handle emergencies with confidence. Practicing decision-making under simulated stress conditions can improve response times and reduce errors. Additionally, understanding common scenarios and their responses can help anticipate challenges and make quick, effective choices during a crisis.
By honing the skill of fast, sound judgment, responders can take control of the situation and provide the best care possible in a timely manner, significantly improving the chances of a successful recovery.
How to Retake the First Aid Exam

Sometimes, despite preparation, a test may not go as planned, and retaking it becomes necessary. When this happens, understanding the process for reattempting the assessment is key to improving performance. Whether you didn’t pass or simply wish to reinforce your knowledge, there are steps you can follow to ensure better outcomes on the next attempt.
Steps to Retake the Assessment
To retake the assessment, follow these steps to ensure you are fully prepared:
- Review Your Previous Performance: Start by understanding where you went wrong. Reviewing the areas you struggled with will allow you to focus your efforts and avoid the same mistakes in the future.
- Seek Feedback: If available, ask for detailed feedback on your prior attempt. This can help you identify specific areas of weakness and give you insights into what needs improvement.
- Study the Material Thoroughly: Ensure that you have a solid understanding of the topics covered. Make use of study guides, practice tests, and training resources to help reinforce your knowledge.
- Take Practice Assessments: Engage in mock tests or quizzes to gauge your understanding and improve your test-taking skills under timed conditions.
Reattempting the Assessment

Once you feel ready, proceed with the retake. Here are a few additional tips:
- Stay Calm and Confident: Don’t let previous results discourage you. Approach the retake with a calm, positive mindset.
- Manage Your Time: Be mindful of time limits during the assessment and pace yourself to answer all questions thoughtfully.
- Double-Check Your Answers: If possible, review your responses before submitting to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Retaking an assessment provides an opportunity to correct mistakes and improve your knowledge. With thorough preparation and a focused approach, success is within reach.
Preparing for Real-Life Rugby Emergencies
In any physical sport, unexpected situations can arise where immediate action is required to ensure the safety and well-being of participants. Being prepared for real-life emergencies involves understanding potential injuries, knowing how to respond, and being able to act swiftly under pressure. This preparation is crucial for anyone involved in managing player safety on the field.
Key Areas to Focus On
When preparing for emergencies, there are several critical aspects to consider. These areas are vital for a quick, effective response in real-life situations:
- Injury Identification: Understand the common injuries that can occur during high-impact activities. Be able to quickly identify whether an injury is minor or potentially serious, such as sprains, fractures, or head trauma.
- Emergency Protocols: Familiarize yourself with the established protocols for managing emergencies. This includes knowing when to call for professional medical help and how to communicate effectively with medical teams.
- Basic Life Support (BLS): Knowing how to perform essential life-saving techniques, such as CPR or the Heimlich maneuver, is essential in the event of a serious emergency.
- Safe Transport: Be aware of how to move injured individuals safely, particularly when spinal injuries are suspected, without causing further harm.
Training and Preparation

It’s important to undergo regular training to stay updated on best practices for managing emergencies. Consider the following steps to stay prepared:
- Attend Workshops: Participate in relevant training courses, such as first responder or basic medical courses, to stay equipped with the knowledge needed to act confidently.
- Review Emergency Plans: Familiarize yourself with the emergency response plan in your organization or team, ensuring that everyone involved knows their role and responsibilities in the event of an emergency.
- Simulate Scenarios: Practice mock emergency situations to build confidence and familiarity with the necessary procedures. This will help you stay calm and decisive when an actual emergency occurs.
- Equip Yourself: Ensure that you have the necessary medical supplies available, including first-aid kits, defibrillators, and communication devices, to assist in emergencies.
By thoroughly preparing for possible emergencies, you will be better equipped to respond effectively when the situation arises. Quick, knowledgeable actions can make a significant difference in preventing further harm and ensuring the safety of everyone involved.